What is Forging process? Any idea! In this article, we will learn the basics of forging process along with forging definition, meaning, different types, advantages, disadvantages, applications, defects, etc. Let’s explore!
What is Forging Process? Definition & Meaning
Forging Process Basics
While working on various materials, shaping them to the desired profile is one of the most popular aspects. This comes under the bulk deformation of materials.
- Bulk deformation is nothing but just the shaping of materials equipped with a small surface area to volume ratio or surface area to thickness.
- Forming is the process that helps in getting various kinds of thickness in these materials.
- The use of sheet metal forming processes is quite broad and popular.
In various industries, it is used on a massive scale. Some of the prominent examples of those are the automobile industry and beverage industries, which use cans massively. Sheet metal forming processes includes,
- rolling process,
- forging process,
- drawing, and
- extrusion process, etc.
Here, we will discuss forging, which is one of the effective ones among all the forming processes.
Forging Definition
Forging is one of the historical processes through which our ancestors used to make weapons, jewelry, coins, etc., in a simple language; Forging is how deformation of materials takes place through compressive stress.

There are numerous and wide forging applications for,
- manufacturing gears,
- crankshaft,
- bolts,
- calve bodies,
- connecting rods,
- disks, and
- tiny components for various circuits.
Apart from this, this process has numerous advantages; we can attain maximum accuracies even for small parts. With this process, the material saving is an added advantage and a par level of surface finish.
What is the Use of Forging?
As we know, forging is a manufacturing process that provides various sizes and shapes of the metal by different cold and hot forging operations.
- Unlike other manufacturing processes, forging operation is performed on the metals.
- The forging process is specifically used to change the workpiece’s size and shape by compressing or heating it in the whole process.
- It helps to make different kinds of shape, which is used in various manufacturing industries.
Types of Forging
When it comes to the classification of forging techniques, it can be subdivided into different types based on.
- Temperature for Forging
- Arrangement or techniques
As per temperature, forging process is of two types,
- Cold forging
- Hot forging
Based on the constraint on flow by the die and material flow, as well as the type of loading and arrangement, forging can be classified as follows,
- Open die forging
- Closed die forging
- Flashless forging
- Precision die forging
- Roll forging
- Rotary forging
Let’s discussed the basics of all types of forging,
Cold Forging
This forging process is classified based on the temperature and as the name suggests, it happens at lower temperatures.
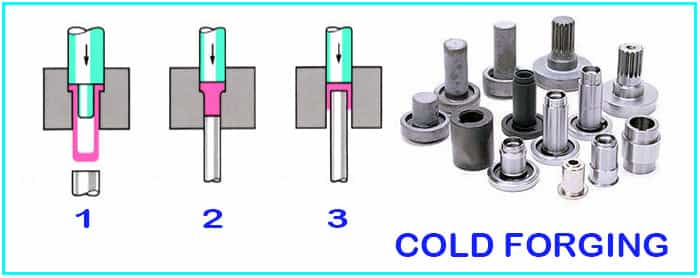
Cold temperature indicates room temperature here not very cold temperature.
- As the high temperature is not required, no separate equipment like furnace, etc. is required.
- No cooling equipment is also required.
The process is simple, like
- Take a workpiece
- Keep it in between two dies.
- Clamp it properly.
- Apply force based on the required change in shape.
Cold forging is used for getting,
- optimal accuracy,
- high strength, etc.
Cold forging needs higher loads because flow stress gets increased at lower temperatures.
Hot Forging
This process is based on temperature and as the name suggests, it happens at higher temperatures.

High-temperature means,
- 300-460 °C for aluminium alloys,
- 700-800 °C for Copper alloys,
- Up to 1200 °C for steel,
- 750 to 1040°C for Ti – alloys,
The hot forging process is carried out at a temperature that is below recrystallization temperature . Without the specified temperature, the hot forging process can not be done and can not be avoided strain hardening problems.
. Without the specified temperature, the hot forging process can not be done and can not be avoided strain hardening problems.
- Hot forging doesn’t provide optimal qualities, but it gives good surface finish than cold forging.
- The material will be less ductile compared to cold forging.
Let’s check other types of forging process,
Open Die Forging
Open die forging is the forging in which a cylindrical billet undergoes the compressive stress between a pair of flat platens or dies.

- In this, the height of the diameter of the billet increases, and the height decreases.
- With this technique, the manufacturing of shafts, rings, disks, etc., can be made.
- With this, we can easily convert square-shaped ingots into round shapes.
Open die forging is further subdivided into few categories. They are as follows:
Fullering
It is the forging process that is used explicitly for reducing the cross-sectional area of the materials by using concave or convex-shaped dies.
Edging
This process of forging is also the same as fullering. In this also the material gets elongated through its length hence the deformation takes place.
In accordingly, the material gets distributed, and the reduction in thickness takes place.
Cogging
This forging technique works on the principle of compression in which the stress develops on cast ingots which are used explicitly for increasing the length of billets or blooms. It also reduces the thickness effectively. For this forging operation, contoured or flat dies are used.
Closed Die Forging
This is one of the kinds of forging, which is also known as impressions die forging.

