Renewable energy is explained along with the definition, various types, examples, advantages or benefits, disadvantages, future perspective, etc.
Let’s explore Renewable Energy!
What is Renewable Energy?
Renewable Energy Definition
Renewable energy is defined as the energy that comes from sources that can be renewed in a short time. This energy is referred to as clean energy and non-exhaustible, i.e. sunlight and wind.
- Renewable energy can replace the exhaustible fossil fuels that are coal, oil, natural gas, etc.
- The fossil fuel is constantly polluting the environment which results in global warming and climate change.
- Renewable energy can be used to produce power, heat, and mechanical energy.

Renewable energy is mainly considered as a new technology, although we are utilizing nature’s power for heating, lighting, and transportation for a long time.
Wind power had been used in windmills for grinding grains and for sailing boats. The sun provided us heat to keep us warm and helped kindle fire last for longer in the evening.
Types of Renewable Energy Sources
The major renewable energy sources are eight in number. We will discuss the basics of all these sources and will cover their benefits along with challenges for their implementation.
They are named as;
- Solar Energy
- Wind Energy
- Hydroelectric Power
- Energy from Hydrogen
- Biomass Energy
- Geothermal Energy
- Energy from Ocean
- Nuclear Energy
Examples of Renewable Energy Group
Solar Energy
This is the most abundant renewable energy source. According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory,
‘the amount of sun’s energy that falls on the earth in one hour is more than the energy used by the whole world in one year’.
From the beginning, we are using solar energy to grow crops, dry foods, and stay warm.
In the present time, we use it to,
- heat homes,
- produce electricity, and
- warm water.
Solar energy is derived by capturing energy from sun rays and converting them into heat, and electricity. The solar cells present in Photovoltaic (PV) systems are responsible to directly convert sunlight into electricity.

Solar cells are made from silicone or other materials. Distributed solar systems use roof panels to generate electricity for homes and companies. Solar farms have the capability to power thousands of homes by concentrating light on solar cells covering a large area.
Floating solar panels are used on the surface of large water bodies, they are useful in areas where land is not available to place solar panels.
- Its benefits are the limitless supply of energy, meaning it has the potential to meet global energy demands single-handedly.
- We will have a clean source so it helps us improve the environment and public health.
- It can eliminate energy costs and enhance the reach of electricity to everyone and everywhere.
On the other hand, some of the limitations are the added cost to install solar setup and weather conditions.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions with clouds cannot bring useful output.
- Solar panels need an open area.
- Energy storage and transmission are other challenges.
Wind Energy
In the past, wind energy was used to run windmills, today we turn turbine blades using the same source. The energy of wind flow is utilized to run the turbine. Wind turbines are attached to electric generators to produce electricity.
- Wind energy is also a form of solar energy.
- The wind is caused by temperature differences in the atmosphere along with the rotation of Earth.
- After the sun energy, this form of energy is utilized in most parts of the world.

Its benefits include the availability of clean energy sources, 24/7 delivery of energy, and job creation. At the same time the transportation of energy to remote areas, noise, and threatening wildlife are the challenges.
Hydroelectric Energy
In renewable energy, hydroelectric energy has the largest share in most parts of the world. This energy is produced by using the energy of fast-moving water. The force of that water is used to turn the turbine blades and electricity is generated using power generators.
Dams are the areas where hydroelectric energy is produced. For this, we can either use a high head where waterfalls from a high point or a high velocity of the water. Both can prove helpful to run the turbines.

The world is already producing a huge amount of electricity with the said source. This means it has a good potential to cover global energy needs. Both small-scale and large-scale production is feasible with water streams and large dams respectively.
The challenges include the requirement of a large area and water availability throughout the year. The storage systems need fossil fuel to pump water. It also disrupts natural waterways and disturbs marine life.
Energy from Hydrogen
Two molecules of hydrogen are present in water in combination with one oxygen molecule. If we separate a single hydrogen molecule with energy, it can be used as a fuel and electricity production.
Being a clean-burning fuel, hydrogen produces less pollution. We can power electric motors where hydrogen is present in fuel cells.

