The turbocharger is explained along with basic details, definition, purpose, components, working principle, advantages, disadvantages, etc. A comparison between turbocharger vs supercharger is also captured. Let’s learn Turbocharger!
What is Turbocharger Engine in Car?
Turbocharger Basics
Let’s try to understand the basics of turbochargers. The engine efficiency and power is the most critical aspect of any automobile vehicle. There are various advancements and tries done to improve engine efficiency and power. Two of them are supercharging and turbocharging. They were known in the same terms as “Turbosupercharger” back in the days, but now they are known separately as,
- superchargers and
- turbochargers.
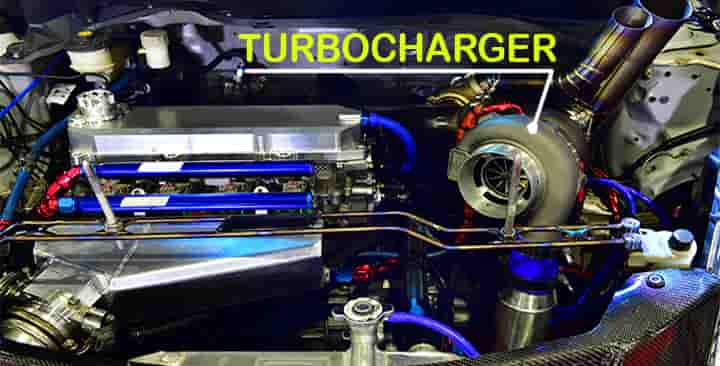
There is a significant difference between these two in their construction as well as working.
History of Turbocharger
In 1905, Alfred Buchi working at Gebruder Sulzer considered as the birth of turbocharger. The patent was patented with the radial engine and axial flow turbine.
- The first successful implementation was done in 1925 by Alfred Buchi on the diesel engines.
- Later in the 1970s turbocharging became common in automobiles to reduce fuel consumption as well as exhaust emissions.
What is the Function of Turbocharger?
In normal engines or naturally aspirated engines, injection happens by multi-point fuel injections and works normally at lower pressure. Naturally aspirated engines, has the following problems,
- Works on low pressure incurs less power,
- Efficiency is less,
- Power output is less,
Now, these are the problems so,
- How can you increase the engine power?
- Would the obvious answer be to use a bigger engine, right?
Now, to avert all the problem, the turbocharger is introduced in the engine and it helps, But if we use a bigger engine, there are more problems with the weight and overall efficiency of an automobile vehicle. By keeping the engine’s size the same, you can increase its power and efficiency by sending more air to get more fuel-air mixture and increase the power by Turbocharging. It helps,
- To improve the volumetric efficiency.
- Recover waste heat of exhaust gases and to use it drive the turbocharger.
- Increase the power output of the engine.
- Increase the overall efficiency of the engine.
We will see in the details about the turbocharger used in automobiles: their working, parts, and the difference with superchargers, etc.
What is Turbocharging?
Turbocharging differs from supercharging in lots of ways, from working mechanisms to parts.
- It’s is a compressor driven by the turbine-powered by the engine’s exhaust gases.
- Whenever high-performance racing cars come into the discussion, turbochargers are one of the essential aspects.
- Turbochargers can increase power output as well as engine efficiency without increasing any weight.
- The key difference between turbochargers and superchargers is their location, and the engine power drives the superchargers.
- Whereas the turbochargers don’t use the engine power, it has a turbine that is powered by the exhaust gases.
- Turbochargers suffer from lag because the exhaust should be made first for the working of the turbochargers.
- The new twin-chargers are also used nowadays.
- They are a combination of superchargers and turbochargers.
Let’s know more about the different parts of turbochargers.