- In this process, impressions are constructed in pairs of dies, then transferred to the job piece during the deformation.
- This process needs some of the core components that make it quite efficient such as flash.
- Flash is among the most crucial part as it helps in the deformation process inside the die.
Closed die forging is also further subdivided into different parts. Some of them are briefly discussed here:
Coining
Coining is among the closed die forging process, which includes the function of complex impressions. This process undergoes a heavy load. One of the most popular applications of this process is minting. Coining is also used for improving the surface finish, which is also known as sizing.
Piercing
It is a kind of closed forging method in which a punch is used to make deep indentations, which helps make a cavity in the workpiece. This process needs a higher load for the operation, and the workpiece is kept inside or outside of the die.
Heading
The heading is the closed forging process in which heads of small components such as bolts, nails are made. This method uses a special kind of machine.
Flashless Forging
The forging technique is that in which the workpiece is subjected to continuous stress within the die cavity.
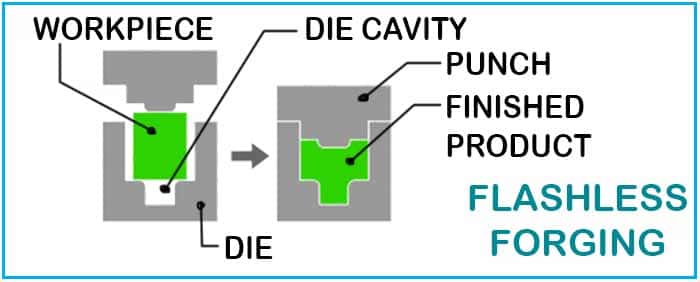
This placement restricts the movement of the material, which makes it quite effective.
- With this forging technique, one can quickly get optimal accuracy.
- One of the best things about this is the no wastage or unavailability of any flash form, making it quite popular.
Precision Die Forging
Precision dies forging is a forging process that is capable of providing complex shapes with optimal accuracy.
- It also prevents the use of after machining techniques, making it quite effective among all the forging methods.
- This forging process engages higher forging loads and precise dies that help in the whole process.
- With this process, mainly the alloys of magnesium, titanium, and aluminum are forged.
There are some limitations associated with this process, as it is quite hard to forge ferrous materials due to the high temperature, die wear, excessive load of dies, etc.
Roll Forging
This is among one of the forging processes that are quite popular. In this process, materials are fed between two cylindrical rotating components.
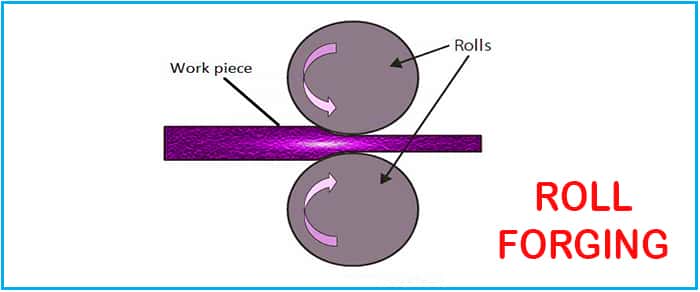
Frictional force helps to reduce the thickness of the metals.
- Here, rollers rotate with the help of attached bearings.
- Nos of rollers depends on the type of metals or jobs.
- Power from the motor is transmitted to the bearings.
- The gap of tolerance or gap between rollers is adjusted based on the requirements.
The process shall be as follows, The process deals with the starting material, i.e., Ingot, which is manufactured with metal dies.
- Ingot, that is hot metal is passed through these rollers.
- Ingot passes through all sets of rollers and gets pressed from the side.
- This process continues and helps to make required sizes.
With this forging process, ingot can be transformed into the followings,
- sheets,
- billets,
- plates
- structural components,
- bars, etc.
Rotary Forging
This is the forging process in which the punch is in orbital rocking motion while deforming the workpiece.
- The orbital motion of the punch provides the name rotary forging.
- In this process, minimal loads are apt, though it takes several steps to manufacture smaller parts.
- With this process, the manufacturing of wheels, bevel gears are obtained quickly.
Defects in Forging Process
Like welding defects, while attaining all the information about forging, it is quite essential to understand the various defects that come amidst the whole process, like
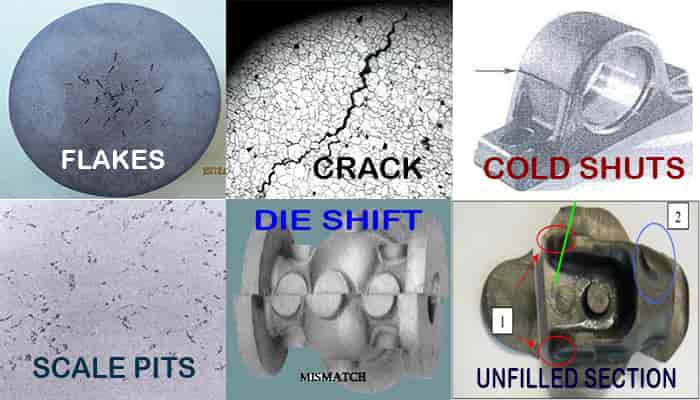
- Unfilled sections formed
- Cold shut defect
- Surface cracking forging defect
- Residual stresses problem
- Incomplete forging Penetration
- Scale pits
- Die shift
- Flakes
- Improper grain flow
Here we are discussing all those prominent forging defects briefly:
Unfilled sections formed
- This defect of forging occurs due to the ineffective design of the die, responsible for generating this kind of unfilled section defects.
- Apart from that, there is one more cause of these defects: the suboptimal heat treatment of metals.
- It mainly occurs when the die is available in two parts; one is moveable while the other is fixed.
Cold shut defect
This defect is among the common forging defects in which the forging operation cannot fill the desired products in the corner of the die.
Surface cracking forging defect
- When there is sub-optimal temperature availability in the whole forging process, the surface cracking defect is generated.
- Maintaining appropriate temperature will help to avoid cracking problems.
Residual stresses problem
- This is among those defects that occur due to the fast cooling and lower effect on the workpiece’s aesthetics.
- To prevent these defects, the forged product should be cooled slow and effective way.