We need energy for hydrogen production, therefore energy from hydrogen is less efficient.
Biomass Energy
Biomass is the organic plant material and animal waste used as a fuel. Different methods are applied to collect energy from biomass. We burn the biomass, heat is released, this heat can generate electricity using a steam turbine. A simple example of biomass is the use of wood in your fireplace.
Mainly biomass energy is considered to be a clean source, however, recent studies specify that many forms of biomass produce higher carbon emissions than fossil fuel.
There are some forms of biomass energy that produce low carbon emissions like sawdust and chips produced from sawmills.
- One challenge of using biomass energy is that we don’t yet have good technology to perform this process efficiently, having low carbon emission and with less energy input.
- New plants need carbon dioxide to grow and this growth takes time.
- Also, we don’t yet have widespread technology that can use biomass in place of fossil fuels.
Geothermal Energy
The core of the earth is about as hot as the sun’s surface. Heat is trapped beneath the earth’s crust from radioactive decay and during earth formation billions of years ago. Sometimes this heat comes out in the form of volcanic eruptions.
- We can use this heat to produce steam.
- Water is sent below the earth through pipes.
- Heat is transferred from the earth’s crust to water which results in steam generation.
- The steam is collected at the end of the pipe on the earth’s surface.
- This steam is used for power generation in steam turbines.
- Another method is deep drilling, where hot underground water is forced to the surface to run thermal power plants.
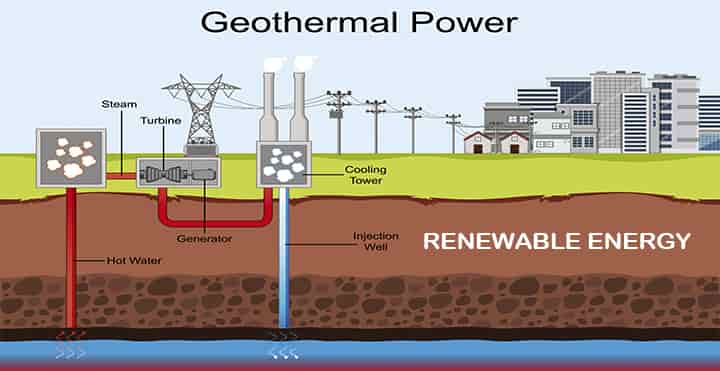
A practical example of the use of geothermal energy is when you are relaxing in a hot spring. Sustainability is one of the benefits of using this renewable energy source, the used water can be returned back into the reservoirs. Geothermal energy is not very common, but it has a significant potential for clean energy production.
Its drawbacks include high setup and operating costs. Some areas being considered geological hotspots are vulnerable to earthquakes where this process is applied.
Energy from Ocean
We can get energy from the ocean in two ways, tidal and wave energy. Both of them are in the developmental stage.
Different devices like wavebob (wave energy converter) etc. are used to take energy from the ebbs and flows of tides.
- Tides are created by the rotation of the earth and gravity from the moon.
- Ocean energy is present in abundance, but yet untapped.

It is a consistent form of renewable energy as we are not relying on factors that are essential for solar and wind energy. The produced energy can be easily transferred as most of the population lives near water bodies.
- At the same time, we need to keep the system safe when huge waves are flowing in stormy weather.
- Other drawbacks are that landlocked areas cannot benefit from this energy.
- It can also disturb marine life and the delicate ecosystem in case of tidal barrages.
Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is the energy released in processes that affect atomic nuclei. The nucleus of an atom contains a high amount of energy that needs to be extracted.
The energy is released a significant amount by controlled nuclear fission in nuclear reactors. Another method is controlled nuclear fusion, still not perfected.
- Nuclear fission is a separation process (uranium to lighter nuclei) used in nuclear reactors for power production and performing industrial processes.
- The same process is utilized for atomic bomb production.
- Nuclear fusion is a combination process (hydrogen to heavier nuclei).
- Just like fission it also can be used to produce electrical power.

