What are compressors? It is explained along with types, different parts or components, basic working principles, applications, etc. Let’s get into the article!
What are Compressors? Definition & Meaning
The compressor is pretty much an important component in most industrial machines and even for some household applications. From internal combustion engines to refrigerators the compressors are used and have a very important role in the operations. They have a wide range of applications. Let’s know more about them in detail.
- The compressor is basically, increases the pressure of the fluid by reducing its volume.
- The word compression obviously means reducing the volume of fluid.
- Later the fluid will be used for various applications or further processes.
- The gases are compressible and the compressor makes the best use of that characteristics.
- There is a vast variety of compressor types available right now. They are used according to the required applications.

The compressors and pumps are kind of similar but no worries. We will differentiate between these two in this article itself. So, the compressors are mostly used in the stages. The later stage is smaller than the first one. To increase the discharge pressure the stages are used. The more stages more will be compression. After getting the basic knowledge of what are compressors, let’s know about the wide range of compressor types.
Types of Compressors
The compressors are divided into two types. One is the positive displacement compressor that is mostly used and the other one is the dynamic compressor. We will see the types and later each of them in detail.
Positive displacement
The positive displacement compressor is the compressor, that compresses the air by the displacement of a mechanical linkage reducing the volume. In simple words, this compressor draws a discrete amount of volume of gas inside and forces them to exit the outlet of the compressor. Positive displacement compressors are classified into two types,
- Reciprocating compressors
- Rotary compressors
These compressors are further classified as follows,
Reciprocating compressors
- Diaphragm compressor
- Double-acting compressor
- Single-acting compressor
Rotary compressors
- Lobe compressor
- Scroll compressor
- Liquid Ring
- Screw compressor
- Vane compressor
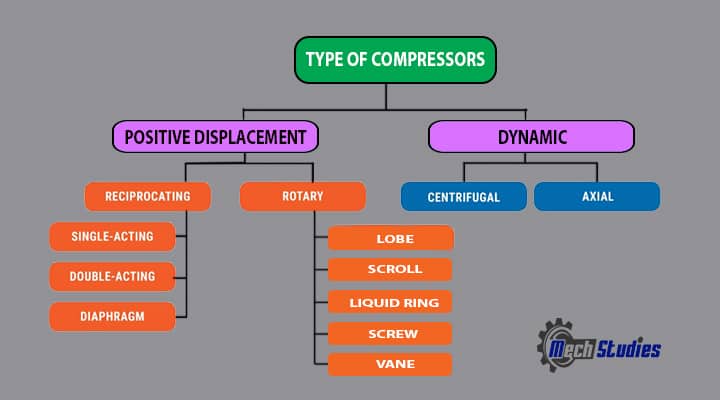
Dynamic Compressors
The dynamic compressors work at a constant pressure. Though the performance of the dynamic compressors is affected by external conditions. In these compressors, the air is drawn between the blades with the help of rapidly rotating impellers. Later the gas is discharged via a diffuser. These compressors are only having two types, depending on the main direction of the gas flow.
- Centrifugal compressor
- Axial compressor
Before going into the details of each compressor, let’s know about the general parts or components used in the compressor.
Parts of Compressors & Description
What are the Basic Parts of Compressors?
The compressor parts are follows,
- Pistons
- Connecting rods
- Actuators
- Bushings
- Gaskets & seals
- Rotors
- Valves
- Motor
- Intercoolers
- Couplings, etc.
Compressor Parts Description
Piston
The pistons are the integral part of the reciprocating compressors.
- The pistons create the air pressure with the aid of the piston and connecting rod movements.
- Pistons reciprocate up and down.
- For supporting the piston and guiding the piston the liner is available.
- The piston rings are used wherever necessary according to the types and purpose.