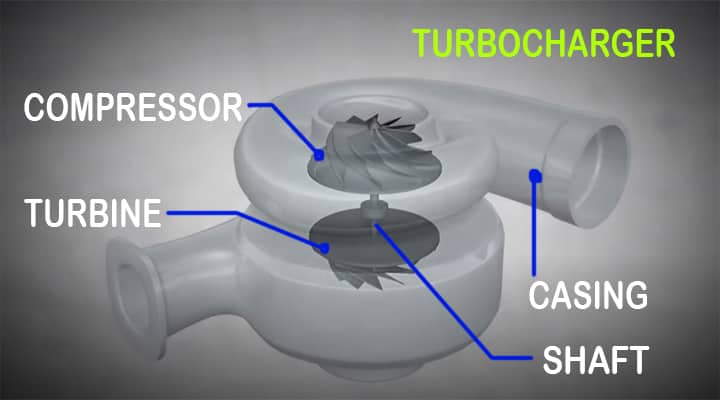
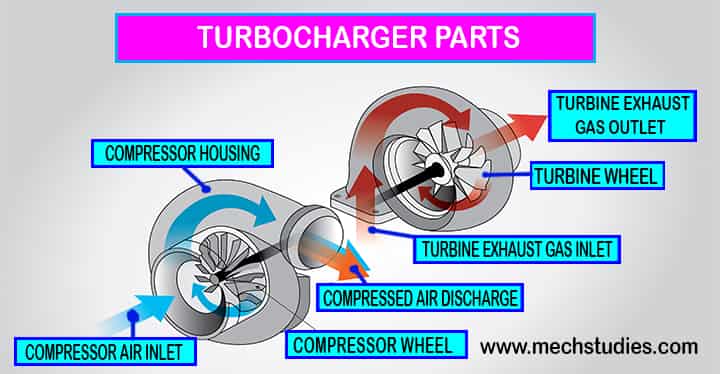
Parts of Turbocharger
There are a few main components of turbocharger and these are as follows,
- Casing
- Turbine
- Twin-turbo design
- Twin scroll design
- Compressor
- Hub rotating assembly
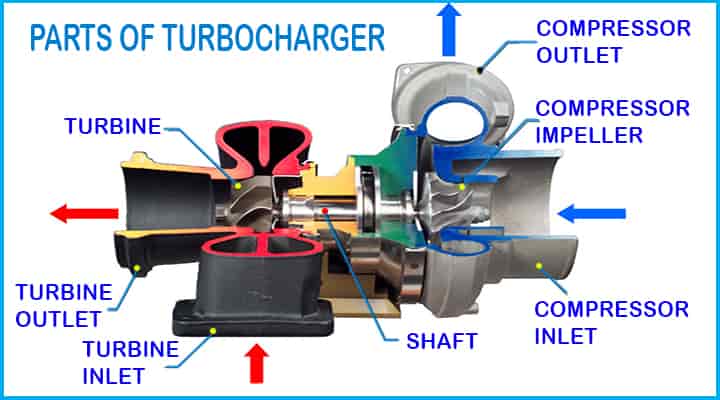
Let’s learn all these turbocharger parts in brief,
Casing
A turbocharger is having a casing where all other parts are mounted. Refer Fig. 3
Turbine
Now we know the exhaust gases are passed on to the turbine to drive the compressor. The turbine spins at very high speed (250000 RPM).
- The turbine size and impeller size is deciding factor for lots of aspects in the turbochargers.
- In simple words, if the turbine wheel is big and the compressor is big, then the flow capacity will be large.
- Manufacturers provide various sizes and shapes according to the requirements.
The performance of the turbocharger is closely related with the turbine size. Large turbochargers need more heat and pressure to spin which cause the lag at the start of the engine. Similarly, the smaller turbochargers need less heat and pressure to spin but can’t get the performance and acceleration compared to large turbochargers. To avoid this the twin-turbo designs are employed.
Twin-Turbo Design
Twin-turbo as the name suggests it has two turbochargers arranged in series or parallel arrangements. In parallel arrangements, the turbochargers get half-half exhaust gas power. Whereas in sequential turbochargers, one of them runs at low speed and the other at a fixed speed according to load.
- The same principle is employed in the two-stage variable twin-turbos design.
- The small turbocharger runs at low speed and the large one at higher speeds.
- These two turbochargers are connected in series so they can multiply by another.
- This configuration helps to avoid the turbo-lag
 to some extent.
to some extent.
Instead of using the one large turbine twin-turbo design is used.
Twin-scroll design
This design has two exhaust gas inlets and two nozzles. One of them is smaller and useful for the quick response, other one is the larger one used to gain the peak performance.
- This arrangement with the help of camshaft timings is able to open the exhaust valves in the different cylinders at the same time.
- Because of this arrangement, exhaust gas can manage or used efficiently which gives lesser NOx emissions and reduces the turbine lag.
Compressor
Generally, a centrifugal compressor is used in turbocharging. It has the impeller and construction same as used in the centrifugal supercharger. But in turbocharging, the compressor will be powered up by the turbine that moves with the help of exhaust gases. The compressor gets the fresh air and transfers the fresh to the engine manifold.
Hub rotating assembly
This hub has the shaft which connects the compressor, impeller and the turbine. It also consists of bearing systems (thrust bearing or ball bearing) to allow the shaft to rotate at high speed with less friction.
How Does Turbocharger Works?
