The supercharger is explained along with basics, definition, parts, working principle, advantages, disadvantages, etc. Let’s learn Turbocharger!
What is Supercharger Engine in Car?
Supercharger Basics
Let’s try to understand the basics of superchargers. The engine power, as well as the efficiency of the engine, is the most vital aspect in the modern era. There was so many research on the advancements of the engines and supercharging is one of them to increase the engine power. Earlier this process was known as “Turbosupercharger” but nowadays, it is segregated into two different processes,
- superchargers and
- turbochargers.
We have already learned turbochargers in the last article, here, we will learn superchargers.

History of Supercharger
If we dive into history, Dugald Clerk first used the supercharger in 1868 on the two-stroke engine. Later Gottlieb Daimler got the German patent for supercharging an internal combustion engine in 1885. Superchargers were in use for a long time, and after improvements in compressors, their use got better and better.
What is the Function of Supercharger?
We have seen that injection happens by multi-point fuel injections in normal naturally aspirated engines, and these are normally operated at lower pressure. There are few disadvantages in naturally aspirated engines, like
- Working under low pressure, which provides low power,
- Power & Efficiency is less,
Now, we have to avoid this problem, the supercharger comes into picture. Let’s see what is the purpose of the supercharger?
- Increase the engine power output for the engine’s given weight and size for aircraft, marine, and automobile engines.
- Increase the efficiency of the engine.
- Contribute to more air-fuel mixture burning.
- Raise the charge density before entering the combustion chamber.
What is Supercharging?
A supercharger’s definition is that it’s an air compressor used to pass or induct more air into the internal combustion engine. So, it will pass more air to create more air-fuel mixture to increase engine power.
- It will give more air to the IC engine to burn more fuel and increase power output.
- Superchargers are connected to the engine crankshaft with the help of belts, chains, or gear.
Before getting to the supercharger’s types and components, let’s know their purpose in the automobile engine first.
Parts & Diagram of Supercharger or Supercharging
Parts of Supercharger
There are mainly four parts of a supercharger, as follows,
- Drive gear
- Driven impeller gear
- Internal oil gear
- Pulley
Supercharger Diagram or Supercharging Diagram
Let’s see a simple diagram of a supercharger, to have a primary concept of working philosophy. Here, the diagram is covered the entire circuit from the air intake to the supercharger to the final exhaust from engine cylinder to have a clear concept.
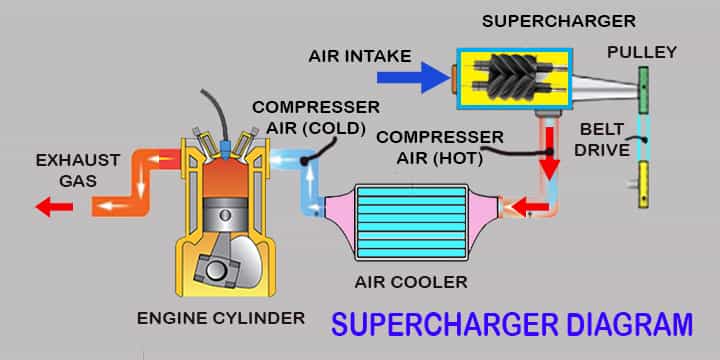
Let’s delve into the types of superchargers!
Types of Superchargers with Diagrams
Centrifugal Type Supercharger
Centrifugal type supercharger is one of the most used types of superchargers.
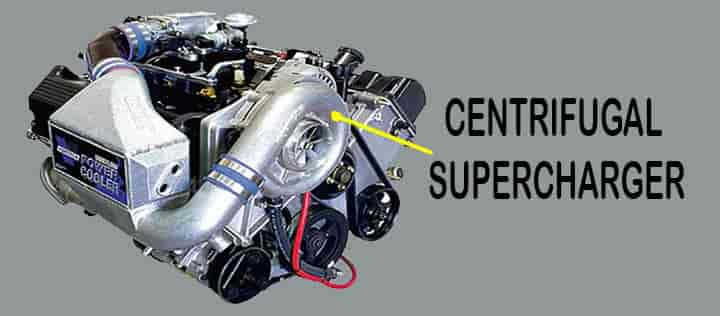
- Centrifugal type supercharger comes under the classification of dynamic superchargers.