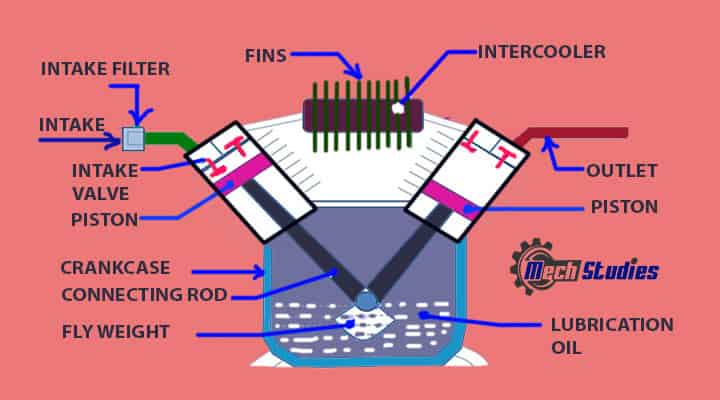
Connecting rods
The connecting rods are attached to the piston and used to move the piston up and down. They take the heavy workload and thus they are made by keeping durability in considerations.
Actuators
The actuators are responsible for creating rotary and linear movements.
are responsible for creating rotary and linear movements.
- They force the air to come out from the outlet ports.
- But if any leaks or deficiencies happens the actuators may experience some decrease in the output air force.
Bushings
The bushings are used to create a space between the moving parts.
- These are kinds of protection devices for the compressor.
- Incorporated in the internal parts of the air compressor they provide protection from breakdowns.
Gaskets and Seals
These are protection devices for the compressors. The air in the compressor should not be leaked and they should tight and sealed completely to avoid any accidents or breakdowns. These are provided to various parts of the compressor where leak protection should be implemented, Like,
- valve plate heads,
- crankcase,
- intercoolers,
- oil seals etc.
Rotors
The rotors are the parts of the rotor compressors.
- There are two interlocking arrangements of the two rotors that compress the air from the inlet valve.
- In case of the rotary compressor, they are the one that compresses the air.
Valves
The valves are the controlling equipment’s for the operation of compressors.
- The vales does the work like allowing air in and out, draining water, air flow regulation.
- These are checked regularly because the operation depends on the valves, if the valves perform abnormally it will directly affect the compressor.
Motor
The motor is used to run the operation of compressed air. However, there may be other drivers that can be used, like –
- Variable Frequency Drive.
- Steam turbines or Gas Turbines etc.
Intercoolers
The intercoolers are used to increase the overall performance of the compressors. It can be used to set the stages in the compressor.
Couplings
They prevent leaking from the high-pressure systems. Now it’s time to go into some brief details of each of the compressor types. Starting from the positive displacement compressor.
No products found.
Positive Displacement Compressors
Reciprocating Compressors
Let’s try to understand what are reciprocating compressors? Reciprocating compressors as the names suggest they are reciprocating nature with piston inclusion.
- They use pistons and are driven by crankshafts. Reciprocating compressors can be either single or multistage.
- They can be driven by electric motors or internal combustion engines.
- They are available in smaller ranges like 5-40 horsepower that are commonly used in automotive applications.
- Also, in wide ranges with the power of 1000 horsepower are used in large industries and petroleum applications.
Reciprocating compressors are further classified based on the number of discharge strokes per crankshaft revolution.
- Single Acting Reciprocating compressor: In this type, only one discharge stroke is completed in one crankshaft revolution.
- Double – Acting Reciprocating Compressor: In this type, two discharge strokes are completed in one crankshaft revolution.
In case of air compressions, the double-acting multi-stage reciprocating compressors are best suited. But they are costlier than the rotary compressors.
