Rolling mills along with types of rolling, definition, working process along with rolling of metals are described. Let’s start rolling of metals in Rolling Mills!
Rolling of Metals in Mills, Basic, Types
Rolling of Metals
Let’s explore the rolling of metals as well as Rolling Mills! There are numerous manufacturing processes through which we, mankind, have gained the upper hand. While getting an understanding of various manufacturing processes, it is quite essential to get an understanding of the rolling process.
- This is one of the historical manufacturing processes that our forefathers are also implementing.
- This process has its perks as it helps efficiently in getting the desired shape.
- Rolling is among the most critical and influential methods of the manufacturing process that keeps its place.

This article is concentric on one of the efficient manufacturing processes that hold a massive impact. Here, we will provide all the relevant information regarding this process.
Let’s roll out the sheet of information about the rolling process. This process can be carried out in cold or hot conditions. The rolling process can provide the components that are equipped with optimal mechanical properties than cast components. With this process’s help Slabs, Sheets, Bars, Rods, Structural components of different lengths can be produced.
What is Rolling Process?
Rolling is a process in which the material is drawn with the action of friction between two rotating cylindrical rolls that helps reduce the thickness of the material.
- In this process, the two cylindrical rollers are attached with bearings driven with the help of a powerful motor.
- The tolerance between the rolls can be effectively calibrated as per need.
- This gap or tolerance is known as the roll gap of a calibrated opening.
- It is one of the most efficient and credible metalworking processes that help in gaining massive production.
- In this process, it is relatively easy to attain close control over the final product as well.
Types of Rolling
Types of rolling are wide for this process. However, we will learn rolling types in this article after understanding the basic terminology & working philosophy of the rolling process.
Terminology in Rolling of Metals
Before going to the details process, we will learn few terminologies used in Rolling process.
Ingot
- It is casted metals and has a very high temperature around 1200 deg. C
- It is fully with porosity and blowholes.
- Size of the ingot depends on the project requirements and it can be different sizes.
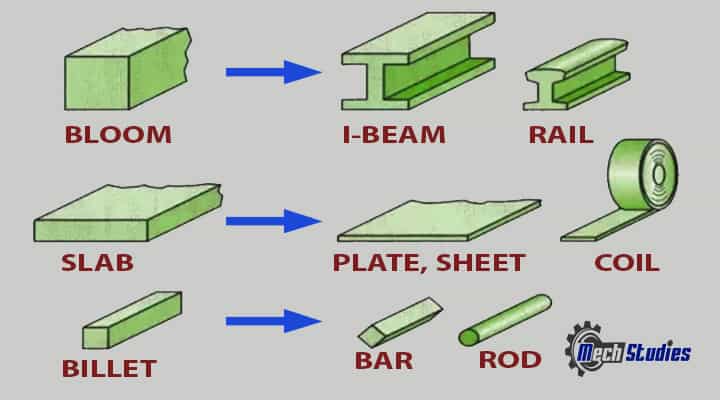
Blooms
- Bloom is the first material which is made from the ingot.
- This is the first materials produced from the ingot.
- It is produced at very high temperature.
- It may be square or rectangular in shape and size can be 150 mm x 150mm or 150mm x 200mm or 250mm x 250mm.
- I -beams, channels are examples.
Billets
- Billets are produced from blooms.
- The size of billets is about 50mm x 50mm or 100mm x 100mm or 125mm x 125mm.
- Pipes, wires, bars etc. are produced.
Slab
- Slab is made from ingot or billet.
- It may be rectangular in shape and size will be 600mm to 1500mm width and 50mm to 160mm thickness.
- Plates, strip, sheets etc. are produced.
Plate
- Slab is rolled further to form plate.
- It can be finished or may be semi-finished.
- The thickness of plate is more than 6 mm.
Sheet
- This is formed from plate.
- Very thin and maximum thickness is around 6 mm.
Strip
- It is produced from sheet.
- Maximum width is 600mm.
- Maximum thickness is 6mm.
Foil
- Very thin strip.
- Maximum width is 300 mm.
- Thickness 1.5 mm maximum.
Bar
- Long and straight metal piece.
- Uniform cross section.
- It may be circular i.e. rod or it may be square in shape.
Wire
- It is formed from bar.
- Very thin.
- Size is 9.5 square mm in cross section.
