Windmills are described along with basic definition, meaning, parts of the windmill, working, uses, electricity and power production, diagram. Let’s explore!
What are Windmills? Definition, Meaning, Purpose
Let’s start with the basics of windmills in terms of definition, meaning, and purpose.
Windmills Definition
Windmills are one of the important parts of renewable energy equipment. The windmills are historic and were used for a long time.
- Basically, the windmill converts wind energy into a useful amount of energy.
- In the early days, windmills were used to grind grain into flour.
- Transferring water from one place to another is also another use.
- In many windmills, oil was produced from grains.
We will see a little bit briefly about the history of Windmills in the next section.

Windmills are developed over a period of time with lots of advancements. In the 18th century, they were used widely in European regions. Nowadays, as we are moving slowly towards renewable energy sources wind power is one of the important energy sources. The world is already into making the turbine, and mills more effective and efficient. There is little difference between Wind turbines and Windmills, which we will cover later in this article. So, for now, let’s recall some history of Windmills.
History of Windmills
The windmills date back to A.D. 590 in Persia, and the first recorded design of the windmill was found in Persia. Humans are using windmill powers for centuries. The early, first use of windmills was using as a power source for the sailboats, propelling the ships across the water.
Later initially the windmills were used for pumping the water and later they were also used to grind grain into flour. In China, in 1219 AD the vertical windmills were much more spread while in European regions the horizontal windmills were widely spread. The windmills were power-driving machines for the whole of Europe in those days.
- Now coming in the 19th century, the use of Windmills was getting reduced as steam power took over.
- This caused the use of Windmills to decline, now only a few are used to power the world.
- The large windmills were in decline, but the small windmills used for pumping water in farms were greatly increased.
- Halladay Windmill was introduced in 1854 and later the Aermotor and Dempster designs were used.
- Some of these two designs are still used nowadays.
Parts of the Windmill with Diagram
The components or parts of Windmills are the same as Wind turbine obviously with some modifications and changes. But most of it serves the same purpose.

Parts of the windmill are as follows,
- Tower
- Blades
- Rotor
- Nacelle
- Brakes
- Shaft
- Generator
- Paddle wheel
- Anemometer
So let’s check these parts of windmills to have a basic idea.
Parts of the windmill #1 Tower
The height of the tower is decided according to the size of turbine used and the location it’s going to be placed. The thumb rule for the wind turbine tower is, the height of the tower should be the same as the diameter of the circle of its blades while rotating.
- The taller the turbine is built with the help of the tower more wind will be subjected to the wind turbine.
- Though wind does not have the same speed at various distances from the ground.
- They are made of materials like steel, concrete, or steel lattice.
Parts of the windmill #2 Blades
The blades are hollow and are made of composite material that is light and strong. New advancements are being done to make them larger for getting more power, lighter and stronger.
- The blade motion is known as blade pitch and it can rotate about 90 degrees to its axes.
- The shape of the blades is aerodynamic like the shape of airplane wings.
- They are not totally flat-shaped they twist at the roots and the tip.
- The windmills either have two or three blades. When the wind will blow it will cause it to lift and rotate.
Parts of the windmill #3 Rotor
The rotor is the one that accommodates the blades on the periphery. The rotor is equipped with three rotor blades, which are attached to the hub. Though the wind turbine may have 4-5 or any number of blades as per the requirements but the 3-blade arrangement is the most efficient and is widely used.
Parts of the windmill #4 Nacelle
The nacelle houses the generator of the wind turbines. It can be either gear-driven or direct drive. It includes all the components that are going to be placed at the top.
- All the complicated systems, and components are included in the housing.
- Also, the gearbox is used to adjust the rotational speeds.
- The gearbox is a kind of costly and heavy part of the windmills.
Parts of the windmill #5 Brakes
As the name suggests it purpose. The brakes can be applied hydraulically, pneumatically, mechanically or electrically in case of emergency situations.
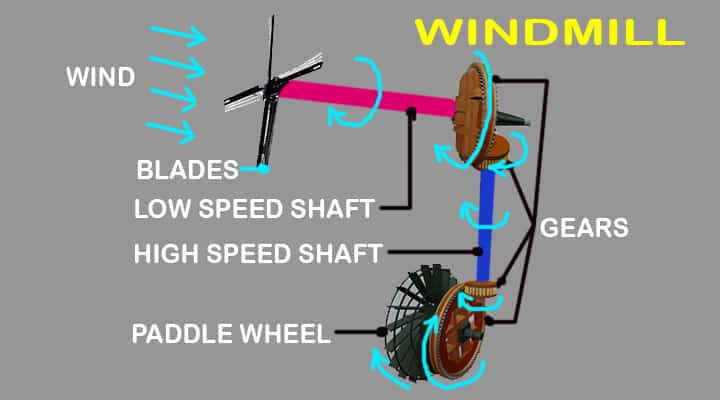
Parts of the windmill #6 Shafts
There are two types of shafts are used in windmills. One of them is a lower shaft that will transfer mechanical energy from the rotor to the gearbox. While the high-speed shafts will transfer the mechanical energy from the gearbox to the generator or paddle wheel based on the type of windmills.
Parts of the windmill #7 Generator
Different windmill has different components specifically in terms of generator or paddle wheel. In case, electricity is to be produced, the generator is used to induce a magnetic effect which transformed it into electricity.
Parts of the windmill #8 Paddle Wheel
In case, water needs to be transferred, a paddle wheel is used. Many times a big screw is also used to transfer water

