Welding defects are simply defects or unacceptable imperfections in the welding process. This article holds the elaborative analysis of different welding defects, its various types, and the subsequent causes and remedies. Let’s delve into the broader perspective of varying welding defects.
What are Welding Defects?
Welding Defects Basics
Let’s try to understand the basics of welding defects. Welding is a process that helps to join materials, basically metals or thermoplastics with the help of the heat that makes the different parts to melt.

Subsequently, the parts get cooled and cause fusion.
- Though this process is quite efficient, different welding defects affect the longevity and performance of welding.
- These defects are quite complicated, but the holistic understanding of their causes and remedies can prevent the low quality and life of welded parts.
- Longer lasting and high quality of the weld is the core need.
- With the proper detection of these welding defects, one can easily deduce the severity and take appropriate action.
- Even a mere defect that doesn’t hold much importance can easily make a welded structure ineffective to work as per need.
Welding Defects Definition
Welding defects are the defects that generate due to numerous reasons such as poor or faulty techniques used by the unskilled or inexperienced welder or due to the core difficulties in the welding process.

- However, it is not only the manual approach, but the welding defects also persist in automated robotic welding due to different reasons such as parameters abnormalities, the inadequate supply of gas and water etc.
- The parameters that define an excellent weld depends upon the optimal fusion between the filler materials and the shape acquired with apt penetration.
- Welding defects are not acceptable.
- Welding process are defined in respective codes & standards.
- All designers as well as welder shall strict to design requirements.
- Welding process shall be followed based on the materials, electrode etc. all other parameters.
What are the Primary Reasons for Welding Defects?
Now, there many corresponds for that welding defects are produced,
- Faulty technique
- Wrong welding procedure
- Problem in electrode selection
- Inexperienced welder
- Improper weld parameters
- Lack of knowledge
- Wrong process conditions
- Insufficient gas supply, etc.
All welding defects need to be corrected & we will discuss here types of welding defects along with causes, and remedies in detail. We have referred to a few basic welding video courses at the end.
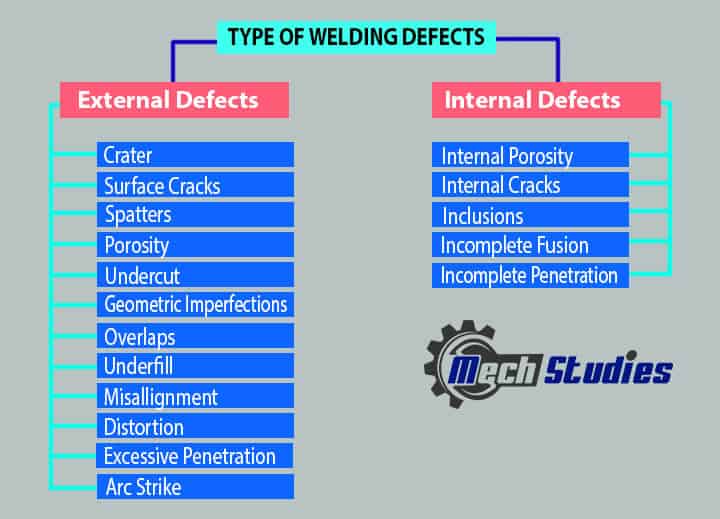
Types of Welding Defects
Where the defects are encountered, incurs the classification of welding defects. These are as follows:
- External Welding Defects.
- Internal Welding Defects.
External Type Welding Defects
External welding defect shall be as follows,
- As the name suggests, these defects are external.
- Mainly found on the surface of welding portion.
- External welding defects are sometimes visible in naked eyes.
General welding defects are,
- Crater,
- Surface Cracks,
- Spatters,
- Porosity,
- Undercut,
- Geometric Imperfections
- Overlaps,
- Under-fill,
- Misalignment
- Distortion
- Excessive penetration,
- Arc Strike, etc.
Internal Type Welding Defects
External welding defect shall be as follows,
- Internal welding defects exist in the material at some depth and are hidden from naked eyes.
General welding defects are,
- Internal porosity.
- Internal Cracks.
- Inclusions.
- Incomplete Fusion
- Incomplete Penetration
We can summarize the types of welding defects, as follows:
Welding Defects with Causes & Remedies
The following are the most common welding defects that occur due to different reasons. Here, we are providing an elaborative description of each one of them with their causes and remedies. Let’s start with the list of defects:
- Weld Damage / Mechanical Damage
- Craters
- Lamellar Tearing
- Inclusions
- Porosity
- Undercutting
- Concave and Convex Welds
- Geometric Imperfections
- Misalignment
- Overlap
- Cracking
- Spatter
- Incomplete Fusion/Penetration
- Distortion
- Insufficient Reinforcement
- Misalignment in Weld Bead
- Arc Strike Type
- Remaining groove
- Burn through
- Warpage
These are some of the fundamental defects that affect the welding and its core effectiveness related to quality and longevity. Let’s discuss all types of Welding defects in brief along with various diagrams to have a clear concept as well as a basic understanding.
