Heat pumps and air conditioners are both types of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems utilized for both cooling and heating residential spaces. When it comes to maintaining a comfortable indoor environment, heating and cooling systems play a vital role. Two of the most widely favored choices for cooling and heating solutions are heat pumps and air conditioners. While both systems aim to regulate indoor temperatures, they function differently and have their unique advantages.
We live in an era where technology is evolving faster than you think. There is no exception to this rule in the automobile industry. People are adopting electric vehicles at a rapid pace because they are concerned about the environment. Air conditioning is now considered a norm in automotive technology: 96 percent of cars sold in 2022 had air conditioning. A vehicle’s air conditioning needs range from 5 to 15 percent of its propulsion energy in summer months.
Heat Pumps vs Air Conditioners or AC Overview
Heat pumps and air conditioners contribute to maintaining a comfortable indoor environment, their distinction lies in the capacity to offer both heating and cooling (heat pumps) versus solely cooling (air conditioners). The decision between the two systems relies on the climate of the area and the specific heating and cooling requirements of the property.

Heat Pumps
- Heat pumps can both heat and cool a home, while air conditioners only cool.
- Heat pumps surpass air conditioners in terms of efficiency, as they require less energy to deliver an equivalent level of heating or cooling.
- Heat pumps may have a higher initial installation cost compared to air conditioners, but they can lead to significant energy savings over time, making them a cost-effective choice for homeowners.
Air Conditioners
- Air conditioners are less expensive to install than heat pumps.
- Air conditioners are more reliable in extreme weather conditions, such as very hot or very cold weather.
- Air conditioners are a good option for homes that only need cooling.
Why to Learn About Heat Pumps and Air Conditioners Difference?
There are a few reasons why it is important to learn about heat pumps and air conditioners First, if you are considering buying a new HVAC system, you need to know the difference between two systems so that you can choose the right one for your needs. Second, even if you already have an HVAC system, it is important to understand how it works so that you can troubleshoot problems and make sure that it is operating efficiently.
Heat Pumps vs. Air Conditioners: Working Principle
Heat pumps and air conditioners are both HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems that use the same basic principle to transfer heat from one place to another. Nonetheless, significant distinctions exist between these two systems, encompassing their effectiveness, capacity to regulate temperature, and overall expenses.
Heat Pumps: Working Principle
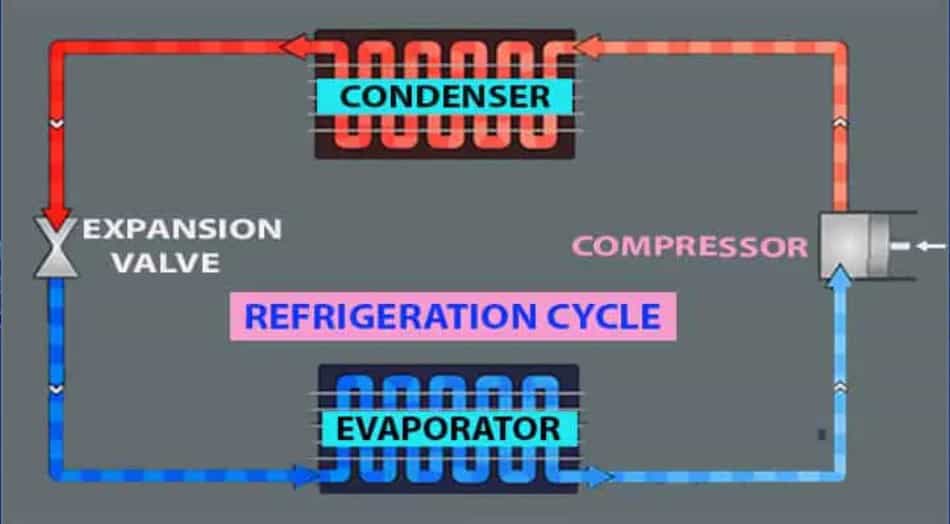
A heat pump is a device that transfers heat from one place to another. It can be used to heat or cool a home, depending on the season. Heat pumps work by using a refrigerant, which is a substance that can change from a liquid to a gas and back again.