As the paddle wheel is attached to a big gear, when the big gear rotates, the paddle wheel also rotates and water starts to transfer.
Parts of the windmill #9 Anemometer
The anemometer is one that measures the wind speed. The measurement of the wind speed is necessary for checking maximum power and checking emergency situations. Now is the time to know the types of windmills. Let’s check each one of them in brief detail.
Types of Windmills
There are two types of windmills, one is horizontal-axis windmills and the second one is vertical axis windmills. Let’s check each of them in detail.
Vertical Axis Windmills
The vertical axis windmills were pretty much popular in their early days. Their design as like the blades was perpendicular to the ground. They were seen first in Persia later in the 11th century they were spread over Asia, Europe and other regions. Though there are some issues with the vertical axis windmills and later they were replaced by the horizontal windmills.
Horizontal Axis Windmills
The horizontal axis windmills became so much popular and replaced the vertical axis windmills. These were first developed in the 12th century used in Northwest Europe. Due to the fruitful results like high efficiency and productivity the horizontal turbines were spread all over the world. There are four types of horizontal axis windmills we will see in more detail.
Post Mill
One of the oldest horizontal axis windmills is the post mil. The post mill is mounted on a single vertical post. It was like, the windmill can be turned to bring the sails into the wind. The use of the post mill was at the peak in the 18th and 19th centuries. But later declined after the high-speed steam-driven milling machinery. There are different types of post mills.
- Sunk post mill
These are the small mills but had the problems of stability. Because they were bowing down because of strong winds.
- Open trestle post mill
These are somewhat big windmills and the trestle (the frame on which the mill is supported) was not buried inside the ground. So, that’s the reason these are known as the open trestle post mill.

 via Wikimedia Commons
via Wikimedia Commons
They were used in lots of countries, in UK, Germany, New England, the USA these still exist in some parts.
- Post mill with roundhouse
In this type of mills the owners started to build roundhouses around the trestles. The space around the trestle is used for the storage.
- Midlands post mill
These were generally found in the Northwest of England.