1# Welding Defects Mechanical Damage
What is Mechanical Damage in Welding Defects?
The weld damage or mechanical damage is a defect that makes the welding below par levels.
- Visually an arc strike seems on the surface of welding of the remelted metals.
- One can see the small nicks and dents on the surface as well.
What are the Main Causes of Mechanical Damage?
- It occurs due to the excessive force applied while chipping.
- In the annual welding process, it occurs due to hard hammering while chipping
- Ineffective handling of the welding electrode holder
- Careless arc engagement to the metal parts.
- Incorrect use of grinders.
- At the same time, the major cause of weld damage in robotic welding is due to careless material handling.
- This defect leads to tiny cracks in the heat affected area of the weld metal.
What are the Remedies of Mechanical Damage?
- In manual arc welding, it can be prevented by careful handling of different tools such as arc holder, welding electrode etc.
- Other parts should not fall on the welded metals after welding.
- Hammering should be moderate, heavy hammering can damage the welded parts.
- In robotic welding, this can be prevented by careful handling and effective maintenance of welding equipment.
2# Welding Defects Craters
What are Craters in Welding Defects?
Craters are a common problem that looks like an abnormal deposition or depressions on the welding surface.
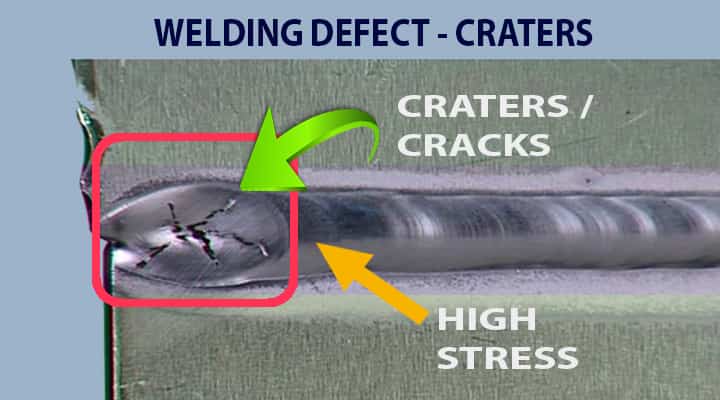
- Specifically, it indicates the imperfect weld terminations.
- If the crater is not filled before arc discontinued, outer edge will cool fast than crater.
- Unusual stress is created.
- Due to this stress, crack is formed.
What are the Causes of Craters?
- It occurs due to the improper weld terminations.
- If torch angle is not correct.
- Ineffective parameter setting.
- Improper electrode selection.
- Not selecting a proper welding technique.
What are the Remedies of Craters?
- It can be prevented by taking proper measures to attain perfect weld terminations.
- This can be done through the setting of the robotic welding machine or by giving formal training to the manual welder.
- Setting proper torch angle to reduce the stress.
- Select a proper technique based on the recommendations.
- Size of electrode shall be proper.
3# Welding Defects Lamellar Tearing
What is Lamellar Tearing in Welding Defects?
Lamellar tearing is among those defects that deteriorate the surface of metal joints.
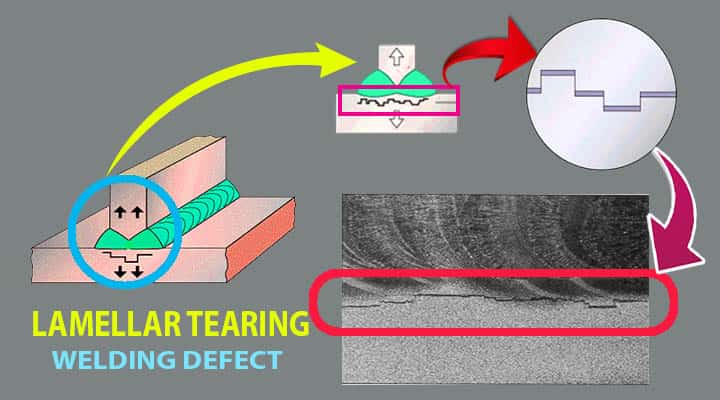
- The occurrence of this kind of defect makes it quite hard to gain the quality of the welding.
- It appears generally in rolled steel plates.
- It appears below the welding parts.
What are the Causes of Lamellar Tearing?
- It occurs due to the accumulation of weld metal deposit on the surface of the weld metal where there is optimal restraint.
- Development of strain.
- Improper weld orientation.
- Improper material selection.
What are the Remedies of Lamellar Tearing?
- This can be prevented by using materials that are of the best quality and conducting welding tests at the end.
- Proper weld orientation.
4# Welding Defects Inclusions
What are Inclusions in Welding Defects?
Different materials are deposited on the welding metal. Inclusions are nothing but the deposition of these extra materials such as,
- Sulfide,
- Slag,
- Oxide,
- Tungsten,
- Copper,
- Flux,
- Metallic etc.

