In this article, we will learn what geothermal energy or geothermal power plant is, along with the definition, basics, pros or benefits, cons, advantages or disadvantages, etc. Geothermal energy is most widely used now a day and used either directly or indirectly in various industries.
What is Geothermal Energy? Definition, Meaning
Geothermal Energy Definition
Geothermal Energy, is the energy that is stored in the depth of the earth’s surface as heat. A geothermal power plant uses geothermal energy to produce electricity. Basically, geothermal energy, a type of energy that is taken from the depth of the earth’s surface.
- It is generated during the formation of the planet.
- It is based on the radioactive decay of materials.
- It is stored in the rocks as well as in the hot fluid at the center of the earth.
- It helps to generate electricity.
- A geothermal power plant is produced based on geothermal energy.

Where Does Geothermal Energy Come From? Meaning
Geothermal energy is the resource of natural energy as the earth has huge storage on the earth’s surface. The word “Geothermal” came from the GREEK word, ‘geo’, and ‘therme’. ‘Geo’ means “Earth”, ‘Therme’, means “heat”. ‘Geo’ and ‘therme’ together form geothermal and the meaning becomes ‘heat from the earth’ or ‘heat generated from the earth’.
Geothermal energy means,
- Storage of cooling energy in aquifers and bedrocks.
- Storage of heating energy in aquifers and bedrocks.
- Ground-source heat pumps.
- Energy piles in building foundations.
- High-temperature geothermal energy systems.
- This is a clean renewable source of energy.
- It is generated with the help of earth heat and several components like a Separator, turbine, Generator, Condenser, Cooling tower, etc.
How Does Geothermal Energy Created or Obtained?
We know the earth core has a very high temperature of more than 4000 deg. C. And its temperature is reducing towards the surface. Due to the difference in temperature between the center and the surface, there is a huge temperature differential. Magma is an extremely hot liquid and semi-liquid rock located under Earth’s surface. To understand geothermal energy, it is required to the different layers of the earth. Earth has few layers and these are,
- Inner core,
- Outer core,
- Mantle, and
- Crust
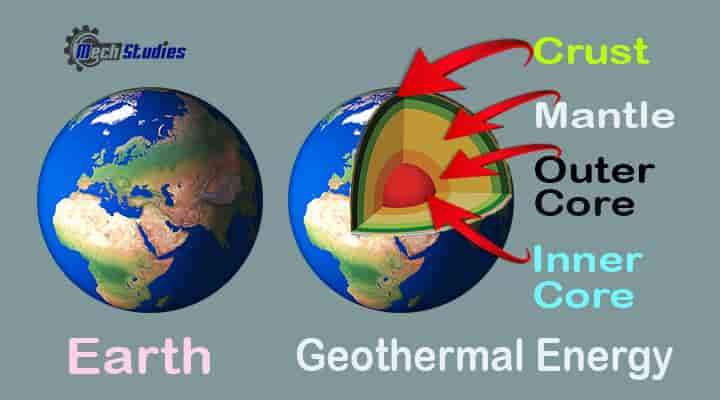
Inner core (1200 km)
- It is in the center of the earth and has a very high temperature up to 7000 deg. C
- Mainly consists of iron.
- Solid with very high pressure.
- It is about 1200 km thick.
Outer core (2250 km)
- It is the next layer to the inner core. Due to the inner core high temperature, the temperature of the outer core is also high but less than the inner core.
- Mainly consists of molten iron and nickel
- The temperature is around 4000 Deg. C to 6000 Deg. C
Mantle (2800 km)
- This is simply molten rock.
- Thickness around 2800 km.
- It consists of the lower mantle and upper mantle.
- The mantle consists of magma.
- The temperature is around 500 Deg. C to 2000 Deg. C
- Magma exists in the fluid state due to high temperature and pressure.
- It consists of various minerals along with various dissolved gasses.
- There are various cracks in the earth’s crust and the liquid magma comes on the earth’s surface as lave through a volcanic eruption.
Crust (70 km)
- It is above the mantle layer, around 0 km to 70 km.
- Landforms, soil, and rocks are the parts.
Water
- The water inside the earth contacts with the mantle layer or magma.
- Due to the very high temperature of the magma, water becomes hot.
- Water transforms into high-pressure steam.
- Thermal energy or geothermal energy is stored in the rocks as well as in the water or steam.
How to Use Geothermal Energy?
There are a few different ways, by which geothermal energy can be used.
- Geothermal Power Plant
- Ground source heat pumps or Geothermal Heat Pumps
- Direct utilization geothermal
What is Geothermal Power Plant?
