Let’s learn pipe vs tube! When it comes to conveying fluids or structural applications, two common contenders emerge and those are pipes and tubes. These fundamental components of our infrastructure may seem similar at first glance, but they have distinct characteristics and applications that set them apart. Understanding the disparities between pipes and tubes is crucial for making informed choices in various industries.
Pipe Vs Tube: Difference between Pipe and Tube Overview
When it comes to material conveyance and structural applications, pipes and tubes are essential components with unique features that cater to distinct needs. To make informed decisions in industries ranging from construction to manufacturing, it’s crucial to delve deeper into their differences and functionalities.

Pipes Overview
- Pipes are primarily designed for the efficient transport of fluids, gases, and solids. They excel in conveying substances from one point to another.
- Pipes come in a wide array of materials, including steel, copper, PVC, and more. The choice of material depends on factors like corrosion resistance, pressure requirements, and intended use.
- Pipes are standardized in terms of diameter and thickness, ensuring consistency in manufacturing and application. This uniformity simplifies design and construction processes.
- Pipes find extensive use in plumbing, oil and gas industries, wastewater systems, and structural projects where fluid conveyance or containment is paramount.
- They are designed to handle high-pressure conditions, making them suitable for applications requiring pressure containment, such as pipelines in the oil and gas sector.
Tubes Overview
- Tubes are known for their precise dimensions and can be manufactured with tight tolerances. This precision is crucial for applications where accuracy is paramount.
- Tubes are often constructed from materials like stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and more, chosen for their specific properties, such as corrosion resistance or heat conductivity.
- Tubes offer versatility in terms of shapes, including round, square, and rectangular profiles. This makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from heat exchangers to architectural designs.
- They excel in heat transfer applications, making them indispensable in industries like HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration.
- Tubes are frequently used for aesthetic purposes due to their polished finishes and variety of shapes. They are often seen in architectural elements and ornamental structures.
- Tubes are commonly employed in industries where structural integrity is crucial, such as aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and construction.
Why to Learn About Pipes and Tubes Difference?
Understanding the differences between pipes and tubes is essential in various industries. It allows for the selection of the right material for specific tasks, whether it’s efficient fluid transport with pipes or precision and structural integrity with tubes. This knowledge enhances project performance and efficiency by ensuring the correct component is chosen.