- They are the most commonly used superchargers in automobile vehicles.
- These are connected to the crankshaft via a belt-pully system.
- The centrifugal superchargers are equipped with an impeller that rotates at very high speed and draws air quickly into the small compressor housing.
- These are mostly used because they are lighter in weight.
Roots Blower Superchargers
These are also known as the lobe type superchargers. We have seen the centrifugal supercharger that uses the impeller, but its roots superchargers use the lobes in epicycloidal shapes.
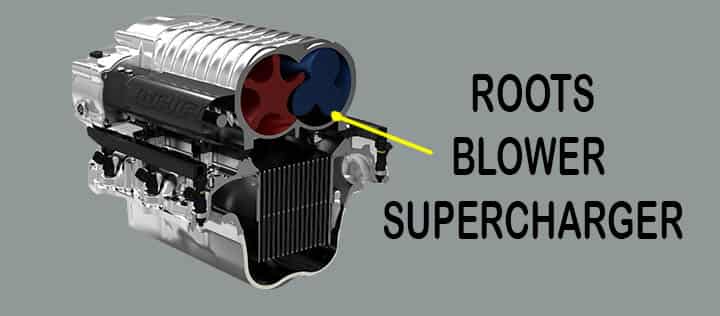
- Roots superchargers are the oldest in design.
- Daimler used roots supercharger back in the 1885 year.
- The working of these roots superchargers is quite simple and easy to understand.
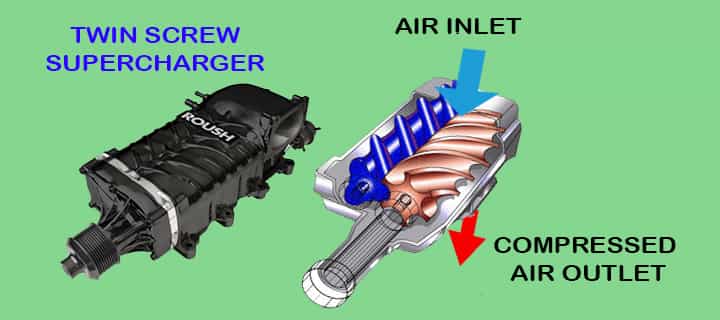
Twin Screw Superchargers
The twin-screw superchargers operate a little bit the same as the roots superchargers. Some types of twin-screw superchargers also sit on the engine.

They are noisy, but sound can be controlled by using sound silencing equipment. They are more efficient than roots superchargers, but at the same they are costly. Let’s learn the working philosophy of all types of superchargers!
How Does Supercharger Work? Diagram
How Does Centrifugal Supercharger Work?
The air-fuel mixture enters the rotating impeller that has a speed of almost 15000-20000 RPM. Now due to centrifugal action, the fuel-air mixture gets high velocity and enters the diffuser.
- If you know the diffuser, it has an elongating structure, which reduces the velocity and increases the pressure.
- The same happens with the charge entered into the diffuser.
- Its velocity gets reduced, and pressure gets increased. Because of this action, the density of the charge also gets increased.
Now the diffuser will pass the charge to the volute casing of the centrifugal compressor. Later from the volute casing, the charge passed to the engine inlet manifold.
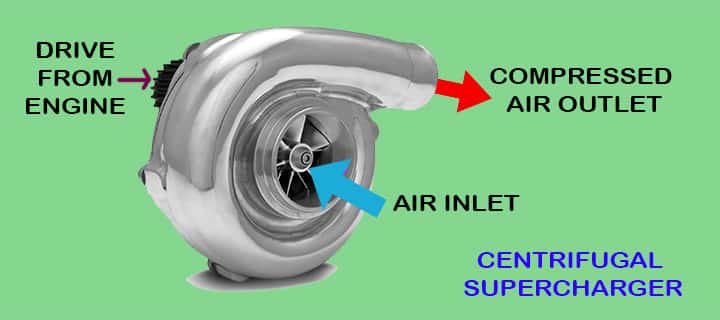
The charge having high pressure and low speed gives the engine opportunity to burn more fuel and achieve a high level of combustion. Due to this, volumetric efficiency increases and provides a responsive, faster vehicle. The centrifugal superchargers have limited speed range, and it’s suitable for aircraft and water pump engines mostly.