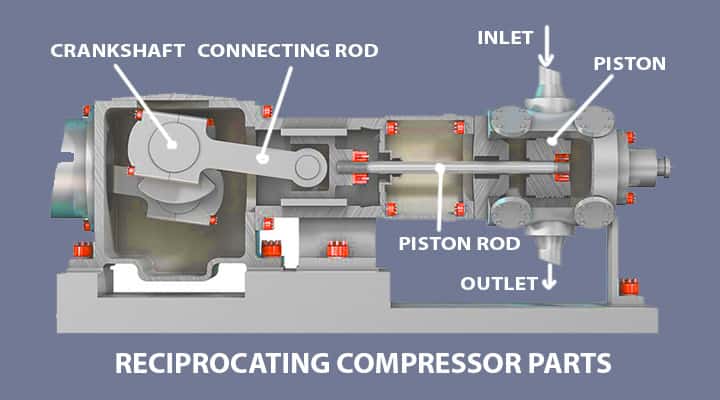
The reciprocating compressors are able to compress a wide range of gases, refrigerants. This characteristic of the reciprocating compressors enables them to be used in various applications by varying size, number of cylinders, etc.
Diaphragm compressors are the variant of reciprocating compressors. They have a flexible membrane that moves back and forth with the help of rod and crankshaft mechanisms. They are suited for pumping toxic and explosive gases.
Advantages of Reciprocating Compressors
- They are small in size especially the single-acting ones.
- These do not require any separate kind of lubricating system.
- Simple and easy maintenance.
- Multistage compressors are more efficient in operation.
Disadvantages of Reciprocating Compressors
- The relatively high cost of compressions.
- High space requirements
- High noise
Rotary compressors
Rotary screw compressors
It has the two helical screws meshed with each other. The helical screws push the gas to move into smaller space and hence get compressed.
- They are used for applications from 3 horsepower to 1200 horsepower.
- If we talk a brief about it working the helical screws are used that are closely meshed with each other.
- One is male and the other is female, by maintaining the precise alignment without any contact they compress the gas.
- After forcing the gas through the compressor, the gas exits at the end of the screws.
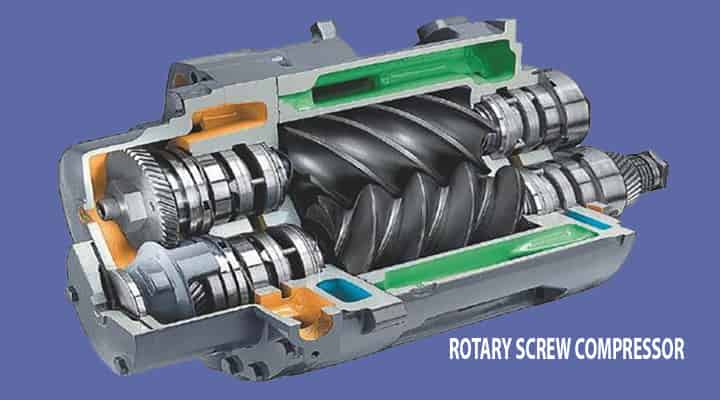
They are generally used for larger industrial applications for the supply of compressed air. Mostly used where the demand for continuous air is required.
Advantages of Rotary Screw Compressors
- Rotary screw compressors have a long life compared to other compressors.
- The demand capabilities are good.
- They are quiet in operations.
Disadvantages of Rotary Screw Compressors
- High initial costs.
- Requirements of special maintenance
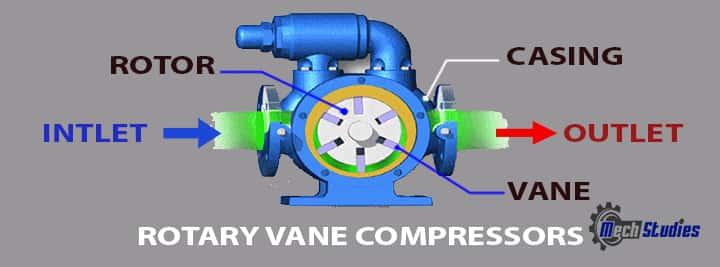
Rotary vane compressors
Rotary vane compressors are equipped with blades that are inserted in the radial slots available on the rotor. The rotor is mounted in kind of an offset with the larger housing. When the rotors turn blades will slide in and out of the slots.
- Hence because of the in and out of the blades, the increasing and decreasing volume is created.