When you want to select a pipe or a tube, you should know the schedules for selecting the right materials. Let’s see how different the pipe vs tube schedule or chart looks like:
Pipe Schedule:
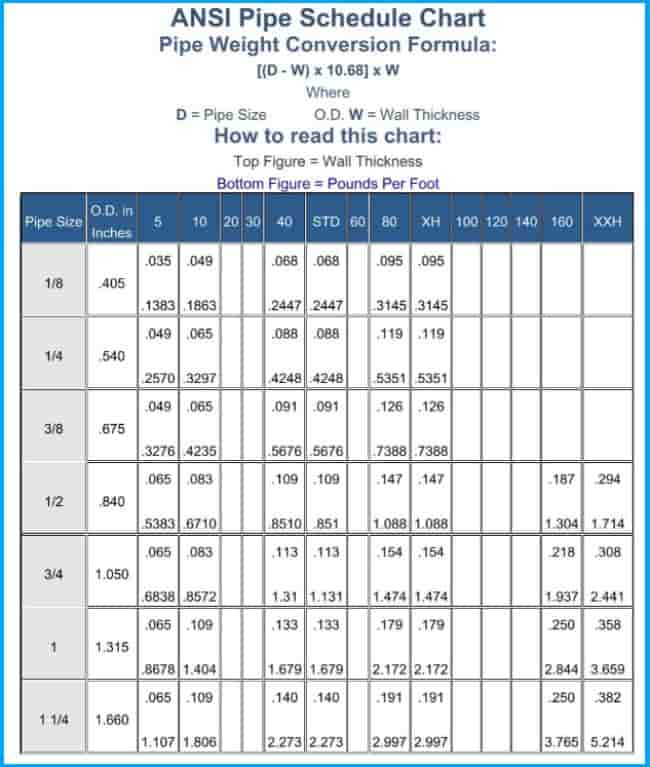
Tube Size Chart
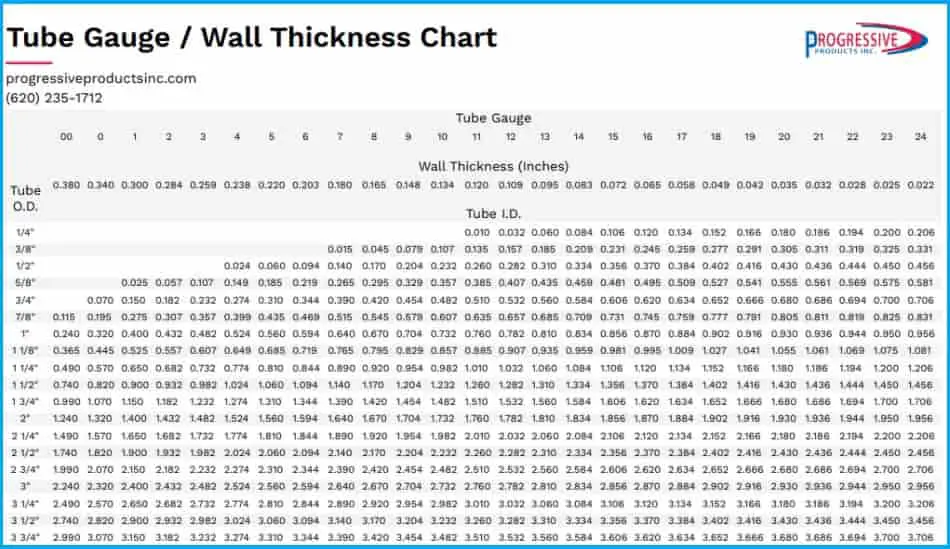
Now, I hope its clear that both pipe and tube are different in terms of their basic selection! Now, efficiency is a key consideration. Using the appropriate conduit for a given task improves overall project efficiency. Choosing a tube when a pipe is needed can result in inefficiencies, increased energy consumption, and safety risks. Conversely, opting for a pipe in a situation better suited for a tube can lead to unnecessary expenses. Knowledge of these distinctions promotes cost-effective and resource-efficient solutions.
Safety is paramount in industries requiring pressure containment or structural integrity. Incorrectly choosing between pipes and tubes can pose safety risks and compromise project integrity. Understanding these differences helps mitigate these risks and ensures compliance with industry regulations, reducing potential legal and regulatory issues. Learning about pipes and tubes is fundamental for informed decision-making, promoting efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness in a variety of applications.
Pipe vs Tube: Working Principle, How Does These Works?
Grasping the working principles of pipes and tubes is paramount for individuals and professionals involved in fluid transport and structural applications. These fundamental components operate based on distinct principles, and a deeper understanding of their workings is essential for optimizing their utilization.
Pipes: Working Principle

- Pipes are primarily engineered for efficient fluid transport, such as conveying water, oil, gas, or chemicals from one point to another in industries and households.
- They are available in a wide range of materials, including steel, copper, PVC, and more. The choice of material depends on factors like corrosion resistance, pressure requirements, and intended use.
- Pipes are standardized concerning diameter and thickness, ensuring uniformity in manufacturing and application. This uniformity simplifies design, construction, and compatibility with various fittings and connectors.
- Pipes are versatile and suitable for transporting liquids, gases, and solids. They find extensive use in plumbing, oil and gas industries, wastewater systems, and structural projects where fluid conveyance or containment is essential.
- They are designed to withstand high-pressure conditions, making them ideal for applications requiring pressure containment, such as pipelines in the oil and gas sector.
Tubes: Working Principle

- Tubes are known for their precision and can be manufactured with tight tolerances, ensuring exact dimensions and consistency.
- Tubes are often constructed from materials like stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and more. Material selection is based on specific properties, such as corrosion resistance, heat conductivity, or aesthetics.
- Tubes offer versatility in terms of shapes, including round, square, and rectangular profiles. This flexibility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from heat exchangers to architectural designs.