Let’s the working principle of a turbocharger,
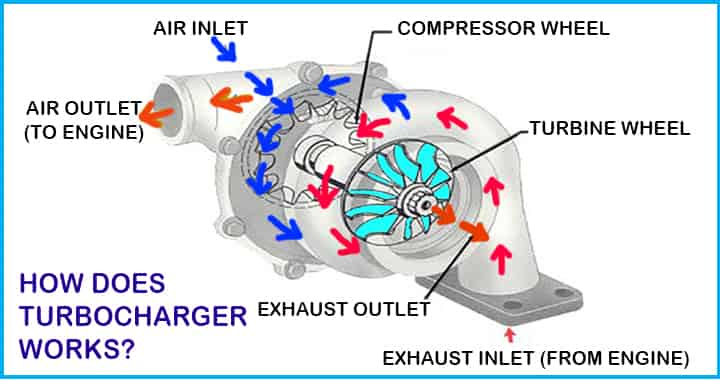
We know already the objective of the turbocharger is to improve the volumetric efficiency of the engine by increasing the density of the intake gas.
- When the driver presses the pedal, the engine starts, and exhaust gases are produced.
- The turbocharger starts on the start of exhaust gases coming out.
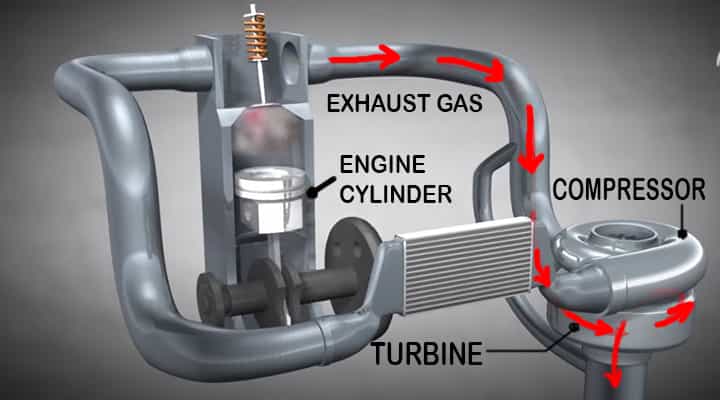
The exhaust gases are passed on to the turbine.
- Due to the speedy exhaust gases, the turbine wheels start to spin.
- A common shaft is connected between the turbine wheel and the compressor wheel.
- The power which is generated by the turbine helps to drive the compressor, as both are connected.
As we have seen in the above section, differently designed turbines can be used in turbochargers. The compressor impeller starts to rotate and creates low pressure which helps to induce fresh air through a filter.
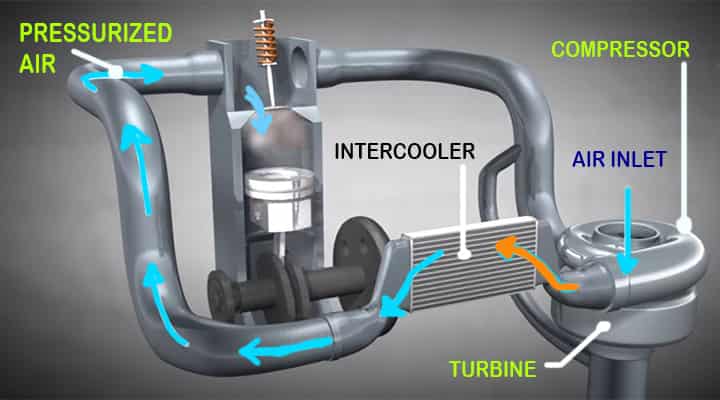
This air is compressed and its pressure and temperature are increased.
- An intercooler is used to reduce the temperature of the air and avert the engine knocking problem.
- Finally, air transfers to the engine manifold with pressure.
- The engine gets the pressurized readymade air supply which is responsible for improving the volumetric efficiency and power output of the engine.
Diagram of Turbocharger
We have already learned the parts and working principle, let’s see a simple diagram based on our understanding,
Pressure Boost in Turbocharger Engine
There is one more use of turbochargers in automobile vehicles.
- The turbochargers can be used to increase fuel efficiency without increasing the power.
- A turbocharger can utilize the wasted energy from the combustion process and gives it back to the turbo “hot” side.
- The hot side of the turbine is the one that drives the turbine whereas the other side can be used to compress the air and transfers the air to the engine.
Because of using the wasted energy, the fuel can be burned to its highest possible efficiency and thus the fuel efficiency can be increased.