How Does Rolling of Metals Work?
Rolling Process Basic Concept
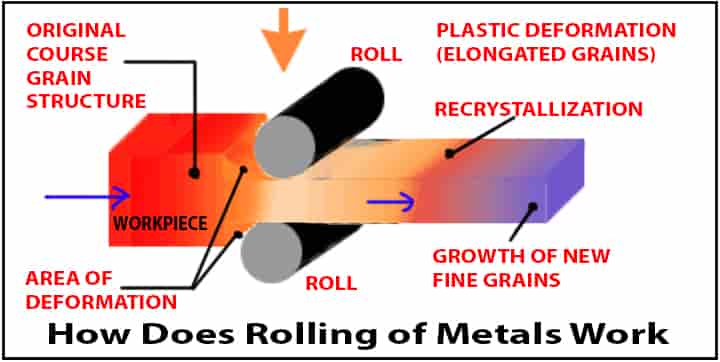
It is quite essential to understand the steps associated with the rolling process as it will provide a holistic idea about the whole process. So, how does the rolling of metals work? We will learn the basics first.
- The metal is heated at some temperature in which the grain of the crystal structure
 is changed into a new shape.
is changed into a new shape. - It helps to reduce the ductility and the strength of the metals.
- These soft metals are easy to change in shape as the requirements of force for the deformation are less. Now, learn working philosophy!
Working Philosophy of Rolling Process
Let’s learn the rolling process step by step!
- In this, the workpiece or material undergoes plastic deformation due to the compressive forces.
- The length gets elongated, and the cross-sectional area decreases, but the total volume remains the same.
- The rolls will squeeze the material or workpiece by inducing compressive stress due to the rotating action.
- The process deals with the starting material, i.e Ingot, which is manufactured with metal dies.
- Ingot can be of any geometrical shape and size.
- It is obtained by acquiring a molten metal in a furnace.
- Molten metal with appropriate temperature is poured into the metal die cavity and allowed to cool.
- After this process, the solid metal is taken out, and this metal is known as Ingot.
This Ingot is now passed through the rolls to get the desired shape per need, such as,
- billets,
- bars,
- slabs,
- plates,
- sheets, or
- structural components.
Basic Parameters in Rolling Process
While using the rolling process as an effective manufacturing process, we understand that numerous parameters define the whole process’s efficiency. Here, we are providing some of them as it will help in understanding the entire process efficiently.
Deformation Resistance Capabilities of Metals
- Deformation is one of the essential aspects of the rolling process as it indicates the capacity of metal towards resistance to plastic deformation.
- It is the resistance of the metal for the external load. Deformation resistance is directly proportional to the difficulty to deform plastically.
- Deformation also comes into play when there is a temperature change. Deformation resistance is inversely proportional to the increasing temperature.
Roll Specifications
- The roll specifications matter a lot in the rolling process as it is directly proportional to the rolling load and the length of the arc of contact. With the decrease in roll diameter, the arc of contact and rolling load’s length also decreases.
- There is the need for an optimum flat workpiece, then the use of small diameter rolls is used, which are backed up by large rolls.
Friction Between Workpiece and Rolls
- The frictional force is among the most critical factors that come into play in this process. It is used to pull the metal into the rolls.
- The frictional force also provides a significant fraction of the rolling load.
- Friction changes from point to point with the arc of contact of the roll.
- The product of high friction is the high rolling load which increases the efficiency of the rolling process.
- The coefficient of friction is inversely proportional to the tolling speed. It helps attain thinner gauge sheets that can be obtained in the cold rolling process as in that process, the coefficient of friction remains smaller.
Availability of Roll Tension
- The roll tensions are capable of decreasing the rolling load. If an optimal amount of tension is present in the roll, then the process doesn’t need excessive roll loading capacity.
- Tension has different qualities as it helps in reducing the wear of rolls. In addition to that, it also provides adequate flatness and uniform thickness in the sheet.
Types of Rolling of Metals
The rolling process can be classified based on various aspects. It can be classified into three types which contain other parameters. Here we are providing the classification of the rolling process:
- On the basis of the temperature of the metal during rolling
- On the basis of the roll’s numbers
- On the basis of the roll’s arrangement
- On the basis of products to be rolled
These are some of the aspects on which rolling processes can be classified. These are further discussed elaboratively.