It is a plant which is used geothermal energy to produce electricity.

Diagram of Geothermal Power Plant & Geothermal Energy
Geothermal plants extract thermal energy from the earth’s crust. Produces geothermal power and uses it in various industries. Let us see, simple schematics of a geothermal power plant.
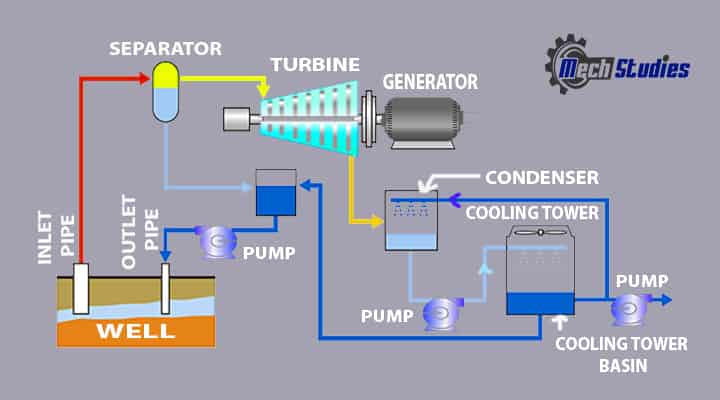
Parts of Geothermal Power Plant
In the turbine section, some amount of unused steam, or we can say steam not used for the production of electricity comes to the condenser through the pipe and there it loses high temp and pressure, and then it comes to the ground. Before understanding the working principle, we will learn the different components of geothermal power plants. It consists of,
- Inlet pipe
- Flask tank
- Separator
- Heat exchanger
- Turbine
- Generator
- Cooling tower
- Grid line
The layout which describes the several processes occurs with several types of equipment like:
Inlet pipe
- This is the pipe that connects the earth and the surface equipment.
- This pipe supplies hot water or steam to the plants.
- This pipe is connected to the flash tank or heat exchanger.
Flask tank
- It is the tank where the pressure of hot water is reduced.
- It is used in flash steam power plants.
Heat exchanger
- It is the heat exchanger where heat is exchanged between hot water and cool water.
- It is used in binary cycle power plants.
Separator
A separator is used in geothermal power plants to separate the steam and hot water.
Turbine
- Steam is passed through the turbine.
- Turbine blades got hits.
- The turbine blades rotate.
Generator
- The generator is connected to the turbine.
- The turbine rotates mean the generator also rotates.
- The generator has a starter and a rotor.
- Due to the magnetic effect, electricity is produced.
Power grid
- The generator is connected to the powerhouse.
- From the powerhouse, electricity is distributed.
Condenser
- Exhaust steam is passed through the condenser.
- Both pressure and temperature are reduced.
- It is cooled in the condenser.
- Condensate is transferred to the earth through the outlet pipe.
Cooling Tower
- Rejected heat from the condenser is taken by the cooling tower.
- This heat is further released into the atmosphere.
- Circulating water is cooled.
Outlet pipe
- This is the pipe that connects the condenser and the earth.
- This pipe transferred water to the earth.
Types of Geothermal Power Plants
There are three different kinds of geothermal power plants,
- Dry steam type plant
- Flash steam type plant
- Binary cycle power plant
Dry Steam Geothermal Power Plant
In this geothermal power plant, dry steam is directly taken from the geothermal energy source to the turbine to generate electricity. Main Components of Dry Steam Geothermal Power Plant are
- Inlet pipe
- Turbine
- Generator
- Power Lines
- Condenser
- Cooling Tower
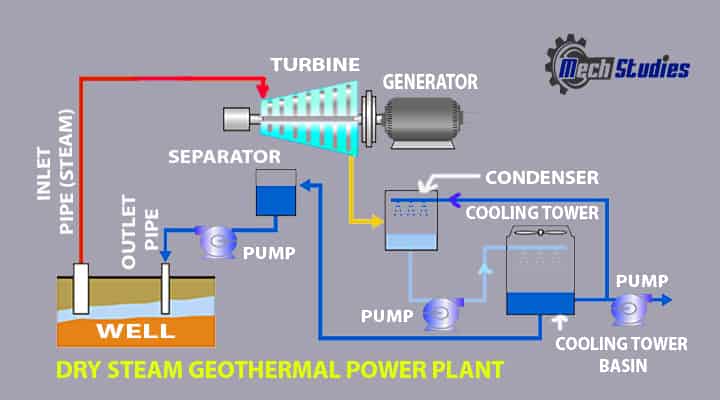
Working Principle of Dry Steam Geothermal Power Plant
- Direct steam is directly taken from the earth.