This defect is mainly a product of different defects such as incomplete penetration, undercut, and lack of fusion in welds.
- Slag inclusions are capable of reducing the cross-sectional area of the materials.
- It can be the starting point for cracks.
- In a nutshell, this defect can produce a defect, i.e. known as cracking of welding joint.
- These inclusions can be grouped or linear, isolated.
What are the Causes of Inclusions?
Inclusion occurs due to,
- Incorrect current setting,
- Improper cleaning amongst the multi-pass welds,
- Electrode manipulation is not proper.
- Sag increases that deposit on the weld joint.
- Mainly produces from the contamination or from the byproduct of chemical reactions during welding.
- It can be produced from physical effects.
What are the Remedies of Inclusions?
- This defect can be repaired with the help of re-welding and grinding down the deposition.
- Proper electrode
 manipulation by welder.
manipulation by welder.
5# Welding Defects Porosity
What Does Welding Defects Porosity Mean?
This is one of the common defects that occur while welding. It is pores or cavities that generate because of the entrapment of non-metallic and gaseous material during the process of solidification after welding.
- This defect generally causes harm to the welded part based on size, orientation to stresses and quantity.
- If porosity occurs in the weld center, then it doesn’t cause much fatigue, though it is capable of reducing the static stress carrying capacity of the welded part as well as the core weld.
What are Types of Porosity?
Depending on the formation of Porosity, it can be as follows,
- Gas Porosity:
- Wormholes:
- Surface Porosity:
- Cluster porosity
- linear porosity,
- Pit Porosity,
- Blowhole Porosity,
- Crater pipe,
Gas Porosity
- These are spherical shaped small cavity,
- These are generated due to the trapped gases in the weld metal.
- There are many gases like oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, water vapor, helium, argon, carbon monoxide, carbon di oxide etc. may be present in the molten metal which cause porosity.
Wormholes
- If the trapped gasses are tubular form or cylindrical or elongated cavities during solidification, then that porosity is called wormholes.
- Wormholes can appear in single or in groups on the weld surface.
Surface Porosity
- Porosities which occurs on the surface and break it.
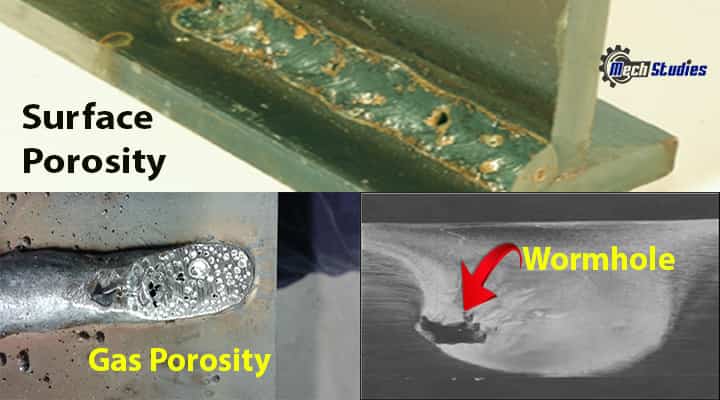
Cluster porosity
- These type of porosity basically localized group of pores.
Linear porosity
- In this type, pores are aligned.
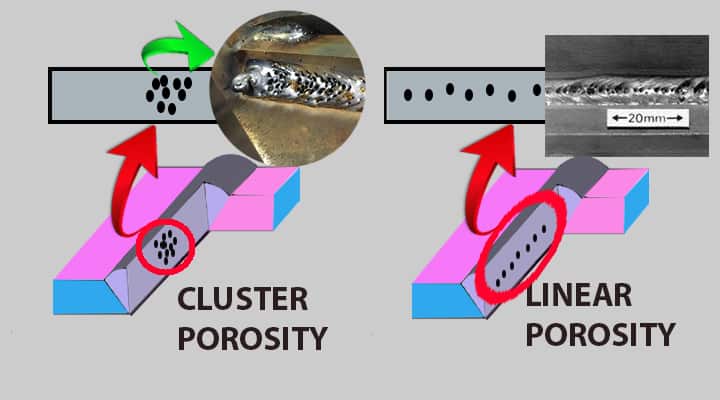
Uniformly distributed porosity
- In this type, pores are distributed uniformly in the welding area.
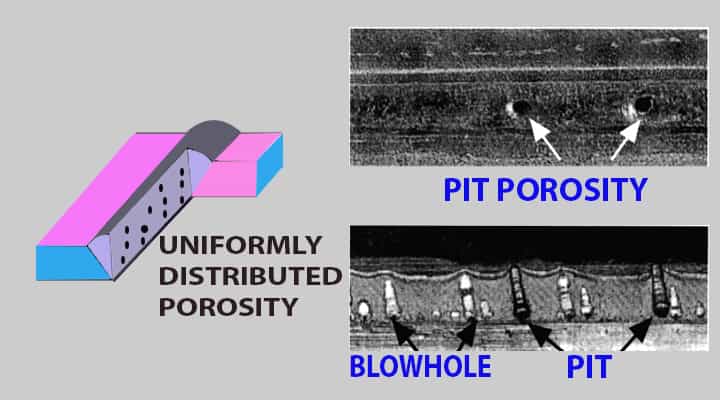
Pit Porosity
- If porosity is seen in the weld face, it is called pit porosity.
