When it comes to heating our homes, gas furnaces have long been a reliable and efficient solution. The comforting warmth they provide during cold months is a staple of modern living. However, a question often arises: can a gas furnace work without electricity? It is a query that delves into the intricate interplay between traditional heating methods and our modern reliance on electrical power.
Will A Gas Furnace Work Without Electricity? Role of Electricity
We will unravel the complexities of gas furnace operation and the crucial role electricity plays within this system. While gas is the primary fuel source that generates the heat, various components within a gas furnace require electricity to function efficiently. From ignition mechanisms to blower systems and control devices, each part is intricately connected to ensure the furnace’s optimal performance.
Parts of a Gas Furnace
A gas furnace, at its core, is designed to efficiently convert natural gas or propane into heat, effectively warming our living spaces. To achieve this, it relies on a complex assembly of components, each playing a crucial role in the heating process. Understanding these key components provides insight into how the furnace operates and the role electricity plays within this system.
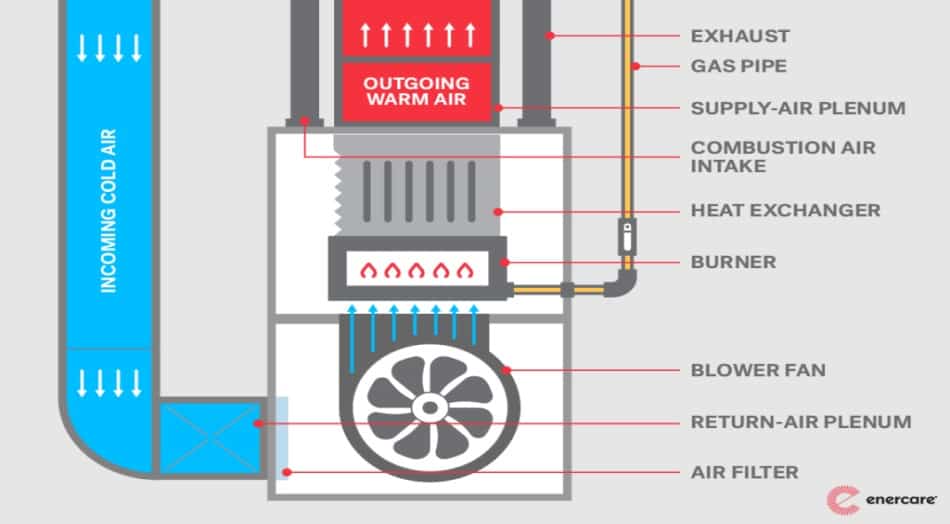
- Burner: The burner is where the combustion of gas takes place. It releases flames that generate the heat required for warming the air.
- Heat Exchanger: This component absorbs the heat generated by the burner and transfers it to the air circulating throughout your home. It ensures that the combustion gases are safely vented outside.
- Ignition System: The ignition system is responsible for igniting the gas within the burner. Different ignition methods include pilot light ignition, hot surface ignition, and direct spark ignition. Electricity is often crucial for these ignition mechanisms to function, initiating the combustion process.
- Blower System: The blower, also known as the fan, is responsible for moving air through the furnace and into the ductwork that distributes warm air throughout your home. Electricity powers the blower, enabling it to circulate heated air effectively.
- Control Systems: These systems manage various furnace functions, including regulating temperature, monitoring safety features, and controlling the ignition and blower processes. Control boards and sensors are integral to these systems, often requiring electricity for operation.
Dependence on Electricity: Ignition, Blower, and Control Systems
A modern gas furnace represents a sophisticated integration of engineering and technology designed to provide efficient and consistent heating for homes. While the primary source of heat is natural gas or propane, electricity is an essential partner in enabling the furnace to function optimally.
This interdependence is rooted in the various components that collectively create a seamless heating experience. Let’s delve deeper into these aspects and explore why a modern gas furnace simply cannot work without electricity.

- Ignition Mechanisms: The days of manually lighting a gas furnace are largely behind us. Modern furnaces employ advanced ignition mechanisms that require electricity for operation. For instance, hot surface ignition involves an electrically heated element that ignites the gas upon contact. Direct spark ignition uses electrical sparks to initiate combustion. Without electricity, these mechanisms are rendered inoperable, leaving the furnace unable to kick start the heating process.