- Steam is having high pressure.
- High-pressure steam hits the blades of the turbine.
- Due to this, the turbine rotates, the turbine shaft is connected to a generator.
- Electricity is produced from the generator.
- Steam is exhausted from the turbine to a condenser.
- A separate cooling tower circuits are cooled the condenser.
- Steam is then cooled in the condenser.
- Cooled condensate from the condenser is circulated back to the depth of the earth.
The first geothermal power plant based on dry steam was first built in Italy.
Flash Steam Geothermal Power Plant
Take high-pressure water from the earth. Water converted into steam which provided to the turbine and produces electricity. Main Components of Flash Steam Geothermal Power Plant are:
- Inlet pipe
- Flash Tank
- Turbine
- Generator
- Power Lines
- Condenser
- Cooling Tower
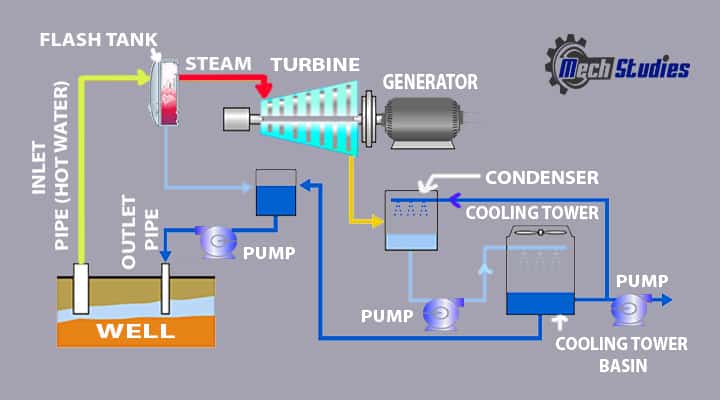
Working Principle of Flash Steam Geothermal Power Plant
- Hot water is taken from the depth of earth through the inlet pipe.
- The pipe is connected to a flask tank.
- Hot water is passed through the flask tank and pressure is reduced.
- Due to the reduction of pressure, hot water is changed into steam.
- Steam is provided to the turbine and electricity is produced at the generator like dry steam power plants.
Binary Cycle Geothermal Power Plant
It uses a heat exchanger and heat from the geothermal water is exchanged to another water stream of water. This water changed into steam and rotate the turbine to produce electricity.
Main Components of Binary Cycle Geothermal Power Plant
- Inlet pipe
- Heat exchanger
- Generator
- Power Lines
- Condenser
- Cooling Tower
Working Principle of Binary Cycle Geothermal Power Plant
- Hot water is taken from the earth and passes through a heat exchanger
- There is another liquid mostly water in the heat exchanger.
- There is a heat exchange between geothermal water and the freshwater, in another circuit.
- Heat exchange happens, geothermal water releases the heat and the freshwater becomes heated and form steam.
- Steam is passing through the turbine and produces electricity at the outlet of the generator.
- After releasing heat, geothermal water is circulated back to the earth.
Apart from geothermal power plants, geothermal energy can be used as,
- Geothermal heat pumps or ground source heat pumps
- Direct utilization
Ground Source Heat pumps or Geothermal Heat Pumps
Ground Source Heat Pumps Definition
We have already learned that geothermal energy is harnessed by geothermal power plants. However, all geothermal energy cannot be harnessed by geothermal power plants. Geothermal heat pumps are the best choice, for small scale applications, like,
- Domestic cooling
- Domestic heating,
- Hot water requirements
- Warming swimming pools,
- Widely used in residential areas, school, colleges, along with commercial buildings.
How Does Geothermal Heat Pump Work?
- In the circuit, water is flowing and this water is used as a refrigerant.
- Water circulates through a pipe or loop.
- In the winter season, when the weather is cold, the water heats up which is buried underground.
- After underground, heat from the water is utilized in the building.
- After releasing heat, water is transferred to the earth.
- In the hot session, it works in reverse and cools the buildings.
- Water is circulated in loops.
Types of Heat Pumps
There are two ground loop systems,
Closed Geothermal Loop System
- Horizontal
- Vertical
- Pond
Open Geothermal Loop System
- Pond
- Standing well
Compressors and pumps can be used to optimize the heat transfer as well as geothermal energy.
Direct Utilization Geothermal
- There are many places, where hot water is very near to the earth’s surface.
- Residential house, agricultural pond, etc. this kind of energy is used.