Nuclear energy produces no pollution and does not contribute to global warming. Safe process operation can produce high energy.
The fuel cost is less as a small amount of fuel can produce a large amount of electricity. Its power station has a very long lifetime.
Nuclear energy is a stable source as it’s not reliant on weather conditions.
- The challenges while using nuclear energy are the high initial cost for this setup and the safe disposal of waste as it is radioactive.
- Large-scale accidents are catastrophic.
- Marine life is affected by thermal pollution from wastewater.
Advantages or Benefits of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy offers a range of benefits. We will discuss them briefly.
- It is an abundant and freely available source of energy.
- Multiple sources of energy can be utilized.
- New Jobs will be created in this sector.
- Electricity is generated at a low cost.
- Renewable energy sources will not impact the environment.
- It is capable of replacing fossil fuel as fossil fuel will run out one day.
- The use of renewable energy will result in stable energy prices.
Disadvantages of Renewable Energy
- We cannot rely on some renewable energy sources all the time like solar and wind power.
- Some renewable energy sources have bad environmental impacts.
- Wildlife and marine life can be affected by installing renewable technologies.
- Energy storage and transmission are always a problem.
- Unfavourable weather conditions can impact the energy supply.
- Safe operation of all integrated parts is necessary which makes the process more complex.
Reason for Low Consumption
Some of the renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydroelectric are popular and viable to meet global energy demands.
They can replace fossil fuels and we can have clean sources of energy in total. Still, they are not consumed according to their potential.
Following are the reasons for their low consumption.
Reliability problems
One problem with them is the reliability. They depend on weather conditions and harsh weather may have drastic effects on the energy production process.
- If the sky is covered by clouds, less solar energy can be captured.
- In the same way, if winds blow at low speed, wind turbines cannot turn. Also, the surplus energy will create more issues.
Area requirement
Lack of sufficient areas for system setup is another reason for low renewables consumption. Not everyone will have spaces on the roof to handle solar panels.
What if we need a large amount of energy? More free space is required. Well, floating solar panels provide an alternative, however, it causes issues for marine life and nature.
Not totally clean
The renewable sources are not totally clean as they still generate pollution. Burning biomass will release toxic gases into the air and cause global warming.
Manufacturing involved in the production of renewable energy technologies is using fossil fuels and emitting heavy pollution.
Location-specific source
Renewables are considered a location-specific source of energy. A renewable source having one result at a place may not be the same in another place.
- Some renewable energy sources are simply not available in specific regions.
- In terms of cost and efficiency, the distance between the source and grid is a major concern.
- Many renewables depend on the weather, climate, and geographical location.
Involvement of politics
Politics plays its role in every part of our lives either positive or negative. Here politics is impacting our journey towards renewables.
- Many countries have economic benefits both with the export and import of fossil fuels.
- They are reluctant to start using renewables and take advantage of their great potential.
- Governments are not providing incentives for adopting this technology.
Technology barrier
We are lacking a clear policy for the implementation of renewable energies. We don’t have established technology at a commercial level for various renewable sources.
- Research is underway to come up with reliable technology.
- There is a lack of awareness and information regarding the benefits and needs of renewable energy among the masses.
- The shortage of finances is another obstacle.
High installation cost
The initial cost to set up renewable energy technology is high. The prices of solar panels have decreased with the passage of time; however, you need a high budget to install a solar energy system on your rooftop.
This is a hurdle in the development of renewable technology.
Future Prospects of Renewable Energy:
Many countries in the world are moving fast towards clean energy. One day we will run out of fossil fuels and the alternative left then will be renewable. It means renewable energy is the future of the modern world. The statistics depict the same story.
According to the International Energy Agency 2020 report , renewable energy capacity will expand 50% between 2019 and 2024. By the year 2024, solar will become 35% cheaper, wind energy capacity will increase 57%, hydroelectric and geothermal will increase 9% and 28% respectively.
, renewable energy capacity will expand 50% between 2019 and 2024. By the year 2024, solar will become 35% cheaper, wind energy capacity will increase 57%, hydroelectric and geothermal will increase 9% and 28% respectively.
Based on the future global energy needs, with depletion of traditional resources and climate change, renewable energy will be able to provide 50% of energy needs by 2050.
Conclusion
With time as innovation brings down costs, the share of different renewable sources will improve. Wind and solar power are the main players.
A clean energy revolution is waiting for us in the future. Therefore, from now on efforts should be made to add renewable energy to the global energy mix.
In this way, developing countries will save money they spend on importing oil at hefty prices so, they can invest this money in the socio-economic development of their people.