Blowhole Porosity
- In this case, porosity is in the sub-surface,
- It is detected, by fracture or radiograph tests,
- It is not extended to the weld face and called as “blowhole.”
Crater pipe
- It forms during final solidification of the weld pool,
- It occurs due to gas porosity.
- It forms due to shrinkage on weld pool solidification.
What are the Main Causes of Porosity?
Apart from the entrapment of gas or any other non-metallic materials porosity occurs due to some other reasons also such as,
- Too short arc gap,
- Unstable arc,
- Poor welding technique,
- Problem in gas shielding,
- Using a longer arc,
- Moisture presence on weld zone,
- Presence of contamination on the surface,
- If electrode is not coated properly,
- Improper surface treatment.
- Oil or rust presence on the surface,
- High gas flow,
What are the Remedies of Porosity
This is a defect that is not acceptable at any point. It can be controlled through different ways such as,
- Improved welding techniques,
- Optimal selection of filler materials,
- Proper selection of electrodes, and it shall be dry, coated,
- Proper maintenance of the work area where welding is operational,
- Minimized speed that allows the gas to escape,
- Cleaning or surface treatment of the materials prior to welding,
- Less arc distance, so that gasses can be escaped,
- Proper shielding, gas flow meter can be used to check the pressure and flow adjustment.
6# Welding Defects Undercutting
What Does Welding Defect Undercutting Mean?
When it comes to one of the severe welding defects, then undercutting takes the prominent place. It is an abnormality that can be summed up as an unfilled groove that exists along weld edges.
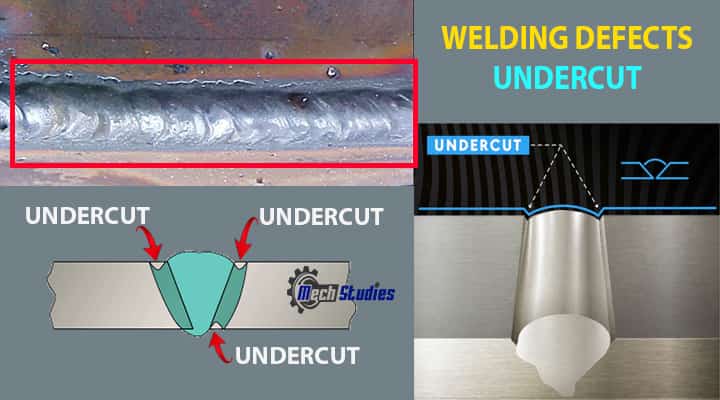
What are the Causes of Undercutting?
This occurs due to different problems such as,
- Excessive current,
- Travel speed,
- Incorrect electrode angles,
- Improper electrode selection,
- Improver welding techniques,
- Using large electrodes,
- Improper gas shielding,
What are the Remedies of Undercutting
This defect can be prevented with the help of the following,
- Maximum attention towards the whole welding process by attaining basic improvements in the entire welding process,
- It can be repaired with the help of welding the grove with comparatively smaller electrodes,
- Selecting suitable electrodes, with proper angle,
- Optimize the arc length,
- Controlling the current,
- Gas shielding should be proper,
7# Welding Defects Concave and Convex Welds
What Does Welding Defects Concave and Convex Welds Mean?
When the weld attains different shapes, then it is known as misshaped welds. These defects constitute mainly two of the shapes,
- Concave,
- Convex,
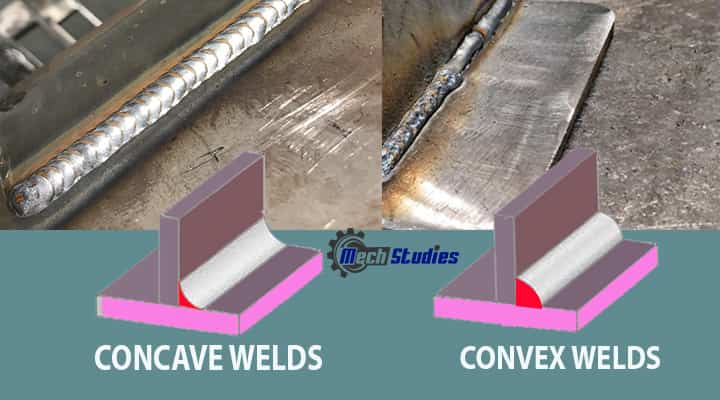

Excellent welding doesn’t acquire both shapes.