01. Rolling Types Basis on Temperature of Metals
On the basis of the temperature rolling process is further subdivided into two categories. These are the following types of rolling:
Hot rolling process: The hot rolling process is effectively used for converting ingots to plates, billets to bars, and billets to different desired structural shapes.
- This process is used for thick and heavy sections.
- This process provides optimal and uniform mechanical properties, but the surface finish is below par.
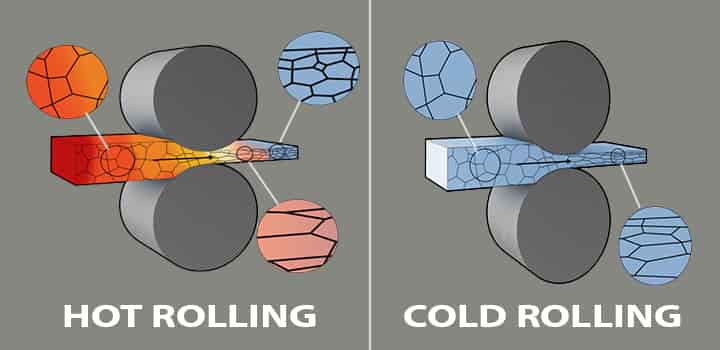
Cold rolling process: The cold rolling process is specifically for transforming the section plates to bars or foils, or wires. This process is effective and efficient for obtaining surface finish with optimal properties.
02. Rolling Types Based on Rolls Numbers
This kind of arrangement in the rolling process is attained or decided on the basis type of metal being rolled, amount of reduction required, properties, and shape of the product.
- Based on these, the minimum number of rolls is finalized.
- This process may consist of two rollers at a minimum, and the higher end is concluded based on the aspects discussed.
While discussing different kinds of the mill here, we have to also keep a check on some specific terms.
- The most prominent one which we are going to use is the “mill.”
- The mill is nothing but a reference to the type of rolling process.
- It provides an understanding of the whole, a setup that consists of the arrangement of rolls and the type of operation being carried out.
The following are the types of rolling processes based on rolls arrangement and their numbers:
Two (2) high roll mill: This kind of rolling process is equipped with two rolls. The rolls are located above one another.
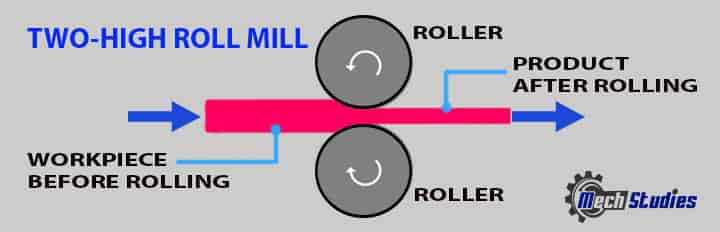
- In this arrangement, a controlled gap or opening is among the rolls.
- This gap explicitly provides an idea of the desired thickness of the product.
- Both the rolls are cylindrical and mounted on the bearings.
- The rotary function of the rolls is due to the motors attached.
- In this kind of arrangement, there is a tolerance for changing the rolling direction.
- It can be changed just by changing the direction of rotation of the rolls.
- These kinds of rolls are mainly used for the production of billets and blooms.
Three (3) high roll mill: This arrangement in the rolling process specifically contains three rolls which are located one above the other. These rolls are situated at their centers in a vertical plane.
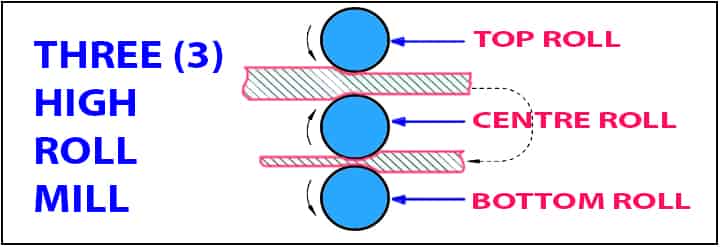
- In these three rolls, the outer one rotates in one direction, and the center one rotates in the opposite direction.
- With this, one can attain an optimum reduction in the thickness of the product.
- Apart from all of this, this kind of mill provides higher output.
4-high roll mill: This is the arrangement of a rolling process that has four rolls in the setup. Here among the four rolls, two are of smaller form and specifically responsible for the product’s deformation.