- They excel in heat transfer applications, making them indispensable in industries like HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration.
- Tubes are commonly employed in industries where structural integrity is crucial, such as aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and construction, providing reliable support and stability.
- Due to their polished finishes and variety of shapes, tubes are often used for aesthetic purposes in architectural elements and ornamental structures.
Understanding these operating principles is critical for making educated material selection and design decisions. Knowing the differences between pipes and tubes, whether for efficient fluid movement or exact structural integrity, ensures that the proper component is chosen for the right purpose, leading to optimal outcomes in a variety of sectors.
Differences between Pipe and Tube: Meaning for their Sizes
When it comes to selecting the right conduit for various applications, understanding the differences between pipes and tubes is essential. These two cylindrical structures may seem similar, but they have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for specific purposes.
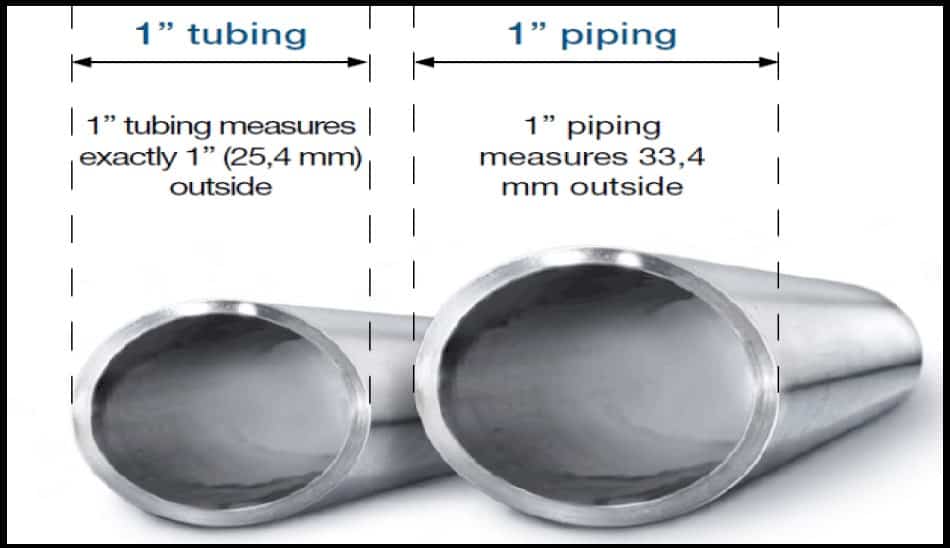
| Aspect | Pipes | Tubes |
| Shape | Usually round, but can have various shapes, including square and rectangular | Generally round, occasionally available in other shapes |
| Manufacturing Process | Standardized, often hot-rolled or cold-rolled | Precise, hot-rolled, cold-rolled, or extruded |
| Dimensions | Standardized sizes based on nominal diameter and schedule | Precise measurements for outside diameter, inside diameter, and wall thickness |
| Strength | Designed for high-pressure applications and fluid transport | Offers structural integrity, suitable for applications requiring strength |
| Usage | Ideal for transporting fluids, such as water, gas, and oil | Suited for structural and mechanical applications, heat transfer, and precision projects |
| Joining Methods | Typically welded, threaded, or connected with fittings | Welded, brazed, or connected using compression fittings |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective due to standardized production | May be costlier due to precision manufacturing |
| Corrosion Resistance | Corrosion-resistant materials available for specific applications | Corrosion resistance varies based on material |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, primarily for linear installations | More flexible and can be bent or shaped as needed |
| Applications | Plumbing, industrial processes, conveyance of fluids | HVAC systems, structural components, automotive, aerospace |
| Environmental Impact | Depends on material used and application | Depends on material used and application |
The table above provides an overview of the differences between pipes and tubes, so that you can make an informed decision regarding which one would be most suitable for your project. You can explore the video on Pipe vs Tube from ”Metal Supermarkets” below
Pipes and Tubes: Which is more Efficient?