Lack of reinforcement or excessive concavity prevents the weld from getting suboptimal throat thickness as compared to the desired weld size.
Apart from that convexity provides below par level weld contour where there is multilayer welding the probability of slag inclusions due to this while it also causes a local notch effect or poor stress capability in the finished weld.
What are the Causes of Concave and Convex Welds?
It occurs mainly due to,
- The amalgamation of incorrect or improper speed and
- Electrode current.
What are the Remedies of Concave and Convex Welds?
This defect can be prevented with the help of the following,
- Using proper weaving pattern,
- optimal current and
- proper electrode size.
Apart from that it can be repaired by either grinding back the weld on each side up to base metal and opting for re-welding.
8# Welding Defects Misalignment
What Does Welding Defect Misalignment Mean?
Misalignment is the type of welding defect that comes under the geometric imperfections attained in the process of welding.
- It is essential to acquire a stable setup that provides a useful work area, the absence of which causes setup or fitting problems.
- This also occurs when we try to join metals with different thickness.
What are the Causes of Misalignment?
Some of the main reasons for this are,
- the setup or fitting problem and also the
- thickness of metals available for welding.
What are the Remedies of Misalignment?
It can be prevented by keeping a tab on the setup process and fitting of the metals.
9# Welding Defects Overlap
What Does Welding Defect Overlap Mean?
This defect is just a protrusion of weld material beneath the weld root or weld toe. Additionally, it is the excessive flow of weld metals.
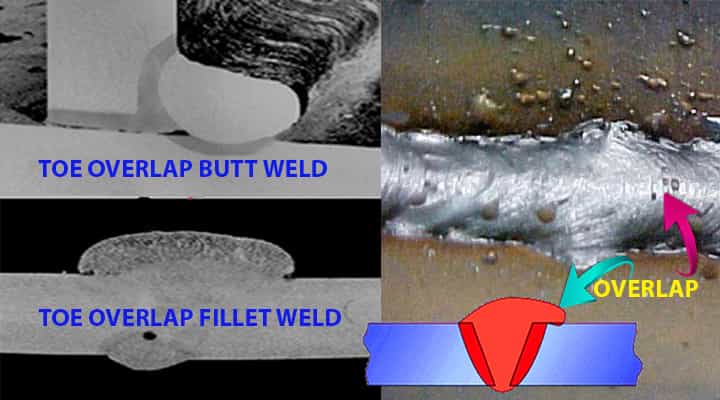
What are the Causes of Overlap?
- The predominant reason for this defect is improper welding techniques.
What are the Remedies of Overlap?
The overlap can be prevented with the help of the following,
- Attaining an improvement in welding techniques.
- When it comes to repairing the defect, the grinding process can help in best possible ways.
- It removes the excess weld metal and the base metal can be attained through surface grinding.
Check out a nice video
from weld.com!
10# Welding Defects Cracking
What Does Welding Defect Cracking Mean?
Cracks in welding are one of the most dangerous defects that can cause a lot of damage. This damage can be lethal when the material is in fatigue-loading conditions. Apart from that, it has several types, and each one of them should be prevented to attain quality weld and maximum strength. Here, we are providing a brief description for each one of them:
Longitudinal crack
These are the type of cracks that occur due to the metal hardness problem. It usually runs along the weld direction.
Causes of Longitudinal crack
The main reasoning behind the occurrence of this problem is,
- Uneven cooling of the welded part as the weld materials get cooled at different rates.
There are some other reasons also that generated longitudinal cracks such as,
- wider weld bead, and
- root gap is too large,
- high current or welding speed and
- the shrinkage stress in those areas which are under high constraint.
Remedies of Longitudinal crack
This can be prevented with the help of
- A proper selection of welding consumables,
- Attaining pre-heat process that helps in even cooling of the welded part and welding towards the area which has less constraint.
- Apart from this, it can be repaired by re-welding after cutting the cracked part or by grinding out.
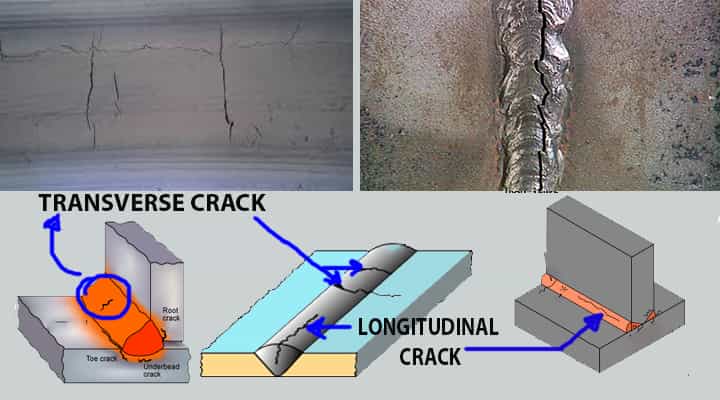
Transverse Crack
Shrinkage stress is the main problem behind the cracks. This defect is a crack that occurs at the toe of the weld.
