In this article, we will learn about Cold Spring or Cold Springing or Cold Pull in piping system along with basics, definition, meaning, uses, why to use, when to use, advantages, disadvantages, etc. In many cases at site, during piping installation, a slight deformation may require to install the piping system properly. This deformation is done based on requirements and it is intentional and here comes, the term, “cold spring” or ”Cold Springing” or ”Cold Pull” is introduced.
What is Cold Springing or Cold Pull? Definition
Cold Springing or Cold Spring or Cold Pull Basics
In case of long run pipe, due to the change in weather, or due to temperature change, thermal expansion or compression happens.
- If temperature increases, then pipe tends to expand
- If temperature decreases, then pipe tends to compress.
If a large pipe is already fit at site, then what will happen if atmospheric temperature increases and vis versa? The changes in temperature induces the thermal stress into the long run pipe. Now, Cold spring or cold springing or cold pull helps to compensate this change in thermal stress by intentional deformation and normalize the pipe.
Cold Spring or Cold Pull Definition
Cold springing is defined as an intentional deformation process created by cutting short (i.e., cut short) or cutting little longer (i.e., cut long) than the required pipe spool to compensate the thermal stress created by temperature difference.
Cold Springing Characteristics
- It’s simply a slight lengthwise deformation process without changing the diameter of the pipe.
- It reduces the effect of temperature difference.
- It reduces the thermal stress created with in the pipe specially on the elbows or corner or expansion loops.
- It reduces the reaction forces at the anchor points.
- It is applicable for long run pipe between two anchors.
- Cold spring helps to make up the displacement and strain required for thermal stress.
- It subsides the effect created by hot stress and hot reaction.
- Hot stress may cause creep damage or permanent deformation of the pipe.
Why Does Cold Springing Require in Long Piping System?
Based on the above explanation, meaning, and definition, we understand the reason to use cold springing. Let’s summarize the reasons for cold springing:
- To reduce thermal stress
- To reduce hot stress
- To reduce the tendency of creep damage
- To reduce the hot reaction
- To help to compensate the effects and manage the system healthy
- To help to control the space for movement
- To reduce the loads on equipment in the hot state
- To increases the loads on equipment in the cold state
Process of Cold Spring: 4 Simple Steps
The following step-by-step process shall be considered for cold pull:
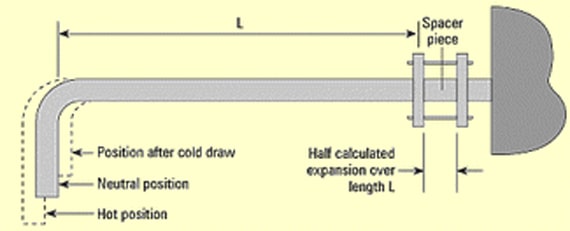
Step-01: Measure the normal length of the long pipe or spool without considering the temperature change. It may be between two anchors or joints.
Step-02: The second step is to determine the expansion of the long pipe due to temperature changes. Calculate the amount of expansion caused by thermal growth during full operation.
Step-03: The next step is to remove half of the calculated expansion from the original pipe.
Step-04: Now the pipe has to pull back at its original loop and stretched by bolting with the joints to make the system in such a way that stress will be acting always in one direction. So, if the temperature rise due to its cut short length, it will not be stressed. In normal working conditions, stress will be acting in opposite direction and make the piping loop stable.
For example, if piping stress is ‘Tp’ at the maximum temperature case, then the range of stress will be acting on the pipe will be ‘0’ to ‘T’. However, if we apply cold springing then the stress range will be changed from ‘–Tp/2’ to ‘Tp/2’.
Practical Approach for Cold Springing or Cold Pull
Now, let’s try to understand the practical approach for cold spring.
- The entire process shall be in presence of an efficient and experienced Stress Engineer.
- A spacer piece is used to assemble the pipe at site.
- The length of the spacer piece is equal to the ½ of the expansion calculated due to high temperature. The length of the expansion shall be calculated by a Stress Engineer with the help of the CAESAR report or AutoPIPE report.
- The spacer piece is installed between two flanges or joints, wherever the cold springing is required. Engineer has to check the location of spacer piece based on the force application and its direction.
- Installed the entire piping
 system.
system. - Properly anchored between flanges.
- Remove the spacer and the pipe will be automatically tight.
How to Calculate the Displacement of Pipe Required to Compensate During Cold Springing?
There is a formula to calculate the displacement of pipe for cold spring process and it is written as
D = Dc + (C x Dh), Where,
- D = Restraint displacement or Spacer piece to be adjusted during cold springing.
- Dc = Cold spring displacement without the restraint.