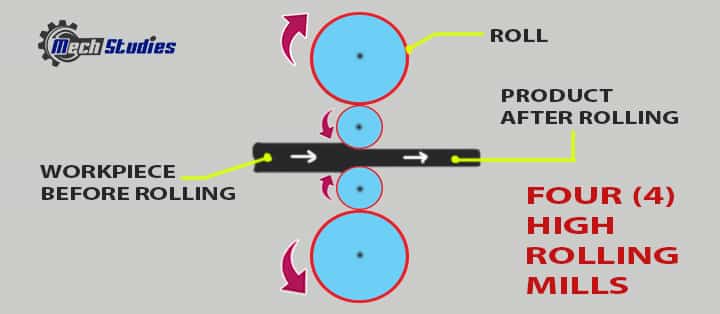
- The two backup rolls are for preventing the deflection while rolling.
- This kind of mill is used for higher reduction in the products and is more rigid in work.
The above types of rolling processes are based on several rolls.
03. Types of Rolling Based on Arrangement
The following are on the base basis of arrangement:
Tandem roll mill: A Tandem roll mill is the rolling process arrangement in which four high mills are in synchronization one after another. The product undergoes each one of them, which provides a reduction in thickness.
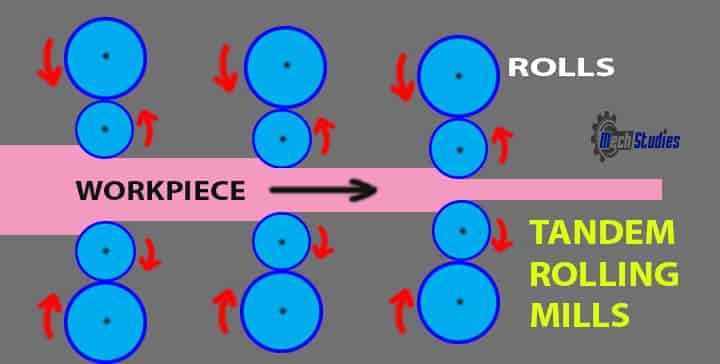
- In this arrangement, each mill is known as a stand; thus, the name tandem comes.
- This is specifically used for the decrease in thickness.
- There is a need for utmost smoothness, and optimal surface quality, this kind of arrangement is used.
Sendizmer roll mill: Sendizmer is a clustered form of roll arrangement used to produce thin foils and sheets.
- With this arrangement, strong metals can be rolled with ease.
- With this process, we can attain an optimally high reduction ratio.
Planetary roll mill: These roll mills are equipped with tiny rolls that are present along the circumference.
- This arrangement looks like planets on the rolls, which effectively ensures it is named as a planet.
- This arrangement of rolls is capable of providing a higher reduction.
- It is also capable of offering roll tension at the end and the beginning of the product.
- This method of arrangement is used for getting strips or sheets from a metal slab.
Cluster roll mill: This is the kind of arrangement in the rolling process in which numerous rolls are used in the attachment. Specifically, in this arrangement, the small rolls are supported with two sets of rolls on both sides.
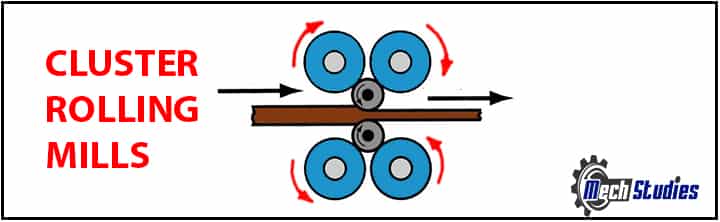
- This kind of roll arrangement provides stability and rigidity to the mill.
- This is capable of delivering better deformation.
04. Rolling Types Based on Product to be Rolled
This is the subdivision that is specifically based upon the products to be manufactured. These are the following kinds of mill arrangement for the roll forging process based on products to be formed:
- Billet mill: Billets are made up of blooms in these mills of different dimensions.
- Blooming mill: In these kinds of roll forging arrangements, only blooms are produced from ingots. These blooms have a lump sum dimension of 150x150mm.
- Slab mill: These slab mills produce slabs from blooms.