Incomplete forging Penetration
- This is among the common defects of forging as it occurs where manual intervention lies.
- Specifically, if the workpiece is hammered by hand, this kind of defect comes into the vicinity.
Scale pits
- The sale pits are deposits or scales that occur in the workpiece accumulated in the die. It causes low strength of the forging.
- The major impurities are present in the form of slags or dust particles.
Die shift
- This kind of defect happens due to the ineffective design of the die or the setup.
- This defect can be prevented by attaining or planning for an effective and proper design of the die.
Flakes
- Fast cooling after the forging process is the main cause of flakes.
- This rapid cooling enables the upper die to perform an accurate forged operation.
Improper grain flow
- Improper grain flow is the defect that changes the core pattern of the material, which reduces its thickness.
- This can be prevented by designing effective die design.
Advantages of Forging
Forging is not just a manufacturing process that helps effectively; rather than that, it has some of the prominent advantages that allow the user. The use of these forging will be quite clear after getting a holistic knowledge about these advantages:
- With forging, one can attain higher strength products than those in casting.
- The operation associated with this process is quite a low cost.
- The materials obtained by this process are equipped with optimal mechanical properties such as strength and hardness.
- One can attain those materials with the help of this process which is structurally refined.
- The forged products are easy to One be welded.
- Accuracy is among the foremost attributes that can be obtained with this process.
- With this manufacturing process, it is quite easy to get numerous shapes and sizes.
- The input attributes such as skilled operators are not needed to perform this function. We have to get an understanding of the operation once.
Limitations of Forging
Apart from some of the critical advantages, forging has some disadvantages that should be grasped to get efficient results. Some of the core disadvantages are as follows:
- In most of the end products, the need for secondary finishing operation is mandatory to attain smoothness.
- We can get limited products as there is a size constraint related to the press size.
- The maintenance cost of machines is relatively high.
- In hot forging, the working conditions don’t have the desired temperature then the material gets distorted.
- The implementation cost at the initial period is relatively high.
- There is a specific material that cannot be forged.
- It is quite challenging to maintain the tolerance level as the whole process is quite complicated.
- In hot forging, the possibility of scaling of dies is a big concern at high temperatures, and the dies are wholly equipped with scales that wear down the whole die.
- Huge safety precautions should be taken while operating the machines as the temperature while forging remains high.
Applications of Forging
The following are some of the popular applications of forging in industrial as well as daily life:
- One of the popular uses of this manufacturing process is making crankshaft, camshaft, which is one of the widely used components.
- This process is also used in shipbuilding.
- Small equipment, weapons, cutlery, and other daily use materials such as bolts, chisel, knives, etc., are made through this process. Specifically, cold forging is the best method for manufacturing this equipment.
- Most of the defense equipment is made with the help of this process.
- The automobile industry uses this process widely for manufacturing various components.
- This process is also used to manufacture machinery equipment, industrial tools, hand tools, and numerous hardware.
Conclusion
The proper knowledge of the forging process and its different aspects, such as advantages, disadvantages, applications, etc., makes us equipped with all the knowledge. This helps us in numerous ways to get all the insights about this effective process of manufacturing various products. This process is of maximum efficiency due to which it is widely used in almost every industry. With this, it is productive to get all the above information.


I also conceive thence , perfectly indited post! .
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thank you, I?ll try and check back more often. How frequently you update your website?
i really love a good read like, please keep us updated with info.
Nice post. I learn some thing tougher on distinct blogs everyday. Most commonly it is stimulating to learn to read content from other writers and exercise a specific thing there. I’d would rather use some together with the content in my weblog no matter whether you don’t mind. Natually I’ll provide you with a link in your web weblog. Many thanks for sharing.
This is one awesome article post.Thanks Again.
Your blog is amazing dude” i love to visit it everyday. very nice layout and content ,