- That’s how the air gets compressed in the rotary vane compressors. Alongside, with the piston compressors, these are one of the oldest compressors.
Advantages of Rotary vane compressors
- Vane compressors create good vacuum for suction.
- These compressors work well for the continuous air supplies.
- Longer life expectancy of vane compressors.
- Suited for moderate pressures.
Disadvantages of Rotary vane compressors
- Vibrations are more.
- Maintenance is high because of a greater number of moving parts.
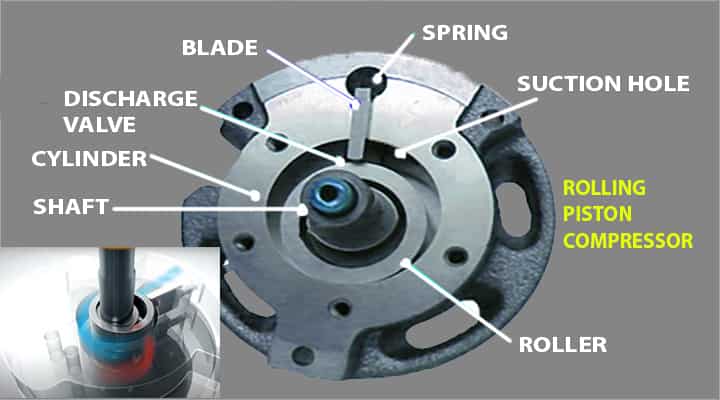
Rolling piston
The rolling piston as the name suggests it has the piston included which makes a partition. The partition is made between the vane and rotor.
- Hence the rolling piston will force the gas against the stationary vane and that’s how the air will get compressed.
- These rolling pistons offer higher efficiencies due to less losses.
- But the structure of rolling pistons if used for refrigerants it doesn’t allow the capacities beyond 5 tons.
Advantages of Rolling piston
- They are compact and light.
- Machines parts are well balanced and less noisy.
- Low initial costs.
- Simple lubrication.
Disadvantages of Rolling piston
- Discharge pressure per stage is low.
- No flexibility in case of capacity and compression ratio.
Scroll compressors
The scroll compressors are also known as spiral compressors because of its shape and structure. They are used in air conditioning, as an automobile supercharger, and as a vacuum pump.
- It has two interleaving scrolls to pump and compress the fluids.
- The geometry can be involute or Archimedean spiral.
- One of the scrolls used is fixed and other orbits eccentrically without rotating.
- Another method for producing the compression motion is co-rotating the scrolls, in synchronous motion, but with offset centers of rotation.
- The relative motion is the same as if one were orbiting.

Advantages of Scroll Compressor
- They are quite in operations.
- Simple design and fewer parts involved
- Low maintenance requirements.
- Oil-free designs.
Disadvantages of Scroll Compressor
- Low capacity
- Relatively they are expensive.
- If one element fails you may need to buy a whole new element.
- Compressed air may get very hot.
Dynamic Compressors
Centrifugal compressors
These are the sub-type of the dynamic compressors and are also known as radial compressors. They achieve compression with the help of kinetic energy added to the flow of fluid with the aid of a rotor or impeller. Later the kinetic energy is converted to the potential energy by slowing the flow via a diffuser.
- If we talk about its working, the fluid enters the compressor without any whirl or anything.
- But when the flow passes through the centrifugal impeller, the impeller will force the flow to spin faster.
- Later this kinetic energy is converted to potential energy in the form of pressure.