- Blower System: The blower system is responsible for circulating the warm air produced by the furnace throughout the living spaces. This circulation ensures even heating distribution and maintains a comfortable environment. The blower motor, a crucial part of this process, requires electricity to operate. Without it, the blower remains dormant, causing the heated air to stagnate within the furnace and preventing its effective distribution.
- Control Systems and Sensors: The heart of modern gas furnace operation lies in its control systems and sensors. These components monitor temperature, regulate ignition sequences, and ensure safety measures are in place. Control boards, thermostats, and safety sensors all rely on electricity to function properly. A lack of electricity can disrupt these functions, leading to unreliable heating, potential safety hazards, or even system malfunctions.
- Safety Features: Gas furnaces incorporate safety features to mitigate risks associated with gas leaks, overheating, and other potential hazards. These safety mechanisms often rely on electrical components to detect abnormalities and trigger shutdowns if necessary. Without electricity, these protective measures might be compromised, posing risks to both the furnace’s operation and the occupants’ safety.
- Smart Technology: Many modern gas furnaces are compatible with smart thermostats and remote control systems. These technologies allow homeowners to monitor and adjust heating settings remotely, promoting energy efficiency and convenience. Smart features depend on electricity to communicate with the furnace and execute commands, enhancing user experience and control.
Modern Gas Furnace and their Dependence on Electricity
| Component | Function | Dependence on Electricity |
| Ignition Mechanisms | Initiate combustion for heat generation | Fully dependent; electricity ignites gas |
| Blower System | Circulate warm air through ducts | Fully dependent; blower motor requires power |
| Control Systems | Regulate temperature, safety, and ignition processes | Fully dependent; control boards, sensors require electricity |
| Safety Features | Prevent hazards and ensure safe operation | Dependent; safety mechanisms rely on electricity |
| Smart Technology | Enhance control and energy efficiency | Dependent; smart features require electricity |
A contemporary gas furnace, in essence, is a harmonic union of old heating methods and advanced technology. While the heat source is gas, electricity allows the furnace to operate effectively, safely, and adaptably.
Electricity is the backbone of this sophisticated system, from the initial lighting through the steady circulation of warm air and exact control. As a result, reliance on electricity is more than just a convenience; it is a vital prerequisite for the proper running of a contemporary gas furnace.
Ignition Mechanisms in Gas Furnaces: Understanding Their Function and Electricity’s Role
Ignition mechanisms are the critical first step in the operation of a gas furnace. They play a pivotal role in initiating the combustion process that generates the heat required for home heating. In modern gas furnaces, there are several ignition methods employed, each with its unique characteristics and dependence on electricity.

1. Pilot Light Ignition:
Pilot light ignition was one of the earliest methods used in gas furnaces. It involves a small, continuously burning flame known as a pilot light. This pilot light is fuelled by a steady supply of gas. When the furnace is triggered to heat, the pilot light’s flame is used to ignite the main burner, thus initiating the combustion process.
2. Hot Surface Ignition:
Hot surface ignition is a more modern and efficient ignition method. In this mechanism, an electrical component a hot surface igniter is used. This igniter consists of a ceramic material that heats up rapidly when an electric current passes through it. When the furnace is turned on, the hot surface igniter heats up to a high temperature. When the gas valve opens, the hot surface igniter’s heat ignites the gas, starting the combustion process.
3. Direct Spark Ignition:
Direct spark ignition is another advanced ignition method that relies on electricity. It involves the use of an electric spark to ignite the gas. When the furnace is activated, an electric spark is generated near the burner. This spark ignites the gas, allowing the combustion process to begin. Direct spark ignition is known for its reliability and quick ignition times.
| Ignition Mechanism | Description | Electricity’s Role |
| Pilot Light Ignition | Small, continuous gas flame (pilot light) is used to ignite the main burner. | Initial ignition of pilot light requires an electric spark or flame. |
| Hot Surface Ignition | Electric hot surface igniter rapidly heats up to ignite the gas. | Electricity is essential to power the hot surface igniter, enabling it to reach the necessary temperature for ignition. |
| Direct Spark Ignition | Electric spark is generated to ignite the gas directly. | Electricity is responsible for generating the spark that ignites the gas. |
A contemporary gas furnace, in essence, is a harmonic union of old heating methods and advanced technology. While the heat source is gas, electricity allows the furnace to operate effectively, safely, and adaptably.