- C = Cold Spring Factor.
- Dh = Displacement due to high temperature without the gap and the spacer piece or restraint.
The cold spring factor C can be calculated based on the below formula:
Ci = ½ Li α dT, Where:
- dT = Change in temperature, (°F)
- Ci = Length of cold spring in the specific direction based on co-ordinate, it may either X or Y or Z (in Inches)
- Li = Total length of pipe subject to expansion in the same direction (in Inches)
- α = Mean thermal expansion coefficient, (inch/in/°F)
A System with Cold Spring Vs System without Cold Spring
Let’s see the difference between a system without Cold Spring Vs System with Cold Spring
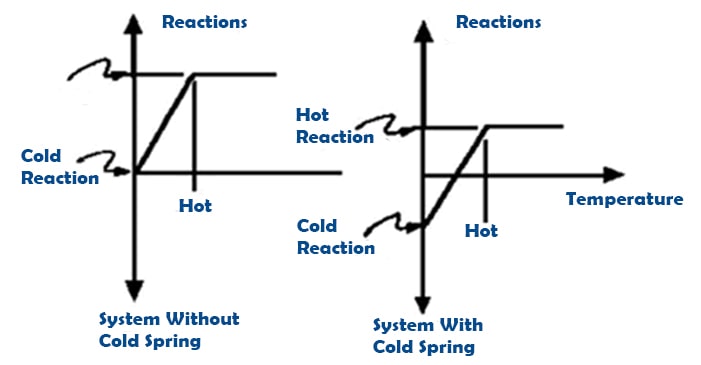
| A system with Cold Spring | A system without Cold Spring |
| It reduces the effect of temperature difference. | It cannot reduce the effect of temperature difference. |
| A slight lengthwise deformation has been done | No deformation has been done |
| It reduces the thermal stress created within the pipe, especially on the elbows or corners or expansion loops | It cannot reduce the thermal stress created within the pipe on the elbows or corners or expansion loops |
| It reduces the reaction forces at the anchor points | It cannot reduce the reaction forces at the anchor points |
| It is applicable for long-run pipes between two anchors. | It is applicable for the small pipe. |
| Cold spring helps to make up the displacement and strain required for thermal stress | It cannot. |
| Stress ranges are optimized and it is -½ to ½ unit. | Stress ranges are not optimized and it is from 0 to 1 unit. |
| Hot stress and hot reaction are reduced. | Hot stress and hot reaction are not reduced. |
| No chances of creep damage | Chance of creep damage |
Basic Considerations of Cold Springing
Basic considerations for cold springing shall be as follows:
- Cold reactions shall be always less than the nozzle or equipment allowable stress. In any cases, it should not exceed.
- During the fabrication process, manufacturer has considered some tolerances based on their recommendations. Cold spring should be more than that value.
- Expansion stress should be excluded for during the calculation from the cold spring effects.
- Finally, this process can only be opted by efficient & experienced Stress Engineer.
How to Calculate the Cold Springing? Example
Cold Springing Problem: Let’s try to understand the calculation process of cold spring. In the above figure, a piping system has been illustrated with it’s length, expansion, flange details. The operating temperature is 500°F and ambient temperature is 70°F. Mean coefficient of thermal expansion is 7-6 in/in/°F.
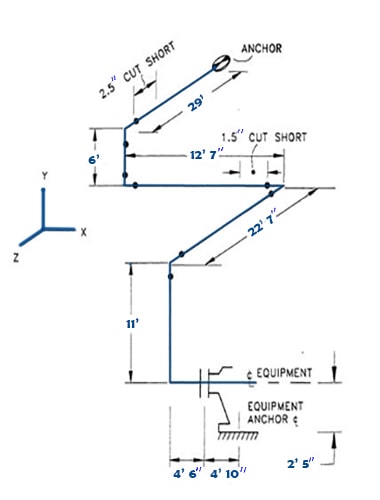
Given data: Temperature difference, dT = 500°F – 70°F = 430°F, α= 7-6 in/in/°F.
Solutions: We know, Ci = ½ Li α dT. Now, let’s calculate the value of Lx, Ly & Lz. From the above diagram, Lx consists of the 12’7”, 4’6” and 4’10”, Ly consists of 6′, 11′ and 2’5” and Lz consists of 29′ & 22’7”. We will convert ft into inch and calculate Lx, Ly & Lz from the equation.