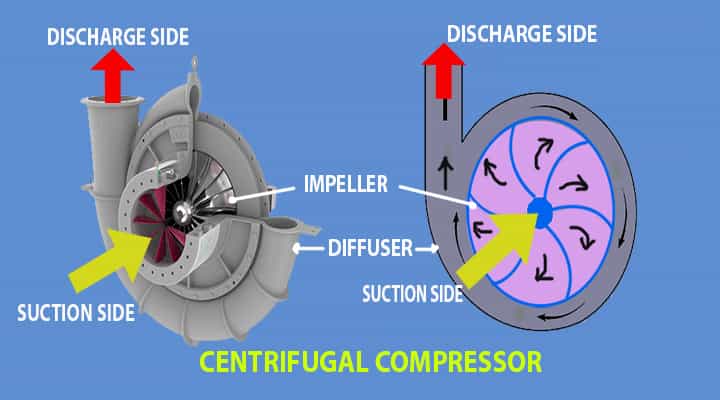
They are used in a wide range of applications like diesel engine turbochargers and superchargers. In the pipelines of natural gases to move the gas from production site to consumers of the gas. In Air conditioning and refrigeration, centrifugal compressors supply the compression in a cycle of water chillers.
Advantages of Centrifugal Compressor
- Low weight and easy to design
- They are oil free in nature
- High energy efficiency
- Wide range of speed of rotations
- They are reliable and have low maintenance
Disadvantages of Centrifugal Compressor
- High compression rates are not suited
- Sensitive to changes in gas composition
- Vibration mountings are needed
- Surging, stalling and choking problems
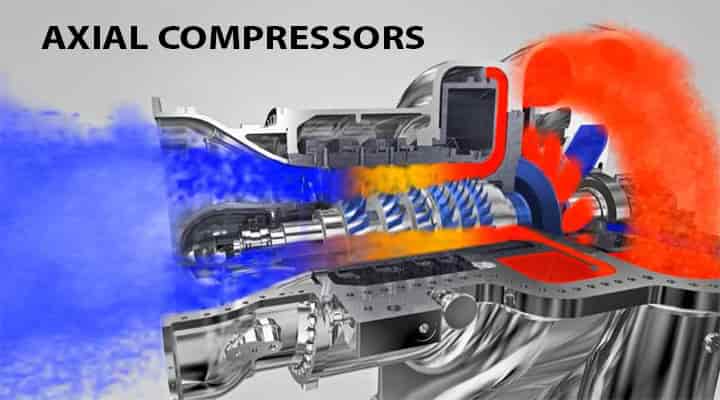
Axial Compressors
The second type of dynamic compressor is the axial compressor. These are the gas compressors that can continuously pressurize the gases. Axial compressor uses the arrays of fan-like airfoils to compress the fluid.
- There are two arrays of foils used in this compressor.
- One is the stationery and another one is the rotating one.
- The rotating airfoil can be called as blades or rotors and they will accelerate the fluid.
- The other one will deaccelerate the fluid and will redirect the direction of fluid for the next stage.
Axial compressors have high efficiencies but they are expensive and require high-quality materials. They are mostly used in large gas turbines, natural gas pumping stations, and chemical plants. Now we have seen both dynamic as well as positive displacement compressors.
Now let’s know the key differences between dynamic and positive displacement compressors.
Advantages of Axial Compressor
- Axial compressors have high peak efficiency.
- Small frontal area for a given flow.
- High ram efficiency.
- Increased pressure rises due to the increased number of stages and negligible losses
Disadvantages of Axial Compressor
- Manufacturing is difficult.
- High costs.
- These are pretty heavy in weight.
- High starting power requirements.
Compressor Capacity (FAD) Calculation
Let’s see what are the basic formula of compressor capacity and how it is calculated. Compressor capacity is calculated in terms of FAD, that is Free Air Delivery and it is stated at actual conditions.
It is expressed, as Q
Q = (P2-P1)/P0 x V/T Nm3/Min, Where,
- P0 = Atm pressure, kg/cm2
- P1 = Innitial Pressure, kg/cm2
- P2 = Final Pressure, kg/cm2
- V = Storage Volume, m3
- T = Time taken to build pressure.
A Nice ANIMATED VIDEO from Learnchannel!