The roundhouse in this mill had a curb and rollers to enable the roundhouse to bear some weight of the mill.
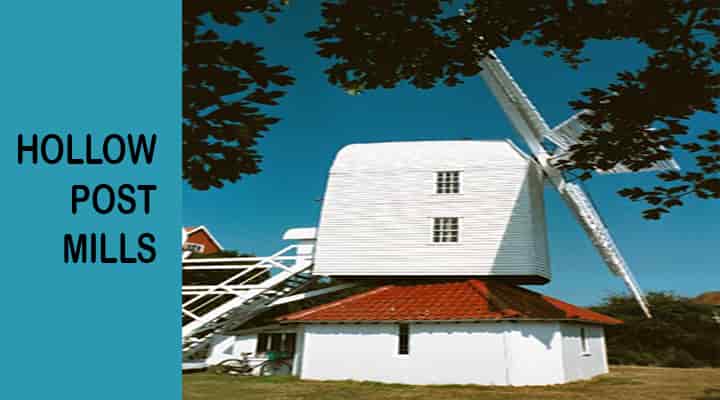
- Hollow post mill
In these mills the main post is bored to take driveshaft. This will enable the mill to drive machinery inside base or roundhouse.

 via Wikimedia Commons
via Wikimedia Commons
These were mostly used for drainage and corn milling.
- Composite mill
These mills were somewhat like the post mills. But the composite mills were lacking the central post on which the body was mounted.
- Paltrok mill
It was invented by Dutch in 1600 and was used for sawing wood. The millhouse was enlarged and supported on this rim by numerous rollers or small wheels.

 via Wikimedia commons
via Wikimedia commons
These mills are technically composite mills although the tower is very short and of large diameter.
Tower Mills
The tower mills were consisting or brick or stone tower. The rotating cap was available in these tower mills that gave advantages like more withstand ability than the post mills. The world’s tallest tower mill is in Schiedam, Netherlands. Mostly the tower mills were used for,