The working principle of a heat pump is as follows:
- The refrigerant is pumped through an evaporator coil, where it absorbs heat from the surrounding air.
- The refrigerant then flows through a compressor, which increases its pressure and temperature.
- The hot, pressurized refrigerant flows through a condenser coil, where it releases heat to the surrounding air.
- The refrigerant then flows back to the evaporator coil, and the cycle repeats.
Air Conditioners: Working Principle
Air conditioners work by transferring heat from one place to another. They do this by using a compressor, which pressurizes a refrigerant gas. The pressurized gas then expands, which causes it to cool down. The cool gas then absorbs heat from the air, which makes the air cooler.
The working principle of an air conditioner can be summarized in the following steps:
- The compressor pressurizes the refrigerant gas.
- The pressurized gas expands, which causes it to cool down.
- The cool gas absorbs heat from the air.
- The warm gas is then returned to the compressor, and the cycle repeats.
Heat Pumps and Air Conditioning: Which is more Efficient?
Heat pumps have demonstrated higher efficiency compared to air conditioners for both heating and cooling purposes. This is because heat pumps can transfer heat from a colder source to a warmer source, while air conditioners can only transfer heat from a warmer source to a colder source.
| Climate Zone | Minimum SEER Rating for Heat Pumps | Minimum SEER Rating for Air Conditioners |
| Climate Zone 1 | 14.3 | 13 |
| Climate Zone 2 | 14.5 | 13.5 |
| Climate Zone 3 | 14.7 | 14 |
| Climate Zone 4 | 15 | 14.5 |
| Climate Zone 5 | 15.2 | 15 |
| Climate Zone 6 | 15.5 | 15.5 |
| Climate Zone 7 | 16 | 16 |
| Climate Zone 8 | 16.5 | 16.5 |
Here are some additional things to keep in mind when choosing a heat pump or air conditioner with a high SEER rating:
- The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the unit will be. This means that you will save money on your energy bills.
- The SEER rating is not the only factor to consider when choosing a heat pump or air conditioner. You also need to consider the size of the unit, the type of unit, and the features that are important to you.
- It is a good idea to get multiple quotes from different HVAC contractors before you make a purchase. This will help you find the best possible price for a high-efficiency heat pump or air conditioner.
Ability to Heat and Cool: Heat pumps offer the unique advantage of providing both heating and cooling capabilities, whereas air conditioners are limited to cooling functions. This versatility makes heat pumps a more flexible and practical choice compared to air conditioners.
Heat Pumps and Air Conditioning: Which is more Costly?
Heat pumps are typically more expensive than air conditioners. However, heat pumps can save you money on your energy bills in the long run.
| Type | SEER Rating | Price | Payback Period | Installation Cost | Capital Cost |
| Air Source Heat Pump (ASHP) | 16 | $10,000-$20,000 | 5-7 years | $3,000-$5,000 | $13,000-$25,000 |
| Ground Source Heat Pump (GSHP) | 20+ | $20,000-$40,000 | 7-10 years | $5,000-$10,000 | $25,000-$50,000 |
| Air Conditioner | 13 | $5,000-$10,000 | 3-5 years | $2,000-$3,000 | $7,000-$13,000 |
Please note that these prices are just estimates and may vary depending on the specific model, size, and features of the unit. The payback period is the amount of time it takes to save enough money on energy bills to offset the cost of the unit. The installation cost is the cost of having the unit installed by a qualified HVAC contractor. The capital cost is the total cost of the unit, including the purchase price and installation cost.
It is important to factor in the cost of installation when comparing the prices of different heat pumps and air conditioners. The installation cost can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the installation and the location of the unit.

It is also important to consider the payback period when choosing a heat pump or air conditioner. If you are not planning to stay in your home for the long term, it may not be worth investing in a high-efficiency unit with a long payback period.
Overall, heat pumps are a more efficient and cost-effective option than air conditioners. However, they are also more expensive upfront. If you are looking to save money on your energy bills in the long run, a heat pump is a good investment.