Compressor Specification
A typical compressor specification shall consist of the followings,
- Designation
- Type of compressors
- Quantity
- Location (indoor or outdoor)
- Duty
- Capacity in FAD (Free air delivery)
- Nos. of stages (as applicable)
- Rated pressure
- Discharge pressure
- Maximum pressure
- Test pressure
- Outlet fluid temperature
- Shaft speed
- Material of Body
- Material of frame
- Material of bearing
- Material of rotor
- Material of suction & discharge flange
- Nominal power
- Electrical power supply
Difference between Dynamic and Positive Displacement Compressors
What are the differences between dynamic & positive displacement compressor? There are a few differences between positive displacement and dynamic compressors.
| Sr No | Positive displacement compressor | Dynamic compressor |
| 1) | The positive displacement compressors compress the air with the help of mechanical linkages, it physically reduces the volume and increases pressure. | In the dynamic ones, the fluid is provided with velocity by the impeller, and then with the help of a diffuser pressure is increased. |
| 2) | It compresses the fixed packets of the fluid. | It will compress the fluid in a continuous manner. |
| 3) | The velocity of fluid doesn’t require to be high. | Velocity of fluid must be high. |
| 4) | PDP will give constant flow rate against variable output pressure. | Dynamic will give a variable flow rate against variable output pressures. |
| 5) | The fluid will directly give the pressure energy. | First fluid have the kinetic energy and then converted to pressure energy. |
One more thing is to differentiate between the pump and compressor. Because of their similarities of work they often get confused so to ease out your doubt here is the difference between the compressor and the pump.
Difference between Compressor and Pump
What are the differences between compressor & pump? There are a few differences between compressor and pump.
| Sr no | Compressor | Pump |
| 1) | Compressor increases the potential energy by pressuring in smaller volumes. | The pump increases the kinetic energy of fluid which will further increase the pressure energy. |
| 2) | Compressor is used to transfer fluid from one place to another. | Pump is used to transfer fluid as well as liquid from one place to another. |
| 3) | Fluid used can be only gas or air | Any type of fluid can be used. |
| Liquid cannot be used | It’s one type of fluid and its widely used | |
| 4) | The volume change is occurred. | There is no volume change from inlet to outlet. |
| 5) | Compressors are more expensive. | They are cheaper than compressors. |
| 6) | Compressors are available with the storage facility. | Pumps don’t have any storage facility. |
| 7) | Discharge volume and intake volume is not the same for pump. | Discharge volume and intake volume is same for pump. |
| 8) | Compressible fluids are used. | Normally incompressible fluids are used. |
| 9) | It doesn’t associate with the cavitation problem. | It may associate with the cavitation problems. |
| 10) | Application: Pump station, water supply, oil & gas industries, etc. | Application: Pneumatic valve, filling air into tyres, power plant, refrigeration system, etc. |
Difference between Compressor vs Condenser
| Compressor | Condenser |
| The main function of the compressor is to compress the cold gas coming to it via the condenser before letting it out in the evaporator. | Once the work is done by the steam or compressed gas the fluid is expanded in the expansion valve and then enters the condenser where the fluid is condensed and transformed from gas to liquid. |
| It reduces the volume of fluid. | It increases the volume of fluid |
| The temperature of fluid increases after compression | The temperature of fluid decreases after condensation |
| The pressure of the fluid increases exponentially | The pressure of fluid decreases rapidly in the condenser |
Now compressor oil is one of the most important factors in the compressor.
What is Compressor Oil? Function & Types
It is important to select the right compressor oil to properly lubricate the parts and avoid damage due to friction.
What is the function of compressor oil?
- Reduce machine wear and tear due to friction
- Cooling the compressor by dissipating heat generated due to friction
- Avoid pressure drop by sealing the compression chamber
- Cleaning the cylinder and piston by carrying waste particles to the filter
What type of oil is used in the compressor?
The oil used can be differentiated into standard mineral oil and synthetic oil.
Standard Mineral Oil
- It is made from a mineral base and is available at cheaper rates.
- These oils are highly volatile and more likely to evaporate at a faster rate.