To thoroughly assess the efficiency of pipes compared to tubes, a detailed examination of their characteristics, applications, and performance is essential. By analyzing their distinct strengths and limitations, we can gain a clearer understanding of the suitability of each conduit type in various scenarios.
| Efficiency Aspect | Pipes | Tubes |
| Fluid Transport Efficiency | Pipes are designed primarily for efficient fluid transport, ensuring a smooth flow of liquids, gases, or solids. Their standardized dimensions simplify design and construction, enhancing fluid conveyance efficiency. | Tubes excel in structural applications but are also used for efficient fluid transport. Their precise dimensions and versatility in shapes enhance fluid transport efficiency in specific situations. |
| Structural Efficiency | N/A | Tubes excel in structural applications, offering precise dimensions and versatility in shapes like round, square, and rectangular profiles. Their precision engineering ensures structural integrity and efficiency in various industries. |
| Materials and Corrosion Resistance | The choice of materials is crucial for efficiency. Pipes are available in various materials, each selected for specific properties, such as corrosion resistance. The right material contributes to both efficiency and longevity. | Tubes are often constructed from materials like stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and more, selected for specific properties, such as corrosion resistance. The right material contributes to both efficiency and longevity. |
| Pressure Handling | Pipes are favored for high-pressure applications, ensuring efficient containment and transport of fluids under significant pressure. Their robust design enhances pressure-handling efficiency. | N/A |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | N/A | Tubes are preferred for heat transfer applications due to their precise dimensions and versatility. They offer efficient heat exchange in industries like HVAC and refrigeration. |
| Efficiency in Specific Industries | Pipes find high efficiency in applications like plumbing and oil and gas industries, where fluid transport is critical. | Tubes contribute to efficiency in structural engineering, automotive manufacturing, and heat exchangers. |
| Cost Efficiency | Pipes and tubes vary in cost depending on materials and dimensions. Assessing the efficiency of each depends on the specific project requirements, where cost-effectiveness plays a crucial role. | N/A |
| Maintenance and Longevity | Efficiency is also influenced by maintenance requirements and longevity. Proper maintenance ensures efficient performance and prolongs the lifespan of pipes and tubes. | Efficiency is also influenced by maintenance requirements and longevity. Proper maintenance ensures efficient performance and prolongs the lifespan of tubes. |
| Environmental Impact | Consideration of environmental impact is vital. Efficient use of materials, along with proper disposal and recycling practices, contributes to environmental efficiency. | Consideration of environmental impact is vital. Efficient use of materials, along with proper disposal and recycling practices, contributes to environmental efficiency. |
Efficiency Considerations
Fluid Transport Efficiency and Versatility: Pipes excel in efficiently conveying fluids, ensuring a smooth flow of liquids, gases, or solids. Their standardized dimensions simplify design and construction, enhancing fluid transport efficiency. Tubes, on the other hand, offer versatility in shapes and precise dimensions, contributing to efficient fluid transport in specific applications.
Structural Efficiency and Impact on Costs
Tubes are highly efficient in structural applications, providing precise dimensions and versatility in shapes like round, square, and rectangular profiles. Their precision engineering ensures structural integrity and efficiency, potentially reducing construction and material costs. Pipes are primarily designed for fluid transport efficiency and may not offer the same structural efficiency advantages.
Materials and Corrosion Resistance
Both pipes and tubes are available in various materials, each selected for specific properties, such as corrosion resistance. The right material contributes to both efficiency and longevity, but the choice may vary depending on the conduit type and application.
Pressure Handling and Longevity
Pipes are favored for high-pressure applications, ensuring efficient containment and transport of fluids under significant pressure. Their robust design enhances pressure-handling efficiency, contributing to their longevity. Tubes may not be as well-suited for high-pressure applications.
Heat Transfer Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Tubes are preferred for heat transfer applications due to their precise dimensions and versatility. They offer efficient heat exchange in industries like HVAC and refrigeration, potentially reducing energy consumption and environmental impact. Pipes may not provide the same level of heat transfer efficiency.
Maintenance and Noise Level
Efficiency is also influenced by maintenance requirements and noise levels. Proper maintenance ensures efficient performance and prolongs the lifespan of both pipes and tubes, but the complexity of maintenance may differ between the two. Noise levels during operation may also vary, affecting their suitability for specific environments.