- Bar mill: In these mills, rods or bars are produced from billets. The standard dimension of these bars or rods is 40x40mm.
- Structural mill: Structural shapes such as channel section, U, I, or L can be produced from these setups.
- Plate mill: In these kinds of forging arrangements, plates are made up of slabs.
- Sheet mill: Sheet mills are capable of producing sheets from plates.
Applications of Rolling Process
Rolling has vivid applications, and these applications make it quite efficient among all the forging processes. Some of them are as follows:
- Roll forging is commonly used for the manufacturing of seamless rods, tubes, etc.
- It is widely popular for the production of ductile parts such as bolts, screws, etc.
- Roll forging is also used for the production of massive length cross-sectional structures.
- Some of the significant and popular products manufactured through roll forging are roofing panels, railroads, partition beams, construction beams, etc.
- With rolling, we can also cut gears on the gear blank.
- One of the popular sectors that uses roll forging for manufacturing various parts is the automotive sector, such as factories, industries, etc.
- Some of the practical manufacturing parts that are used widely are bearings, rings of turbines, etc.
- Steel sheets and massive plates are also the product of roll forging.
Benefits of Rolling
The following are some of the benefits of the roll forging process that provides an upper hand among all the manufacturing forming processes:
- Uniformity is the best attribute of this process. You can obtain uniform specifications of the components by this process.
- With the same rollers, one can produce various products. This provides a practical advantage to the user.
- With roll forging, one can get the optimal speed of production.
- Minimal tolerance is the added advantage of the roll forging.
Disadvantages of Rolling
- It is only suitable for large-scale production, which restricts it from using in small industries.
- The cost of equipment is relatively high.
- Most of the rolling mills provide poor finish, which implies the engagement of finish operations.
Defects in Rolling / Rolled Products
After getting a holistic idea about the whole process, it’s quite essential to understand different kinds of defects generated in the rolled products. These defects will also act as some of the limitations of the rolling process.
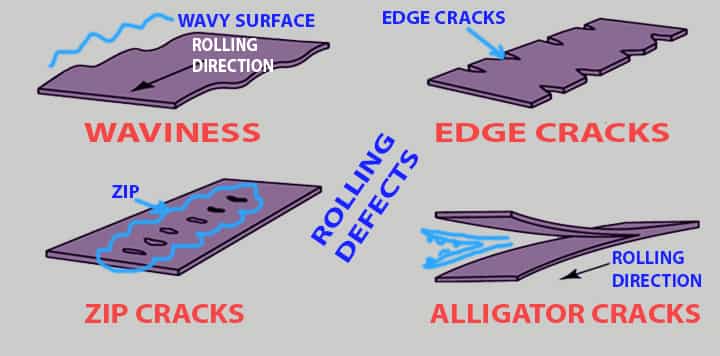
- Surface irregularities: The surface irregularities result from scaling, which gets trapped in the material and remains there in the form of laps.
- Alligator Cracks: These cracks are because the material has some of the metallurgical defects due to which different places in the material are equipped with fractures. Look at the image, this cracks just looks like the mouth of an alligator when they keep opening their mouth.
- Hydrogen cracks: Hydrogen cracks occur because while melting, different gases can get into the molten state, which causes these crack defects.
- Non-Metallic inclusion: These inclusions are just the entrapment that comes as a deposit.
- Waviness or Wavy Cracks: This is nothing but the uneven variation across the cross-sectional area and the width of the sheet. The core reason behind this kind of defect is the roll gap not in a parallel structure. Look at the image, the surface is not plane instead it is a wavy type.
- Zipper Cracking: We have seen the formation of wavy cracks, now zipper crack means one type of waviness. It is formed in the center of the strip and it looks like the zip in our clothes.
- Edge Cracking: This kind of rolling defect occurs when the edges are prevented from elongating, but the center portion increases its length. This occurs due to frictional force, and the material gets curved. Look at the image, the edge of the product is having so many cracks.
Conclusion
With a whole lot of information about the rolling process, it is quite affirmative that we know about this manufacturing forming process in detail. Right from the beginning, where the core definition helps us understand the approach to the last defect section, it makes us aware of the various ambiguities of this process. Apart from that, the different kinds of arrangements and their application help us get the practical idea behind adopting this process. Though this process can be reviewed in detail, we are well equipped with the rolling process knowledge for the time being.