Electricity is the backbone of this sophisticated system, from the initial lighting through the steady circulation of warm air and exact control. As a result, reliance on electricity is more than just a convenience; it is a vital prerequisite for the proper running of a contemporary gas furnace.
Blower System in Gas Furnaces: Crucial Function, Electrical Dependency, and Potential Alternatives
The blower system is a fundamental component within a gas furnace, playing a pivotal role in distributing the heat generated by the furnace throughout your home. Understanding its significance, how it relies on electricity, and potential alternatives for operation sheds light on the essential interplay between gas furnaces and electrical power.
Function of the Blower in a Gas Furnace:
The blower system is responsible for moving the warmed air produced by the furnace’s combustion process into the ductwork that spreads throughout your living spaces. It ensures a consistent and even distribution of heat, preventing hot or cold spots and creating a comfortable environment in every room. The blower also aids in maintaining a balanced airflow, helping to keep the furnace working efficiently.
Electricity’s Role in Operating the Blower:
Electricity is indispensable for the operation of the blower system. The blower motor, which powers the fan responsible for moving the air, requires electrical energy to function effectively.
When the thermostat signals the furnace to produce heat, the blower motor is activated simultaneously, drawing air across the heat exchanger and into the ducts. Without electricity, the blower motor remains inactive, and the warm air generated by the furnace remains trapped within, rendering the heating process ineffective.
Potential Alternatives for Blower Operation:
In cases where a reliable electrical power supply is not available, alternative solutions for operating the blower system become necessary. Here are a couple of potential alternatives:
- Battery Backup Systems: Some modern gas furnaces are equipped with battery backup systems. These batteries can provide limited power to essential components like the blower motor during electrical outages. While this option offers a temporary solution, the battery’s capacity and lifespan are limiting factors.
- Generators: A more comprehensive solution involves using a generator to provide electricity during power outages. A properly sized generator can supply the necessary power to the blower system, enabling the furnace to function as intended even when the grid is down. However, generators come with installation and maintenance considerations.
Control Systems and Thermostats in Gas Furnaces: Ensuring Efficiency, Electricity’s Influence & Manual vs. Electric Options
Control systems and thermostats are the brains behind a gas furnace’s operation, responsible for regulating temperature, safety features, and overall functionality. Understanding their functions, the impact of electricity on their operation, and the choice between manual and electric thermostats provides insight into how these systems contribute to the interplay between gas furnaces and electrical power.

Thermostat Function in Furnace Operation:
The thermostat serves as the primary interface between you and your gas furnace. Its primary function is to monitor the temperature within your home and signal the furnace to generate heat when necessary. When the temperature drops below the desired setting, the thermostat sends a signal to the furnace’s control system to initiate the heating process. Once the desired temperature is reached, the thermostat instructs the furnace to stop producing heat.
Impact of Electricity on Thermostat Communication:
Electricity plays a central role in enabling the communication between the thermostat and the gas furnace’s control system. When you adjust the thermostat’s temperature settings, the thermostat uses electrical signals to convey your preferences to the control system. The control system then determines when to ignite the burner, engage the blower, and ensure safety measures are in place. This seamless communication hinges on a steady supply of electricity; without it, the thermostat’s ability to regulate the furnace’s operation is compromised.
Manual vs Electric Thermostat Operation:
Thermostats come in both manual and electric variants, each with its unique features and benefits:
1. Manual Thermostats:
Manual thermostats are the more traditional option. They are operated manually by turning a dial or lever to set the desired temperature. These thermostats do not rely on electricity for their core function, making them resilient during power outages. However, they lack the advanced programming and remote control capabilities of electric thermostats.