- In this, the base metal seems to have cracked.
- It signifies the brittleness of the material in the HAZ area.
Causes of Transverse Crack
- It is caused due to the transverse shrinkage stresses along the weld.
Remedies of Transverse Crack
- It can be prevented by using a comparatively ductile filler material or by attaining a pre-heating process.
Underbead cracks
Metals become brittle while welding and this is the primary cause for under bead cracks. Specifically, under bead cracks are the type of cracks in the melted metal of the HAZ area.
- Hydrogen embrittlement is the primary carrier that causes this kind of cracks.
- This can be found with the help of a non-destructive test (NDT).
Causes of Underbead Cracks
- It occurs due specifically due to the hydrogen exposure on the parent metal in the heat-affected zone.
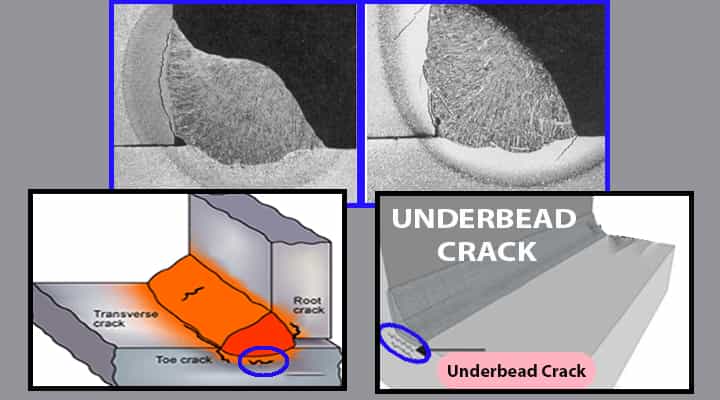
Remedies of Underbead Cracks
- It can be prevented by using those electrodes, which are hydrogen controlled.
- Preheating also helps in controlling under bead cracks.
- It can be repaired with the help of grinding out and re-welding.
Cold cracking
Cold cracking is among the defects that are generated when the welded metal gets a chance to solidify.
Causes of Cold Cracking
The main reasons behind this defect are,
- shrinkage,
- highly restrained welds and
- uneven material fitting.
Remedies of Cold Cracking
- This can be prevented by welding towards areas that are smooth and consist of minimal constraints such as breakage, openings etc.
- When it comes to repairing this defect, the welded part should be removed and re-welded.
Cracking is the defect that can be repaired with the help of grinding or by welding the cracks. The welding of cracks is a cumbersome process that should be attained by welding on the heat-affected zone of base metal. The above are the types of cracks that should be prevented at any cost.
11# Welding Defects Spatter
What Does Welding Defect Spatter Mean?
Spatter is the redundant defects that are nothing but the metal drops scattered from the weld. It sticks to the surrounding surfaces. This is one of the most common types of defects when it comes to welding.
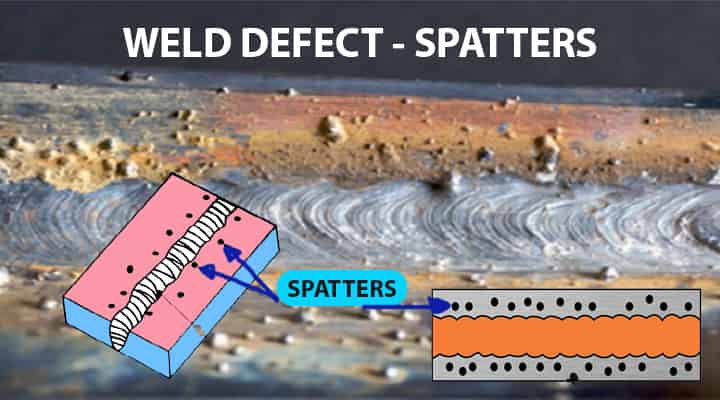
What are the Causes of Spatters?
It occurs due to,
- the poor welding techniques and
- improper welding parameters.
What are Remedies of Spatters?
Spatter can be diminished by;
- Attaining the proper welding conditions.
- It can be repaired with the help of grinding or surface finishing.
12# Welding Defects Incomplete Fusion/Penetration
What Does Welding Defect Incomplete Fusion/Penetration Mean?
Penetration is one of the most critical aspects of welding defects. It is also known as incomplete fusion.
- It is among the lethal defects that are way difficult to detect, and the evaluation of the same is complex.
- This can be dangerous as it effectively hunts down the weld quality and enables the welded part to fail.