- They are susceptible to reacting with other elements as the carbon chain is not 100% saturated
- Major drawback of using standard oil is – the lifecycle is less and adversely affects the functioning of filters due to clumping.
Synthetic Oils
- These oils are high-quality products made from a synthetic base.
- Their lifecycle is 50% higher than the regular standard oil.
- They don’t react with other elements easily thus no clumps are formed
- Absence of sulfur and additives results in smooth valve functioning without any buildup formations.
Have you heard about the compressor surge? How it is damaged compressors? Let’s get the basic details.
What is Compressor Surge?
Compressor surge in many centrifugal and axial compressors results in the damage and destruction of parts. A condition in which the amount of gas present inside the compression chamber is not sufficient and is less than the required minimum quantity and the blades cannot transfer the energy from the shaft to the fluid resulting in the reverse flow of gas is known as the compressor surge.
Compressor surge happens due to the compressor arrangement and the working of the inlet pipe, valve, and the volume of air intake. A severe surge causes flow reversal, resulting in significant stresses that can damage compressor bearings, seals, and other rotating parts. There is also something known as a moderate surge, which is likewise an instability, however, it does not result in a complete reversal of flow. Anti-surge systems are installed in the compressor that detects the mounting surge using various sensors.
Installation of Compressors
Installing the compressor is a big task, much greater than buying it and bringing it at your workshop. Since the functionality of the compressor depends upon it installation, it is a crucial stage and one needs to follow the manufacturer’s compressor installation guide. The optimal installation will result in compressor live longevity, improved uptime, and lowered energy consumption. 5 things to consider while installing a compressor at your workstation:
Compressor Placement
The location or placement of the compressor is highly crucial, the spot selected for the compressor placement should have ample clearance area that can facilitate maintenance, loading, and unloading procedures. As the compressor operation is highly dynamic, this is another reason to think twice before selecting the location and building the foundation to anchor the machine.
As rotary compressors don’t need to be anchored on the ground and can be placed directly without any foundation, the placement should be leveled and flat. Also as dust and dirt are the elements that clog the compressor and compromise its working, the placement area should be away from the window through which waste particles, water, air, etc can affect it.
Selecting the Right Size Pipe
Airflow and pressure depend on the size of the pipe thus if the wrong size pipe is selected it will affect the pressure of compressed and the required airflow. Not just size but the material of pipe also plays an essential role in getting the quality air as output. Frequent pipe bends and long lengths should be avoided to reduce the pipe friction and pressure drops.
Selecting Appropriate Air-receiver
Air receiver is important as it stores the compressed air in it and supplies it to the application area when needed. It acts as a buffer when the air is compressed to deliver air continuously instead of load/unload format. It should contain a relief valve and calibrated pressure gauges. The relief valve needs to be set at a 10% higher value with respect to the working pressure.
Compressor Cooling and Ventilation
Excessive heating up of the compressor will affect the motor and other parts adversely. If there’s no heating up of the space where the compressor is placed then natural ventilation is sufficient. In case where heat is being generated and continuously increasing it is advisable to use exhaust fans and ventilation ducts to dissipate the hot air generated by the compressor exhaust.
Compressor Wiring
Make sure the compressor connections are all grounded and it is operated via three-phase power supply. To avoid damage due to excessive electrical power, proper fuse or circuit breakers should be attached and ensure that the power supplied should not go over +/- 10% of the required voltage given by the manufacturer.
Preventive Maintenance of Compressors
A machine owner should know that small preventive maintenance is always advisable over a breakdown. Doing preventive maintenance regularly will be beneficial for the operator as it will elevate the life of the compressor, decrease downtime due to total breakdown, and save costs with less money spent on part replacements. Two things that show the compressor needs maintenance:
Vibrating Machine Parts
As the compressor generates compressed air using moving parts the vibrations are bound to happen. Continuous vibrations cause equipment to get loosened as the connectors come out which in turn increases the vibrations further leading to part wear, bearing failure, and other mechanical misalignments.