2. Electric (Programmable or Smart) Thermostats:
Electric thermostats, often programmable or smart, offer advanced features and energy-saving capabilities. They allow you to set specific temperature schedules and remotely control the heating system. These thermostats rely on electricity for their programmable functions, connectivity, and touch screen interfaces. While they enhance convenience and energy efficiency, they are dependent on a stable power supply to operate effectively.
| Feature | Manual Thermostats | Electric (Programmable/Smart) Thermostats |
| Operation Method | Manual adjustment using a dial or lever | Programmable or smart settings, often with touchscreen interfaces |
| Power Dependency | No reliance on electricity for core function | Requires electricity for programming, display, and advanced features |
| Temperature Adjustments | Manual adjustments based on user input | Scheduled adjustments and remote control capabilities |
| Programming | Limited or no programming options | Pre-set schedules or user-customizable programs for energy efficiency |
| Energy Savings | Limited ability to optimize energy usage | Enhanced energy savings through scheduling and adaptive features |
| Remote Control | No remote control capabilities | Remote adjustments via smartphone apps or online platforms (smart thermostats) |
| Flexibility | Basic temperature control | Customizable schedules and settings for specific days/times |
| Convenience | Straightforward operation | Advanced features enhance comfort and convenience |
| Adaptability | Limited adaptability to changing schedules | Adapt to changes in occupancy and preferences (smart thermostats) |
| Integration with HVAC Systems | Suitable for most standard systems | Compatibility with a wide range of HVAC systems |
| Price Range | Generally more affordable | May have a higher upfront cost, but potential long-term energy savings |
| Power Outages | Operable during power outages | Requires electricity to maintain programmed settings (smart thermostats) |
Emergency Power Sources for Gas Furnaces: Ensuring Heat during Electrical Outages
In situations where power outages disrupt the normal flow of electricity, having a contingency plan for your gas furnace becomes essential. Emergency power sources, such as battery backup systems and generators, offer solutions to keep your furnace running and your home heated even when the grid goes down.
Battery Backup Systems for Gas Furnaces:
Battery backup systems provide a temporary power source that keeps essential components of your gas furnace operational during short power outages. These systems are designed to supply power to critical functions like ignition mechanisms, control systems, and blower motors.
While battery backup systems do not provide a long-lasting solution, they can offer valuable time until electricity is restored. The main advantage is that they are relatively simple to install and maintain, providing a level of assurance during brief interruptions in power supply.
Generators as an Emergency Power Solution:
Generators are more comprehensive solutions for prolonged power outages. They provide a consistent supply of electricity to various appliances and systems, including gas furnaces. An emergency situation would benefit from this.
Portable Generators: These versatile generators can be moved to different locations and connected to the furnace via extension cords or transfer switches. While they provide a reliable source of power, they require manual setup and fuel management.
Standby Generators: Installed permanently outside the home, standby generators are connected directly to the electrical system and automatically switch on when a power outage is detected. They can power the entire house, including the gas furnace, without the need for manual intervention. However, standby generators involve more complex installation and maintenance.
Considerations for Implementing Emergency Power:
When considering emergency power sources for your gas furnace, several factors come into play:
- Furnace Compatibility: Ensure that the emergency power source is compatible with your specific gas furnace model and its electrical requirements.
- Power Capacity: Assess the power needs of your furnace, including ignition mechanisms, blower motors, and control systems. Choose an emergency power source that can provide the necessary wattage.
- Duration: Determine how long you anticipate power outages lasting in your area. Battery backup systems are suitable for shorter disruptions, while generators are better suited for extended outages.
- Installation and Safety: Proper installation is crucial for both battery backup systems and generators. Follow manufacturer instructions and consider professional assistance for generator installation. Safety precautions, such as adequate ventilation for generators, are essential.
- Fuel Supply: Generators require a fuel source, typically gasoline, propane, or diesel. Ensure you have a sufficient supply of fuel and proper storage.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is necessary to keep emergency power sources in optimal working condition. Check batteries, fuel levels, and components according to manufacturer guidelines.
| Emergency Power Sources | Features and Benefits | Considerations |
| Battery Backup Systems | Provides temporary power during short outages | Limited duration |
| Supports critical furnace components | Simple installation | |
| Requires minimal maintenance | Suitable for brief outages | |
| Offers immediate assurance | ||
| Generators | Offers consistent power for extended outages | Complex installation |
| Can power entire home, including furnace | Fuel supply required | |
| Automatic activation (standby generators) | Professional installation | |
| Requires maintenance and fuel management | Suitable for extended outages |
Turning on a Gas Furnace without Electricity: Emergency Steps
In situations where electricity is unavailable, you can still activate a gas furnace using manual methods. While these steps are not intended for routine use, they can be crucial during power outages or emergencies:
- Check the Pilot Light: If your gas furnace uses a pilot light ignition, check if the pilot light is still lit. If not, follow the manufacturer’s instructions to relight it manually.