- Lx = 12×12 + 7 + 4×12 + 6 + 4×12 + 10 = 163 inch
- Ly = 6×12 + 11×12 + 2×12 + 5 = 233 inch
- Lz = 29×12 + 22×12 + 7 = 619 inch
Putting the value Lx, Ly & Lz,
- Cx = ½ Lx α dT = ½ x 163 x 7-6 x 430 = 0.245 inch
- Cy = ½ Ly α dT = ½ x 233 x 7-6 x 430 = 0.350 inch
- Cz = ½ Lz α dT = ½ x 619 x 7-6 x 430 = 0.931 inch
Summary: So, cut short for pipe runs in X direction, Y direction and Z direction are 0.245 inch, 0.350 inch & 0.931 inch.
Modelling Example of Cold Springing in AutoPIPE
In case of modelling example for Cold Spring, say for AutoPIPE, if a cut short is specified at any point, cut will be applied at the preceding point of the pipe.
Let us create a model with “Cuts: Cold Spring” and “Model 1: Cut-Short. Consider two legs, horizontal leg (H) and vertical leg (V). Now, let us try to apply cut short on U1 load case for H leg and U2 load case for V leg. Refer the below images for brief illustration:
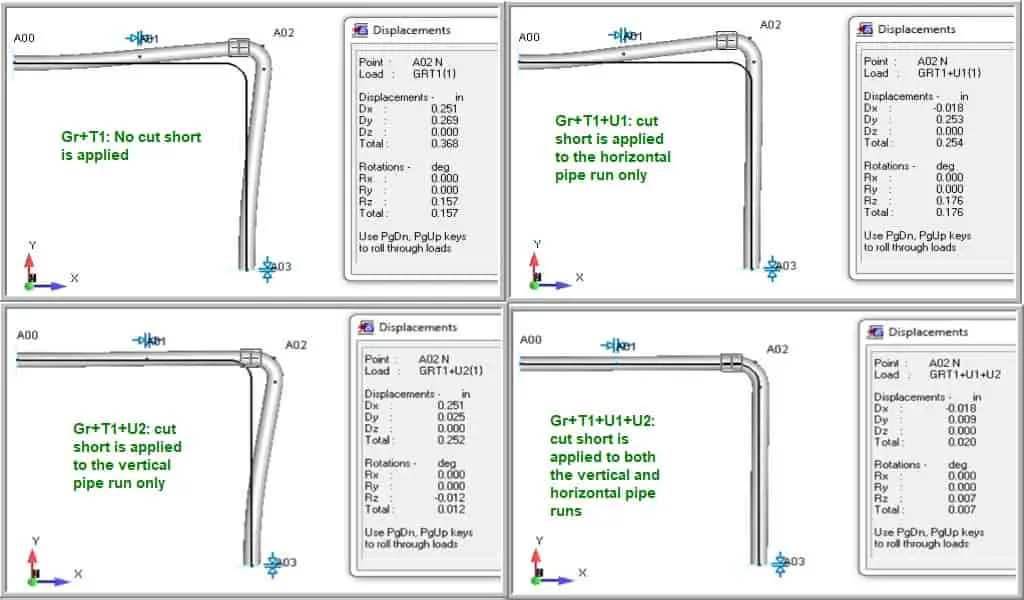
Help Center: Help > Contents> Contents Tab> Modelling Approaches> Modelling Approaches> Cuts: Cold Spring
Remember the below points:
- To reduce the anchor loads, the application of cut short is very helpful.
- The first point in any piping system, cut cannot be applied.
- In any piping bend, cut cannot be applied.
Modelling Design of Cold Springing in CAESER II
Let us try to understand the cold springing in CAESER II and it’s modelling design. In the CAESER II, we need to refer materials 18 & 19 for modelling of cold springing or cut short. There are many approaches for cold pull, however, we are explaining the easy way for basic understanding considering whole length modelling of the design cold spring. Let us see the steps:
1. Reset Property: Follow the cold spring element and reset the material property.
2. Modelling: Modelling to be done for the whole length of the design cold spring.
3. Analysis: You need to run the below cases in the software:
| Load Cases | Description | Inclusion |
| Load Case 1 (OPE) | W+T1+P1+CS | all design cold spring |
| Load Case 2 (OPE) | W+P1+CS | all design cold spring without the temperature. |
| Load Case 3 (SUS) – for code stress check | W+P1 | standard sustained case |
| Load Case4 (EXP)- for code stress check | L1-L2 | expansion case |
4. Equipment operating loads checking: Let us consider the following load cases:
| Load Cases | Description | Inclusion |
| Load Case 1 (OPE) | W+T1+P1+CS | all design cold spring |
| Load Case 2 (OPE) | W+P1+CS | all design cold spring without the temperature. |
| Load Case 3 (SUS) – for code stress check | W+P1 | standard sustained case |
| Load Case4 (EXP) | W+T1+P1+0.66 CS | use hot modulus |
| Load Case 5 (OPE) | W+T1+P1+1.33 CS | use hot modulus |
| Load Case 6 (EXP) – for code stress check | L1-L2 | expansion case |
Cold Spring of Axial Expansion Joint in START-PROF
In case of axial expansion joint, allowable axial displacement increases with the help of cold springing. Refer the below image from START-PROF , where, we see that there is no change on the fixed anchor loads and stresses. This is mainly because of the flexibility of expansion axial joint. For the modelling, refer the following steps:
, where, we see that there is no change on the fixed anchor loads and stresses. This is mainly because of the flexibility of expansion axial joint. For the modelling, refer the following steps:
- Nodes need to be put at any intermediate points and it needs to be close to the expansion joint.
- Exising element or bend shall be there as per the design.
- Prestretch deformation
 information shall be added to the nodes.
information shall be added to the nodes.
What Does Cold Springing Mean in Cryogenic Piping?
Cold pull or cold spring in cryogenic piping means the cut long in that pipes. As the name suggests, cut long implies an insertion of a pipe to make it longer than actually required. Cryogenic piping normally operates at a very low temperature for example below -290C and tends to be shorten at actual. To mitigate the technical requirements, a small increase in length will help the system to run smooth & efficiently.
Main Disadvantages or Drawbacks of Cold Springing
Although cold spring is used in some cases at site, the actual benefits are still in abeyance. Why the cold spring is not widely used? Let’s see the various disadvantages below:
- Cold spring is not helpful for high temperature pipes. For high temperature pipes, it will be very complex to calculate.
- For this process, extra anchors are required.
- Cranes or hoist required to place spacer piece or supports, additional efforts are required.
- In case any of minor error, cold spring gives wrong results.
- Very highly experienced Stress Engineer shall be required.
- Stress analysis shall be done for extra anchors or supports.
- Extra care shall be taken care during construction phase.
- Proper supervision shall be there.
- Cold springing is difficult of large diameter pipe.
- It is difficult of heavy welded pipe.
Limitation for Cold Springing
The limitation for cold springing process shall be as follows:
- Maximum temperature of pipe can be used cold spring is 400 deg. C.
- Wherever pipe is connected to the pump or turbine or any other rotating equipment, cold spring cannot be used.
- This process is not able to use near nozzles.
- Not recommended to use very high diameter and heavy welded pipe.
- ASME B31.1 has defined cold springing, however, no where it is mentioned the process and when it is to be applied.
- In the same way, ASME B31.3 has also indicated the cold springing, however, actual process and timing is not defined.
- When a pipe is in stress ranged condition, cold spring should be avoided.
- Not recommended to use in expansion loop or expansion joint.
Reference for Cold Springing
- ASME B31.1: 119.9 Cold Spring
- ASME B31.3: 319.2.4 Cold Spring
- ‘‘Piping Design and Engineering’’ by ITT Grinnell Industrial Piping.
- ‘’Piping Handbook’’ by Nayaar
Frequently Asked Questions for Cold Springing
What is cold springing pipe or What is cold spring in piping? or What is cold pull in piping?
Cold springing is defined as an intentional deformation process created by cutting short (i.e., cut short) or cutting little longer (i.e., cut long) than the required pipe spool to compensate the thermal stress created by temperature difference.
How are cold springs calculated?
We have learned the equation to calculate cold springing. The formula for cold sprining shall be as follows: C = ½ L α dT. If dT = 430°F, α= 7-6 in/in/°F, L = 163 inch. Then cold spring C = ½ x 163 x 7-6 x 430 = 0.245 inch
What does a Cold Spring mean?
During the hot conditions, if the displacement of pipe is 80mm in a particular direction for example X direction, then the amount of reduction of the pipe shall be considered as ½ of displacement. This reduction shall be as ½ of 80mm equals to 40mm. This value is called cold spring.
What does a Cold Spring Factor mean?
During the hot conditions, if the displacement of pipe is 80mm in a particular direction for example X direction, then the amount of cold springing of the pipe shall be considered as ½ of displacement, i.e., ½ of 80mm equals to 40mm. Here, the cold spring factor is 0.5.
What is a cut short in Caesar II?
A cut short in CAESER II means nothing but creating a very small intentional gap in the piping assembly to compensate the thermal stress caused by temperature difference.
Conclusion
Hence, we have learned about the cold springing or cold pull, its requirements, calculations etc. Please let us know if any doubt. Thank you.

I like this website very much, Its a really nice place to read and get information.
Thank you for visiting us, Appreciate, stay blessed