- Heating, washing, etc. for an individual rooms can be met.
Requirements of a Geothermal Plant
- Proper Location. It should be near the hot water source.
- A seismic study should be done before installing the plant.
- Drilling as well as needs to be verified the site suitability.
Is Geothermal a Renewable Energy Source?
We know, renewable energy means solar energy, wind energy. This energy is not affected by the weather conditions or these sources are not limited. In the same way, geothermal energy is also not affected by the weather and the supply of this energy is not limited.
- It can produce electricity irrespective of weather conditions.
- The resource is huge.
- No burning fuel is required.
- No fossil fuels are used.
- No harmful emissions.
- Sustainable energy
- Based on the above we can say, it is renewable energy.
Geothermal energy pros and cons are described, as below
Advantages or Pros or Benefits of Geothermal Energy
There are many advantages of Geothermal Energy are:
- Renewable energy.
- No fossil fuels are required to generate the Steam.
- Steam or hot water is already available.
- No energy for making steam or hot water.
- Reliable energy.
- No impact on the weather conditions.
- Energy cost is Cheap
- Continuous availability of this energy.
- Less area requirements with respect to other power plants.
- No boiler or steam generating equipment.
- No additional space for producing steam or hot water.
- It can produce heating or cooling as well as electricity.
- Clean energy
- No pollutions.
- Less operating cost.
- Long life
- It can provide between 0.0035 and 2 terawatts of power, as potential capacity.
Disadvantage or Cons of Geothermal Energy
The main disadvantages are, as follows:
- The abrasive geothermal fluid reduces the life of geothermal plants.
- Geothermal energy may not be considered a renewable resource only a sustainable one.
- The heat is generated within the Earth by radioactive decay.
- The distribution of hot water or steam under the earth is not equal.
- The initial capital cost is high.
- The installation cost is high.
- Cost due to drilling, excavation.
- Due to drilling, noise pollution can happen.
- Water removal from the drilling may create problems.
- After a couple of years, new wells may require.
- Geothermal water may contain gasses, which can create problems.
- Low-grade energy availability.
- Thermal energy from the earth cannot transfer a long distance.
Geotherml Power Plant Efficiency
The efficiency of the geothermal power plant varies depending on the location, availability of the geothermal energy source. Normally it varies from 10% to 20%. The efficiency of a geothermal power plant is the ratios of net electricity produced to the energy input. Now, the energy input means total mass of fluid (kg/s) multiplied by the average enthalpy (kJ/kg).
ηact (%) = W / (ṁ × h) × 100
Where
- W : Running capacity (kWe),
- ṁ : Total mass flow rate (kg/s),
- h : Reservoir enthalpy (kJ/kg).
Application of Geothermal Energy
Application of geothermal energy, are as follows,
- Electric Power generation
- Cooling
- Heating
- Hot water requirements
- Cooking
- Swiming pool heating
- Crop dying
- Agriculture
- Crop Drying
Biggest Geothermal Power Plant
There are many geothermal power plants in the world , few of them are listed below,
, few of them are listed below,
- Geysers Geothermal Complex, 1.2GW – California, USA
- Cerro Prieto Geothermal Power Station, 720MW – Mexico
- Makban Geothermal Complex, 458MW – Philippines
- Salak Geothermal Plant, 377MW – Indonesia
- CalEnergy Generation’s Salton Sea Geothermal Plants, 340MW – USA
- Sarulla Geothermal Power Plant, 330MW – Indonesia
- Hellisheidi Geothermal Power Plant, 303MW – Iceland
- Tiwi Geothermal Complex, 289MW – Philippines
- Darajat Power Station, 271MW – Indonesia
Geothermal Energy Survey in India
There are few potential geothermal energy sites, which will help India to grow,
- Puga Valley (J&K)
- Godavari Basin Manikaran (Himachal Pradesh)
- Tatapani (Chhattisgarh)
- Unai (Maharashtra)
- Bakreshwar (West Bengal)
- Tuwa (Gujarat)
- Jalgaon (Maharashtra)
Indian Organizations Working
- Geological Survey of India
- Central Electricity Authority
- Regional Research Laboratory, Jammu
- Indian Institute of Technology, Mumbai
- Oil and Natural Gas Corporation, Dehradun
- National Geophysical Research Institute, Hyderabad
Ongoing Projects in India
The investigation is going on for the following sites,
- Tattapani geothermal area, Madhya Pradesh
- Puga geothermal area, Jammu & Kashmir
Conclusion
We have got the basic idea of geothermal energy as well as a geothermal power plant.