Difference Between Heat Pumps and Air Conditioners Table
Let us see the differences between heat pump and air conditioners in a tabulated form:
| Aspect | Heat Pumps | Air Conditioning |
| Primary Function | Heat pumps work by transferring heat from one place to another | Air conditioners, on the other hand, only work to cool the air. They do this by removing heat from the air and transferring it to the outside. |
| Heat Source | Heat pumps can use the heat in air, water, or the ground to provide heating and cooling. | Air conditioning can be used as a heat source in the winter by reversing the refrigerant flow. |
| Efficiency | Heat pumps are more efficient than other heating systems because they use electricity to move heat rather than create it. | A higher SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating means that the air conditioner will use less energy to cool your home. |
| Climate Suitability | Heat pumps can be used in a wide range of climates, but they are most efficient in moderate climates. | The suitability of AC for a particular climate depends on the ambient temperature range, humidity level, and other factors. |
| Energy Consumption | Heat pumps are more efficient than traditional heating and cooling systems, using less energy to provide the same amount of comfort. | The energy consumption of an air conditioner depends on its size, efficiency, and the climate. |
| Initial Cost | Heat pumps typically cost more upfront than traditional furnaces | The initial cost of a heat AC systemare less |
| Year-Round Use | Heat pumps can provide both heating and cooling, making them a versatile and efficient way to condition your home year-round. | Air conditioning can be used year-round to provide comfort and humidity control. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required | Regular maintenance required |
| Noise Levels | Generally quieter than traditional AC units | Can be noisy, especially window units |
| Lifespan | Typically longer lifespan than AC units | Typically shorter lifespan |
Heat Pumps or Air Conditioners or AC: Which One Do You Want?
You can find out whether your outdoor unit is a heat pump or an air conditioner by checking the manufacturer’s sticker. After that, you can identify the model number and write it down. If you are now backing inside, you will need to enter the number into your internet search engine. Based on the results, you will be able to determine what kind of system you have.
Heat Pump Workflow in Electric Cars in Winter
Cabins in the winter can get very cold & passengers feel uncomfortable sitting in them. Heat is extracted from other parts of the car and used to heat the cabin through a heat pump. It is not necessary for an electric vehicle to use its battery to generate power to heat its cabin using a resistive heater. 1kW of electric energy is converted into 3kW of thermal energy by a heat pump.
Air Conditioners Effects on Electric Vehicle’s Power Consumption
Electric cars become more critical as their range decreases by the same percentage as internal combustion engine cars. A warm interior is less desirable in the cold winter than an air conditioned interior in hot weather. Waste heat from internal combustion engines can heat the cabin almost for free in vehicles with internal combustion engines.
In electric vehicles, this heat source does not exist, so using the battery to heat the car electrically can reduce the range by up to 30 percent. If the air conditioner can operate as a heat pump, the energy consumption & range reduction will be much smaller.
Easy DIY for Heat Pump vs AC
Heat Pump: You should leave the installation of central air conditioners to a professional unless you have an HVAC background or experience. It is important to understand that heat pumps are complex machines that can cause problems for your home if they are not installed correctly.
Air Conditioners: You can install an air conditioner yourself, but most manufacturers won’t recommend it due to the potential for incorrect installation.
Appearance for Heat Pump & Air Conditioner
There are many similarities between heat pumps and air conditioners, not only in their functions, but also in their appearance. Using the manufacturing sticker, finding the emergency heat setting, turning on the heat and checking the outdoor unit for a reverse valve or turning on the heat will help you distinguish between the two.
Durability for Heat Pumps & Air Conditioners
Heat Pump: It takes a heat pump about 15 years to reach the end of its lifecycle. It takes them around ten years to develop in coastal regions, and it takes them closer to twenty-five years in moderate climates.
Air Conditioner: Typically, an air conditioner lasts 15 to 20 years, but it will also depend on the type of climate and the maintenance provided to it.
Heat Pumps vs Air Conditioning: Pros & Cons
Heat Pumps Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
| Efficient way to heat and cool your home | Higher initial cost than other heating systems |
| Can save you money on your energy bills | Not as effective in very cold weather |
| Quiet operation | May not be suitable for all homes |
| Safe and environmentally friendly | Higher initial cost than other heating systems |
Air Conditioners Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
| Increased comfort and productivity | Initial cost |
| Improved air quality | Maintenance costs |
| Reduced energy costs | Noise pollution |
| Increased home value | Health risks (for some people) |
Which One Should You Choose Between Heat Pumps vs Air Conditioners for home?