- grinding corn,
- producing pepper and spices,
- powering sawmills,
- changing wood pulp into paper.
Smock mills
The name of this turbine came from its shape of body because it looks like smock. These are the horizontal towers having six to eight sides. One of the advantages of smock mill is that the top part of flexible. So, this part can be moved according to the direction of wind while other remaining stable.
As we know already the taller the tower more wind it can get so while being main body stable the smock mill could be much bigger and taller. Also, because of this, productivity is high. Smock mills are lighter in weight as compared to tower mills.
Fan mills
The fan mills were designed and used for a single purpose only. It is equipped with four to twenty blades and primarily used for pumping water in farms. So, these are the types of windmills and their brief descriptions.
Check a NICE VIDEO on Windmills from Holland Holiday,
Let’s check the basic working principle of a windmill!
Working Windmills: How Does Windmill Works?
We have already introduced with different parts of windmill, now, let’s try to learn how do windmills work in simple steps.
Step#1 Source of Energy – Wind
The source of energy is wind and this energy is called wind energy. The wind is flowing naturally and consists of energy. The wind strikes the windmill blades and converts its energy into kinetic energy.
The windmill blades are designed in such a way that it can be adjusted with respect to the wind direction. As the wind force acts on the windmill blades, a lift force & drag forces are created. The resultant of these lift force and drag force helps to rotate the blades.
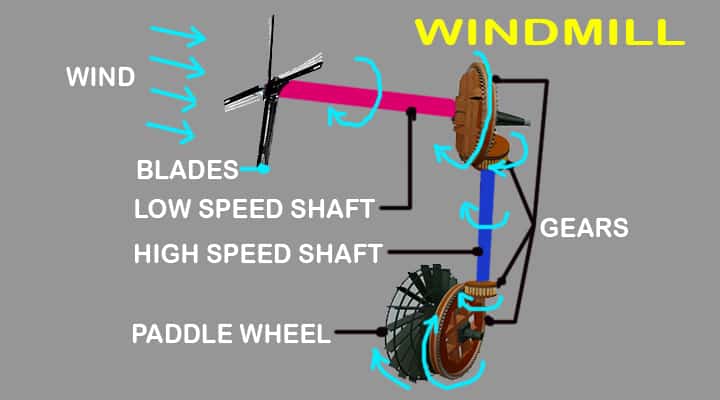
Step#2 Rotation of Windmill Rotor
Blades are mounted to the rotor and the rotor is attached to a hub. Due to the rotation of windmill blades, the attached rotor will also rotate.
Step#3 Low-Speed Shaft Rotation
The windmill rotor is connected to a low-speed shaft which will rotate with respect to the rotation of the rotor. Mainly this shaft is used to transfer mechanical energy from the rotor to the gearbox.
Step#4 High-Speed Shaft Rotation
In the windmill, a high-speed shaft is also there to transfer mechanical energy to the generator from the gearbox.
Step#4 Increase of windmill speed
To control the speed or windmills, there is a gearbox mechanism. It is mounted inside the nacelle. The speed can be controlled or increased by varying the gear ratio by the gearbox.
Step#5 Generator /Paddle Wheel
There is a generator to produce electricity from the rotation of the main shaft. The main shaft is connected to a generator and creates electricity by the magnetic effect between the generator stator and generator rotor.
In many windmills, the paddle wheel is connected to the high-speed shaft through a gear mechanism. When the gear rotates, the paddle wheel also rotates and water starts to transfer.
Step#6 Power Transmission or Water Transfer
The produced electricity from the generator is transferred to a power grid through power cables. Power cables run within the windmill tower and it is distributed upto the consumption points. In case of the Paddle wheel, water is transferred from one place to another. The paddle wheel consists of some blades or small buckets which help to transfer water when it rotates.
Step#7 Controls
Many sensors or transmitter are used now a days to control the windmills. Now let’s check out some advantages and disadvantages of the windmills. So, the windmills are related to Wind Power so the advantages and disadvantages are similar.
Now let’s check out the difference between the windmills and wind turbines. Though the windmills are considered as wind turbines. But compared to the old times there are some differences.
Difference between Windmill and Wind Turbine
| Sr No | Windmills | Wind Turbine |
| 1 | The windmill converts the energy of wind to pump water or milling grains. | It converts the kinetic energy of the wind to generate large amount electric power. |
| 2 | The pressure difference is created over different regions and wind blows over blades causing rotations. | Works on the pricincple of lift and drag exploiting aerodynamic forces generating wind blow against the blades and blades will move relative to the wind. |
| 3 | These are less modernized. | They are technologically advanced and are modernized. |
| 4) | Used for water pumping, grain milling and for agricultural use. | Used to generate the electricity for the regions. |
Advantages of Windmills
There are many advantages of windmills or wind energy, as follows,
- The first advantages would be obviously the never-ending energy source. Wind energy is considered as a replacement for the power production by other non-renewable energy sources.
- Windmill generators doesn’t emit any harmful gases or emissions leading to the environmental damages.
- Land available around the windmills can be used for other purposes. Unlike other power stations where specific land is reserved.
- The wind energy is the most important power source for the remote areas.
- Wind energy combined with solar can be pretty much helpful to generate constant power supply.
Disadvantages of Windmills
There are many disadvantages of windmills or wind energy, as follows,
- The storage costs are expensive at the peak production time.
- The winds are uncertain, hence its not reliable to be dependent on wind power all the time.
- Requires open areas for setup.
- High maintenance costs.
What Windmills are Used For?
Let’s see the uses of windmills,
- Windmills convert wind energy into electrical energy and help to pump groundwater,
- It mainly helped in the earlier days to make flour from grains.
- Helps to extract oils from various kinds of seeds or crops.
- Used to processing small scale commodities like Tobacco, etc.
What’s the future of Windmills?
The windmills are in the use since centuries. Though there were no major advancements till 19th centuries. The new modern wind turbines are slowly taking a big part in developing the renewable sources of energy. Nowadays the Wind turbine are proving to be useful specially in remote areas where other electrical energy sources are difficult to reach. The advancements and mass production of parts are bringing the cost of turbines down and even small groups or people can use the turbines for serving their power needs like schools and colleges.
Conclusion
This is the simple basics of windmills, its definition, meanings, electricity production, etc. Any questions, on windmill or its parts, please let us know.

what could be the possible problem statement of the windmill