- Ignition Switches: Some gas furnaces have mechanical ignition switches that can be operated without electricity. Refer to your furnace’s manual to locate and use these switches to ignite the burner.
- Blower System: While the blower system relies on electricity, some gas furnaces have a manual setting that allows you to operate the blower manually. Be cautious and use this option only as necessary, as running the blower without proper ventilation can pose risks.
- Manual Thermostat: If you have a manual thermostat, adjust it to the desired temperature. Keep in mind that manual thermostats do not require electricity to function.
Furnaces that Work Without Electricity: Gravity and Direct Vent Furnaces
Gravity Furnaces
Gravity furnaces, commonly found in older homes, rely on the principle of hot air rising and cool air sinking. They don’t require electricity for operation. Warm air generated by the furnace naturally rises and flows through ducts to heat the home. However, these furnaces are less common now due to efficiency and safety concerns.
Direct Vent Furnaces
Direct vent furnaces are designed to be more energy-efficient and safe. They draw combustion air from outside and exhaust gases directly outside. While they typically use electricity for ignition and blower operation, certain models offer a manual mode that allows for operation without electricity. An emergency situation would benefit from this.
Alternative Heating Options during Power Outages
In situations where a gas furnace’s operation is hindered by a power outage, several alternative heating methods can provide comfort and warmth:
- Fireplaces and Wood Stoves: Traditional sources of heat, burning wood or logs in fireplaces and stoves offer immediate warmth without relying on electricity.
- Gas Fireplaces and Inserts: Certain gas fireplaces have backup options for ignition and operation, using natural gas or propane as fuel sources.
- Kerosene and Propane Heaters: Portable kerosene and propane heaters provide localized heat, making them useful during outages.
- Portable Generators with Electric Heaters: Using a gas-powered generator, you can operate electric space heaters for temporary heating.
- Solar-Powered Heaters: Solar-powered options capture and store sunlight to generate heat, offering sustainable warmth.
- Layering Clothing and Blankets: In milder outages, simply bundling up with layered clothing and blankets can help retain body heat.
- Thermal Insulation: Properly sealing windows and doors, and using thermal curtains, can help retain indoor warmth.
Each alternative comes with considerations for safety, fuel availability, and effectiveness, ensuring you stay warm and prepared when your gas furnace is not an option.
Products that can serve as alternative heating options during power outages
Mr. Heater Big Buddy Portable Propane Heater:
- Description: A portable propane heater with two heat settings and a built-in blower fan for even heat distribution.
- Features: Suitable for indoor use, auto shut-off safety feature, can heat up to 450 square feet.
Duraflame Electric Infrared Quartz Fireplace Stove:
- Description: An electric fireplace stove that mimics the look of a wood-burning stove and provides infrared heat.
- Features: Realistic flame effect, adjustable thermostat, safe for use around children and pets.
Lasko Ceramic Portable Space Heater:
- Description: A compact electric space heater with adjustable thermostat and oscillating feature.
- Features: Multiple heat settings, safety features like overheat protection, easy portability.
BioLite CampStove 2+ Wood Burning and USB Charging Camping Stove:
- Description: A wood-burning camp stove that generates heat for cooking and also produces electricity for charging devices.
- Features: USB charging port, compact and portable design, eco-friendly energy generation.
Dyna-Glo Vent-Free Wall Heater:
- Description: A wall-mounted propane heater designed for indoor use, providing consistent heat without electricity.
- Features: Vent-free design, adjustable heat settings, battery-powered ignition.
Goal Zero Yeti 400 Portable Power Station:
- Description: A portable power station that can store energy and power small appliances, including electric heaters.