Pipe Vs Tube: Which is more Costly?
When deciding between pipes and tubes for your specific project or application, it’s crucial to assess the relative costs and benefits associated with each conduit type. While both pipes and tubes have their distinct advantages, cost considerations play a significant role in making an informed choice.
| Aspect | Pipes | Tubes |
| Initial Material Costs | Vary based on material, size, and quantity. For example, PVC pipes can cost approximately $0.40 to $1.00 per linear foot, while copper pipes range from $2.50 to $10.00 per linear foot. | Vary based on material, size, and quantity. For instance, steel tubes can range from $2.00 to $10.00 per linear foot, while aluminum tubes may cost between $1.50 and $6.00 per linear foot. |
| Manufacturing Costs | Typically lower due to standardized production processes. | May be higher due to precision manufacturing and specific shapes. |
| Installation Costs | Vary depending on the complexity of the project and materials used. Labor costs typically range from $40 to $85 per hour for pipe installation. | Vary depending on the complexity of the project and materials used. Labor costs for tube installation are similar, ranging from $40 to $85 per hour. |
| Maintenance Costs | Comparable for pipes and tubes, depending on material durability. | Comparable for pipes and tubes, depending on material durability. |
When it comes to selecting between pipes and tubes, cost-related factors are a critical consideration. Both conduits have their advantages and disadvantages, so a thorough evaluation based on your project’s unique requirements and budget is essential.
Initial material costs for pipes vary based on factors like material type, size, and quantity. PVC pipes cost approximately $0.40 to $1.00 per linear foot, while copper pipes range from $2.50 to $10.00 per linear foot. Lower manufacturing costs are a plus due to standardized processes. Installation expenses vary with project complexity, with labor costs typically between $40 to $85 per hour.
Material costs for tubes depend on type, size, and quantity. Steel tubes range from $2.00 to $10.00 per linear foot, while aluminum tubes may cost $1.50 to $6.00 per linear foot. Precision manufacturing can raise manufacturing costs. Installation costs vary by project complexity, with labor costs similar to pipes. Maintenance expenses align with pipes, contingent on material durability
Your choice between pipes and tubes should align with budget, performance, and environmental considerations, ensuring it meets your specific needs.
Pipe Vs Tube: Pros & Cons
Pipe Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
| Standardized sizes and availability | May not be ideal for certain specialized applications |
| Cost-effective due to standardized production | Limited versatility in non-linear designs |
| Suitable for high-pressure applications | Potential for corrosion in certain environments |
| Efficient for fluid transport | Welding may be required for complex systems |
| Resistant to bending and deformation | Limited structural applications |
| Readily available fittings and connectors | Can be heavier than tubes in some cases |
| Well-suited for linear installations | May not offer the precision of tubes in some applications |
Tube Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
| Precise dimensions for specialized applications | Higher manufacturing costs for precision |
| Ideal for structural and mechanical purposes | Limited availability in non-round shapes |
| Offers flexibility in non-linear designs | May require more precise joining methods |
| Can be used for heat transfer applications | May have higher material costs |
| Resistant to corrosion, especially stainless steel | Limited availability of fittings compared to pipes |
| Well-suited for precision projects | May not be as readily available as pipes |
| Can be bent or shaped as needed | Less efficient for fluid transport in some cases |
This comparison of the pros and cons of pipes and tubes assists you in making educated judgments for a variety of applications, taking into account aspects such as cost, adaptability, and special project needs.
Which One Should You Choose – Pipe or Tube?
The choice between pipes and tubes involves careful consideration of your project’s specific requirements. Pipes are the preferred option when the primary goal is efficient fluid transport or high-pressure applications. They offer standardized sizes, cost-effective production, and are well-suited for linear installations. Pipes are particularly reliable in scenarios where resistance to bending is essential, making them a common choice in plumbing and industrial processes.