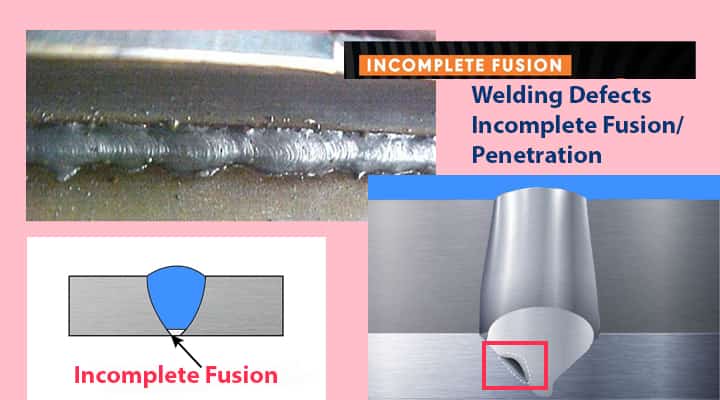
What are the Causes of Incomplete Fusion/Penetration?
- It occurs when there is the absence of cohesive bond of the weld metal to the base metal or the shallow depth attained by the weld metal into the base metal.
- This results in minimal throat thickness.
- Apart from this, different things act as a catalyst for this defect to emerge such as shirt arc length, minimal pre-heating, fast welding speed, low current, minimal electrode size and the unavailability of the arc in the centre of the seam.
What are Remedies of Incomplete Fusion/Penetration?
- It can only be repaired, as the process of detecting is very complicated.
- It can be repaired with the help of grinding the area which has penetration or incomplete fusion and opting re-welding.
13# Welding Defects Distortion
What Does Welding Defect Distortion Mean?
Distortion, as the name suggests, is the change of shape after welding. When two plates are welded, after completion, the size of the plates or the position may change which creates distortion.
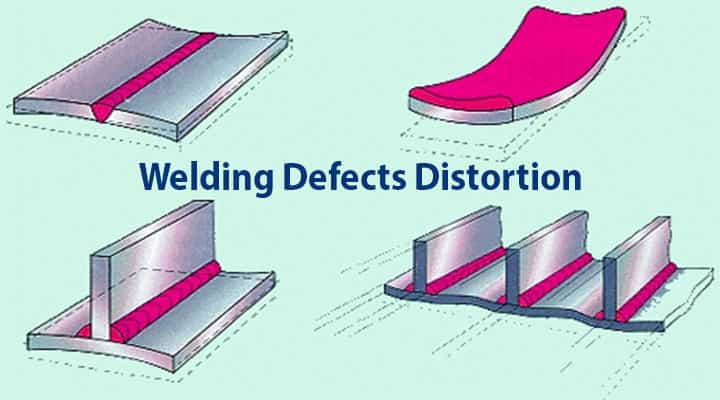
What are the Causes of Distortion?
- Unequal temperature gradient present.
- Large number of weld pass.
- Incorrect welding technique as well as sequence.
- Very slow arc travel speed.
- High residual stresses in the plate.
What are the Remedies of Distortion?
- Suitable welding technique based on the metal.
- Nos. of weld pass should be optimized.
- Optimize the welding time duration.
- Proper electrode selection.
14# Welding Defects Insufficient Reinforcement
What Does Welding Defect Insufficient Reinforcement Mean?
Insufficient reinforcement is another type of welding defect which we see in many projects. Reinforcement in welding means sufficient weld metals decomposition in the joint, especially in fillet or groove welding. Now, insufficient reinforcement welding means the weld metals in the joint are insufficient than required.
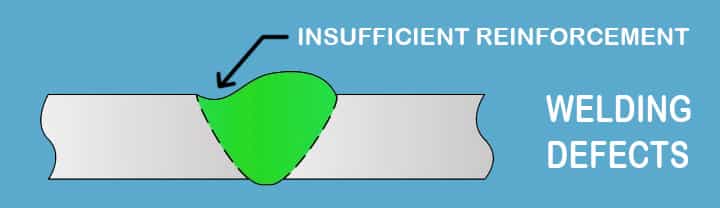
What are the Causes of Insufficient Reinforcement?
- Fast welding process
- Inefficient welder
- Improper checking
- Moving heat source very fast
What are the Remedies of Insufficient Reinforcement?
- Apply slow and steady welding process
- Employ skilled welder
- Proper checking
- Move heat source slow
15# Welding Defects Misalignment in Weld Bead
What Does Welding Defect Misalignment Mean?
Many times, weld bead means the decomposition of filler metals into the joint, maybe alignment improperly. This misalignment incurs another welding defect. It becomes wavy or curvy.

What are the Causes of Misalignment in Weld Bead?
- Fast welding process
- Inefficient welder
- Weld wire not kept properly
- Weld wire is not in line with weld line
- Weld current and the supply of weld wire is not inline
- Improper checking
What are the Remedies of Misalignment in Weld Bead?
- Apply slow and steady welding process
- Employ skilled welder
- Weld wire should be in line with weld line
- Weld current and the supply of weld wire should be inline
- Proper checking
16# Arc Strike Type Welding Defects
What Does Arc Strike Welding Defect Mean?
As the name suggests, arc strike means another welding defect that is created by arc by mistake. In case, the welder wrongly strikes the workpiece with an electrode on the unwanted area which causes an unwanted arc.