Temperature Inconstancy
When compressors are running continuously and suddenly there’s an exponential increase in the temperature, it should be immediately shut down. Dust, grease, and other unwanted particles can clog the compressor or low oil levels can also result in the temperature increment.
Compressor Maintenance Checks
Air filter check
- Before starting the maintenance procedure always ensure that the compressor is off disconnected from the power source.
- Wait for some time to let the pump cool down.
- Extract the air filter top by unscrewing it from the filter base, and separating the top cover from the base.
- Remove the air filter element from the filter base.
- Thoroughly clean the element by blowing it and pulling out all the dust and debris accumulated in it.
- If the element is worn off, replace it with a new one.
- After cleaning and replacing assemble the air filter top and base again.
Compressor Pump Oil Change and Oil Level Inspection
- Always verify that the compressor is turned off and unplugged from the power source before beginning the maintenance operation.
- Place the compressor on a flat and leveled surface to avoid improper measurements.
- Remove the pump filler caps or plug.
- Place the drain tray beneath the oil drain plug and remove the cap to drain the used oil.
- Replace the cap if necessary and make sure it is tightened using white plumbers tape to seal it.
- Refill the pump crankcase with new oil by making sure that the oil is filled only till the halfway point.
General Trouble Shooting Procedures
Increased Compressor Vibrations
- Compressor operation speed can be inaccurate – Tuning it as per model
- Valve functioning needs to be checked
- Balance motor or engine if they are found imbalance.
- Measure the outlet pressure and if found excessive make sure it’s recalibrated.
Machine Overheating Issues
- Check if the pressure is too high based on the recommended pressure.
- Check if the intercooler or other parts are clogged with dust or other unwanted particles
- Check for piston and cylinder clearance as friction can heat up the compressor.
- Ensure lubrication oil is not dried down
Outlet Pressure Discharge is Low
- Clogging of air filter lines can restrict the air delivery potential.
- A damaged valve mechanism can alter compressor pressure.
- Loose piston or worn-out piston rings can reduce the air delivery pressure.
- Loose valve gaskets can also cause pressure drops as the compressed air can escape easily.
What are the Applications of Compressors?
There are various applications of compressors. We can give a few examples to understand it clearly.
Gas Compressor Package: Gas Compressors are used to recover the gas from the well in Oil & Gas project and these compressors are called as gas recovery compressors.
Power generation: In the gas turbine power plant, the compressor is one of the main equipment for power generation.
Air/Gas filling: All air or gas filling activity is associated with air/gas compressors. For examples, air filling to tyres.
Refrigeration & Air Conditioning system: The compressor is the heart of any refrigeration system or HVAC system which operates on vapor compression cycle. This compressor is called a refrigeration compressor. In a vapor absorption system, the compressor is not used.
Service air package: There are many areas like oil & gas industries, power plant, etc., service air is required for clearing or other activities. Here, compressor is the main component, and this compressor is called service air compressor.
Valve operation & instrument air package: Same as service air package, there are many areas like oil & gas industries, power plant, etc., where instrument air is essentials to operate different kinds of pneumatic valves and other activities. Here also, compressor is the main component, and this compressor is called instrument air compressor.
Standards of Compressors
There are few standards used to design compressor, as follows,
- ISO Standards: ISO-13707 and ISO-13631
- API Std. 617: Axial & Centrifugal Compressor & Expander Compressor
- API 618: Reciprocating compressor
- API 619: Rotary compressor
- API 681: Liquid ring compressor
- API 672: Centrifugal air Compressor
- API RP 688: Pulsation and Vibration Control.
Conclusion
So, these are the differences you should know about the compressors and the pump. There are lots of new advancements being made in compressors for increasing efficiencies and performances. Our YouTube animated Videos

Thank you
I like that you mentioned how compressors are pretty much an important component in most industrial machines and even for some household applications. I was helping out my uncle with repairing his car yesterday and I saw that he has an air compressor. I heard before that you could even get various air compressor parts now, like air compressor pipes.