Ultimately, the decision between a heat pump and an air conditioner depends on your specific requirements and budget. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Climate: Evaluate the temperature fluctuations in your area. If winters are relatively mild, an air conditioner may be sufficient. For colder climates, a heat pump provides year-round comfort.
- Energy Efficiency: If energy efficiency and long-term savings are crucial to you, a heat pump is likely the better option.
- Budget: Consider your initial budget and long-term financial goals. Heat pumps may have higher upfront costs but can lead to reduced energy bills over time.
- Existing Heating System: If you already have an efficient heating system in place, adding an air conditioner might be a more cost-effective solution.
- Environmental Impact: If you prioritize eco-friendliness, a heat pump aligns better with sustainable practices.
Which One Do You Choose Heat Pumps or Air Conditioners for Your Car?
Depending on your climate region, a heat pump can be a smart choice for your home because of its energy efficiency. A heat pump needs to use more energy if your region regularly experiences temperatures below 40 degrees.
When you aren’t going to be using your air conditioner frequently, and your climate doesn’t require it to run all the time, an air conditioner can prove to be a better investment for you. The lifespan of air conditioners tends to be a little longer and their costs are lower, but their operating costs may be higher as well.
FAQs
What is the difference between a heat pump and an air conditioner?
A heat pump is a device that can both heat and cool your home. It works by transferring heat from one place to another. In the winter, a heat pump pulls heat from the outside air and transfers it inside your home. In the summer, a heat pump pulls heat from inside your home and transfers it outside.
An air conditioner only cools your home. It does this by removing heat from the air inside your home and transferring it outside.
Which is more efficient, a heat pump or an air conditioner?
Heat pumps are more efficient than air conditioners. This is because they can use the heat from the outside air to heat your home in the winter, which means they don’t have to use as much energy.
How much does it cost to install a heat pump?
The cost of installing a heat pump depends on the size of the unit, the type of unit, and the location of the unit. In general, heat pumps cost more to install than air conditioners.
How long does it take to pay back the cost of a heat pump?
The payback period for a heat pump depends on the cost of the unit, the cost of installation, the energy savings, and the cost of electricity. In general, heat pumps have a payback period of 5-10 years.
Are heat pumps worth the investment?
Heat pumps are a good investment if you are looking to save money on your energy bills in the long run. They are also a good investment if you are concerned about the environment. Heat pumps are more efficient than air conditioners and they produce fewer emissions.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind when choosing between a heat pump and an air conditioner:
The climate in your area. Heat pumps are more efficient in mild climates than in cold climates.
The size of your home. Larger homes require more powerful heat pumps.
The features that are important to you. Some heat pumps have features that air conditioners don’t have, such as humidity control and zoning.
Can You Use Heat Pump on your Car in Hot Weather?
Since heat pumps are used for both heating and cooling during the hot summers, you might ask yourself this question. A heat pump absorbs the excess heat from the cabin and releases it into the atmosphere using an external capacitor which acts as a heater and cooling device.
Winter poses some challenges for electric vehicles. A winter cabin in an electric vehicle can be hard to keep warm. A heat pump can help us address this issue easily.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both heat pumps and air conditioning systems have their merits, and the choice between the two depends on your specific needs and circumstances. For comprehensive heating and cooling capabilities and enhanced energy efficiency, a heat pump is a suitable choice. On the other hand, if cooling is your primary concern and you live in a relatively warm climate, an air conditioner can adequately meet your needs.
Before making a decision, it is advisable to consult with a qualified HVAC professional who can assess your requirements and recommend the most suitable system for your home or business. A well-informed choice will ensure that you enjoy optimal comfort and efficiency throughout the year. The winter months are the time of year when you need heating the most, so you might wonder how a heat pump can remove heat from the exterior. Well, think about the fact that your freezer is extremely cold, but it still transfers heat from the cold environment inside to the coils behind it. Despite the fact that cold environments lack heat energy, there is still heat energy present. Unless the temperature is extremely cold, this process will not work.


Viking Refrigerator Repair Chicago can provide you with quality Viking HVAC repair services.