- In this modern age, centrifugal superchargers are widely used to improve the performance of the engine as well as cars.
- Centrifugal superchargers is really easy to integrate air-to-air or air-to-water intercoolers.
- All these advantages of the centrifugal supercharger have some disadvantages, we will see after getting to know all the types first.
How Does Roots Blower Supercharger Work?
Generally, the roots superchargers have two, three, or more lobes on the rotor. Their structure is such that they rotate in the housing with small clearances.
- It has two shafts, so one shaft gets driven by the engine via a connection like a belt-pulley. So this is how the process starts now.
- Firstly, air enters from the inlet port and gets carried away to discharge ports through rotor lobes.
- The air pockets get trapped, and the compressor’s outlet is due to which the pressure is more at the outlet than the inlet.
The roots superchargers are usually mounted on the top of the engine compared to the centrifugal superchargers mounted on the front side.
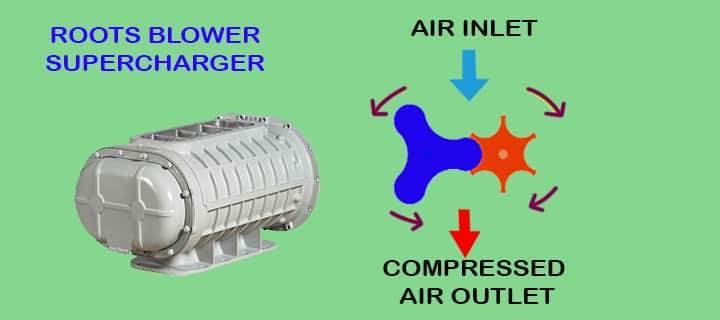
These are most popular in muscle cars because they stick out of the hood. You may have seen the fast and furious movie Vin Diesel muscle car. Like that, the supercharger sits on the engine. But the root supercharger is less efficient compared to the other two. It adds more weight and supplies the air in bursts rather than continuous supply compared to the centrifugal type.
How Does Twin Screw Supercharger Work?
The twin-screw superchargers have the rotor lobes, just like the roots superchargers, the air trapped in the twin-screw superchargers.
- It pulls the air through meshing lobes, and the air gets compressed in the rotor housing itself.
- The rotors have a conical taper that causes the air pockets to decrease in size.
- When the air moves from the inlet side to the discharge side, the air pockets size get decreased.
- Due to the shrinking of air pockets, the air squizzed into a smaller place.
Advantages of Superchargers
There are many advantages of superchargers, as follows
- The ultimate aim of the supercharger is the higher power output.
- The supercharger supplies air, which helps in the complete combustion and results in low smoke emissions.
- It helps to improve cost start.
- The acceleration of the vehicles improved. When the car starts, the supercharger starts immediately, giving a boost from the vehicle’s start.
- The superchargers start as soon as the driver pushes the pedal. Because of this, the superchargers do not face any lag compared to the turbochargers.
- They are easy to install. They can be bolted or mounted on the engine’s top easily.
- The roots and twin-screw are efficient at lower RPMs, whereas the centrifugal supercharger gets more efficient with increased RPM speed.
- Smoke at the exhaust is comparatively less.
You can check a very nice video from Donut Media,
Disadvantages of Superchargers
There are many disadvantages of superchargers, as follows
- The power output undoubtedly increased, but the supercharger draws the power from the engine itself.
- The engine can heat up. Proper heat-dissipating arrangements are necessary.
- The engine must be able to hold high pressures; otherwise, the parts may get damaged.
- The superchargers suck about 20% of engine power, but they give out about 40% power output.
- Turbulence is increased and incurs some heat loss.
- The maintenance cost is more.
Conclusion
Hence, we have got a basic idea about supercharger along with definition, working principles. Any doubt, please write to us in the comment section! Happy reading! Please let us know, if any question!