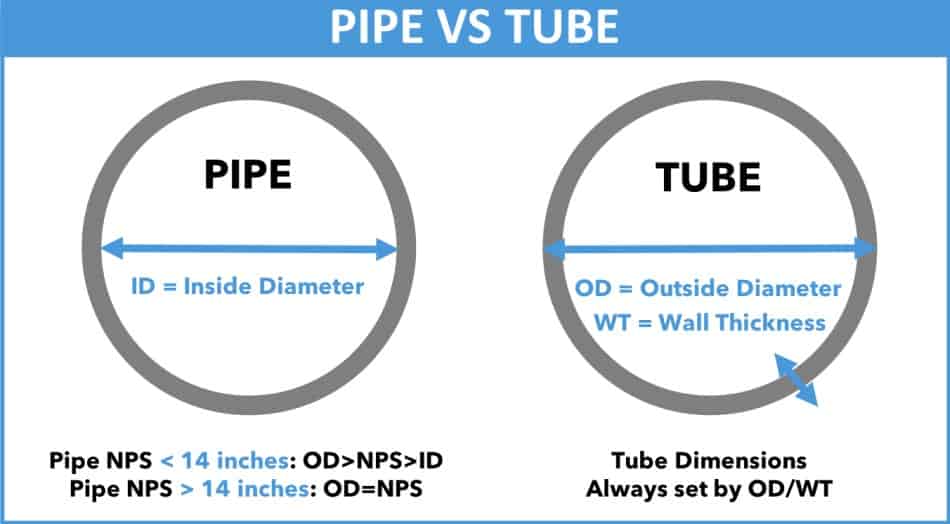
On the other hand, tubes shine in applications that demand precision and specialized dimensions. They are ideal for structural and mechanical purposes, offering strength and integrity. Tubes are also well-suited for heat transfer applications, such as HVAC systems, thanks to their efficient heat conduction properties. Additionally, tubes can be bent or shaped as needed, making them versatile for non-linear designs or complex configurations. If corrosion resistance is a concern, especially in challenging environments, tubes made from materials like stainless steel are an excellent choice.
Ultimately, your decision should align with your project’s budget, performance requirements, and any environmental considerations. Assessing these factors comprehensively ensures that your selection meets your unique needs and preferences, whether you opt for pipes or tubes.
People May Ask: FAQs
01. What distinguishes pipes from tubes in terms of their construction and purpose?
Pipes are primarily designed for efficiently transporting fluids, gases, and solids. They come in various materials and standardized dimensions. Tubes, on the other hand, are known for precision and can have tight tolerances. They serve a wide range of applications, including structural, heat transfer, and precision projects.
02. How do the costs of pipes and tubes compare, and what factors influence these costs?
The costs of pipes and tubes can vary based on materials, sizes, and quantities. For instance, PVC pipes can cost around $0.40 to $1.00 per linear foot, while steel tubes may range from $2.00 to $10.00 per linear foot. Manufacturing processes and precision can affect costs.
03. Which applications are better suited for pipes, and in which scenarios are tubes preferred?
Pipes are ideal for fluid transport and high-pressure tasks, often used in plumbing and industries where resistance to bending is essential. Tubes excel in precision and structural applications, making them valuable in HVAC systems, automotive manufacturing, and projects requiring strength and integrity.
04. Do pipes and tubes require different maintenance procedures, and how does maintenance impact their long-term performance?
Both pipes and tubes require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper maintenance can prevent issues and extend their lifespan. Maintenance needs may differ based on materials and applications but are generally comparable.
05. What environmental considerations should be taken into account when choosing between pipes and tubes?
The environmental impact of pipes and tubes depends on the materials used and disposal or recycling practices. Selecting materials with the right properties, such as corrosion resistance, can contribute to environmental efficiency. Proper disposal and recycling are also crucial for minimizing environmental impact.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between pipes and tubes is vital for various projects. Pipes are best suited for fluid transport and high-pressure tasks, offering standardized sizes and cost-effectiveness. They find use in plumbing and industries requiring resistance to bending.
Tubes shine in precision and structural applications, providing versatility and corrosion resistance. They are ideal for tasks like HVAC systems, structural engineering, and heat transfer. Ultimately, your decision hinges on project requirements, budget, and specific needs. Understanding these differences empowers you to make the right choice, enhancing efficiency and cost-effectiveness while meeting your project’s demands.