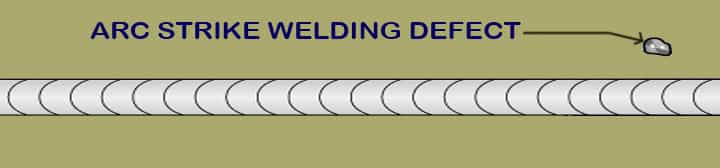
What are the Causes of Arc Strike?
- Inefficient welder
- Workpiece is not properly clamped.
- Not easy access to the joint
- Electrode holder was not properly layed and coating was not proper.
What are the Remedies of Arc Strike?
- Employ skilled welder
- Workpiece should be properly clamped.
- Easy access should be provided to the joint
- Electrode holder needs to be checked.
17# Remaining Groove Type Welding Defect
What Does Remaining Groove Type Welding Defect Mean?
The remaining groove, as the name suggests, means that the remaining portion of the groove is missed to weld. It makes a gap between bead to start point as well as a bead to the endpoint. This remaining groove welding defect can occur in the middle as well.
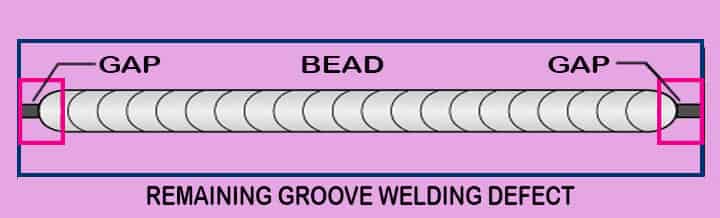
What are the Causes of Remaining Groove?
- Improper control
- Inefficient welder
- If it’s operated by robot, then there may be a problem of controlling the robot
- Problem is supplying weld wire.
- Insufficient supply of gas for arc/gas welding
What are the Remedies of Remaining Groove?
- Proper control
- No interruption of gas supply
- No interruption of weld wire supply
18# Welding Defect Burn Through
What Does Welding Defect Burn Through Mean?
Burn through is another weld defect that needs to be known. In this defect, the weld metal or the parent metals encountered some holes.

What are the Causes of Burn Through?
- Large root face
- Large root gap
- Inefficient welder
- Welding current is very high
What are the Remedies of Burn Through?
- Maintain a proper root face
- Maintain proper root gap
- Competent and experienced welder
- Maintain proper/suitable welding current
- Welding travel speed should not be slow.
- Further welding can help to remove this welding defects.
19# Welding Defects Warpage
What Does Welding Defect Warpage Mean?
This defect is associated with the expansion of the metals or contraction. Warpage means a distortion of metal pieces due to expansion or contraction during the welding process.

What are the Causes of Warpage?
- Expansion or contraction depends on the heat. More heat means probability will increase. Applying high heat can result in warpage.
- No prior knowledge of the metals.
- Inexperienced welder.
- Fast welding speed.
What are the Remedies of Warpage?
- No additional heat to be applied to avert warpage.
- Prior knowledge of the metals is required.
- Experienced welder.
- Slow welding speed.
20# Other Welding defects
We have learned many common welding defects, however, few additional defects are captured, for example:
- Irregular width
- Linear Misalignment
- Height Misalignment
- Irregular shape
- Incorrect profile
- Torn Surface
- Grinding Mark
- Stray Arc
- Root Concavity
- Warpage
- Excessive penetration
- Excess weld Metal
- Shrinkage cavity
- Under-flushing
- Chipping Mark, etc.
High Rated Course for Welding Defects
There are many courses available on the web to learn with the video tutorials. You can grab them as these are very helpful to clear the concept from the core with very less price.
Few of them are illustrated based on the highest rating as well as feedback:
Certification in Welding Technology for Engineers CWI-2022
|CWI-2022|
Introduction to Welding Engineering
Top Online Video Course on Welding Defects
Codes & Standards associated with Welding Defects
Welding is a very critical subject and all types of welding defects shall be corrected or avoided to avert large accidents. Hence, it is mandatory to consider all applicable codes and standards in all applications. The common standards are used for the welding process are as follows,
- BS EN ISO 5817,
- BS EN ISO 6520-1,
- BS EN ISO 10042
These standards have captured all limitations or acceptable limits of welding.
Conclusions
Here, we have considered different types of welding defects with the proper measures to combat them. Some are geometric abnormalities, while others are expected depositions. There are some of the lethal welding defects that are capable of massively affecting longevity and weld performance.
To combat these, we need to detect these defects. Early detection of these defects is mandatory to attain the desired weld as per the designed purpose. Repairing of defects is also necessary as there are some of the lethal ones who question the structural integrity of the structure. Welding is a process that cannot provide cent percent perfect weld as attaining that will be time-consuming as well as costly. It is merely within the working limits that follow the specification of quality control code.