- Features: Multiple AC and USB outlets, rechargeable via solar panels or wall outlet.
Few types of furnaces that can work without electricity
- Gravity Furnaces: Gravity furnaces, common in older homes, rely on the natural convection of air. They do not require electricity for operation as warm air naturally rises and circulates through ducts, providing heat.
- Direct Vent Furnaces: Some direct vent furnaces can operate without electricity. Due to their ability to draw combustion air from the outside and vent exhaust gases directly, these furnaces are useful even in power outages.
- Wood-Burning Stoves: Wood-burning stoves provide heat through burning wood, requiring no electricity. They are especially useful for heating individual rooms during power disruptions.
- Propane and Natural Gas Space Heaters: Vent less propane and natural gas space heaters can operate without electricity. They directly burn fuel to produce heat, making them reliable during outages.
- Pellet Stoves: Pellet stoves burn compressed wood pellets for heat. Some models have battery-operated ignition systems, allowing operation without electricity.
- Coal Stoves: Coal stoves can provide consistent heat without electricity. They burn coal to produce heat, offering an alternative to electrically-powered systems.
- Solar Air Heaters: Solar air heaters capture sunlight to generate heat without electricity. They are environmentally friendly and can provide supplemental heat during outages.
These furnaces offer heating options that do not rely on electricity, making them valuable choices for maintaining warmth during power interruptions.
Modern Innovations and Hybrid Systems in Gas Furnaces: Integrating Electricity and Alternative Energy
In the realm of gas furnace technology, modern innovations have led to the development of hybrid systems that cleverly combine traditional gas heating with alternative energy sources, often supported by electricity. These advancements aim to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and convenience in heating solutions.
Hybrid Furnace Systems with Electricity and Alternative Energy:
Hybrid furnace systems are designed to leverage the strengths of both gas and alternative energy sources, while also incorporating the role of electricity. These systems integrate a gas furnace with technologies such as heat pumps, solar panels, or geothermal systems. By doing so, they offer flexible heating options that can switch between gas and alternative energy based on factors like outdoor temperatures and energy availability.
During milder weather, the system might rely more on the alternative energy source, reducing gas consumption and optimizing energy efficiency. Electricity plays a critical role in coordinating the various components of these hybrid systems, ensuring seamless transitions and efficient heating.
Smart Thermostats and Remote Monitoring:
Another aspect of modern innovation in gas furnaces is the advent of smart thermostats and remote monitoring capabilities. These technologically advanced thermostats can connect to your home’s Wi-Fi network, allowing you to control and monitor your furnace remotely through smartphone apps or online platforms.
While they require electricity to function, their benefits extend beyond convenience. Smart thermostats enable precise temperature scheduling, adaptive learning, and energy-saving modes, ultimately optimizing the furnace’s performance. During power outages, some smart thermostats are equipped with battery backups to maintain essential functions.
FAQs
Can a gas furnace still produce heat during a power outage?
Gas furnaces themselves can generate heat, but their various components, such as ignition mechanisms, blowers, and control systems, rely on electricity for operation. Without electricity, these essential functions cannot work effectively. However, some models have manual ignition options or battery backups for limited operation during short outages.
Are there alternative methods to operate a gas furnace without electricity?
Yes, there are some methods to temporarily operate a gas furnace without electricity. Some gas furnaces have manual ignition switches or settings that allow limited functionality. Additionally, battery backup systems or standby generators can be used to power certain components during power outages, ensuring continuous heating. However, these alternatives are often temporary solutions and may have limitations depending on the duration of the outage and the specific furnace model.
Conclusion: Ensuring Heating Reliability and Informed Choices
The reliance of gas furnaces on electricity for ignition, blower systems, and control functions underscores the importance of planning for power outages. While gas furnaces are central to home heating, understanding their dependence on electricity prompts the consideration of backup plans.
Exploring options like battery backups, standby generators, and alternative heating methods can help maintain warmth during outages. Additionally, innovations such as hybrid systems and smart thermostats offer ways to enhance efficiency and adaptability. By making informed decisions and preparing for potential disruptions, homeowners can ensure comfort and heating reliability even when electricity is temporarily unavailable.