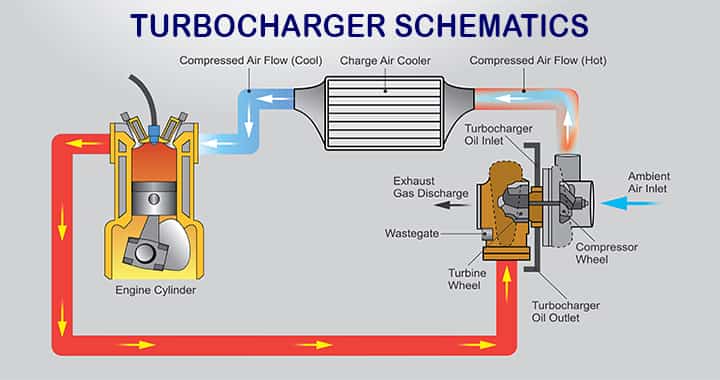
Schematics of Turbocharger
A simple schematics is include below to have a clear concept on oveall system,
Types of Turbochargers
Turbochargers are classified into two types based on geometry. These are,
- Variable Geometry Turbocharger or in short VGT.
- Fixed Geometry Turbocharger or in short FGT
Let’s learn the basic concept of both types of turbochargers.
Variable Geometry Turbocharger (VGT)
Variable geometry turbocharger (VGT) (also known as variable-nozzle turbines or VNT) means as the name suggests, it varies the aspect ratio of the turbocharger based on the conditions. There may be two situations for aspect ratio:
- In case, the aspect ratio is very high, the turbocharger will not be able to create the necessary boost required at low speeds.
- In case, the aspect ratio is very low, the turbocharger tends to choke the engine at very high speeds.
The above conditions creates problems like,
- high pumping loss,
- high exhaust manifold pressures,
- reduces efficiency
- reduce power output
Hence, the aspect ratio needs to be optimized and this Variable geometry charger (VGT) helps to do this.
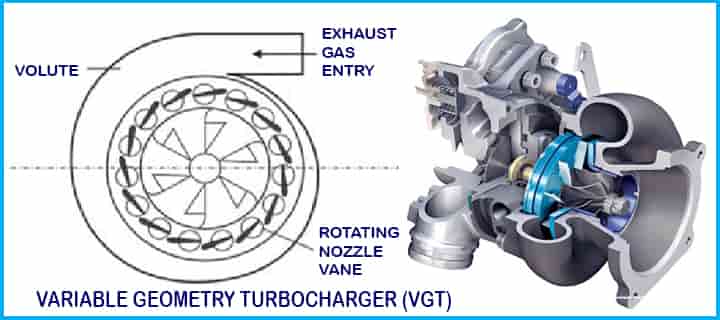
Let’s see how VGT works,
- This type of turbocharger works based on variable air quantities controlled by vanes. Air quantity entered into the turbine can be more or less as per requirements which are controlled by vanes.
- An actuator is installed for the vanes and the actuator can control the opening of vanes.
- The actuator can easily open the vanes or close the vanes based on requirements.
- When the vane is open, the amount of air induction into the turbine wheel is very high and the turbine will rotate very fast and a high boost will be created. Exhaust gasses are expelled at high RPMs with force.
- When the vane is closed, only a little amount of air will be introduced, but the pressure will more to the turbine. Here, exhaust gases will be pressurized and turbo lag will be reduced at low speeds.
Fixed Geometry Turbocharger (FGT)
Fixed geometry turbocharger (FGT), as the name suggests, gives specific or fixed RPM where it gives the highest efficiency. Fixed geometry turbocharger can be designed for two cases,
Low speed
- If FGT is designed considering low speeds, then turbo lag will be reduced.
- Design at a lower speed will not be efficient at high speed and power will be less.
High speed
- If FGT is designed considering high speeds, then power will be high at high speeds.
- Design at higher speed will not be efficient at lower speed and turbo lag will be more.
Advantages of Turbochargers
The advantages of the turbocharger are as follows,
- For the same size of an engine, more power can be generated.
- Compared to the naturally aspirated engine (air is entered naturally) and supercharged engine turbocharger has better thermal efficiency.
- Because of using the exhaust gas power, better fuel efficiency achieved.
- No engine power is used compared to supercharged engines.
- High speed, better average, and better volumetric efficiency.
- The air-fuel mixture is burnt efficiently, resulting in less pollution.
Disadvantages of Turbochargers
The disadvantages of the turbocharger are as follows,
- Turbo lag is the main problem, large turbochargers take time to give a useful boost.
- Turbochargers cannot operate as wide a range as superchargers. They are designed to operate at a certain RPM range where the exhaust gases can drive the turbine.
- Some turbochargers when reached to its max RPM range can provide sudden boost which can be dangerous for the driver.
- Oil requirements are more because the turbochargers run very hot.
Now we know about turbochargers and superchargers. There are some differences between these two you may have seen it already by yourself after reading the post. Still, let’s check out some differences between these two chargers.
Difference Between Turbochargers and Superchargers
| Sr no. | Turbochargers | Superchargers |
| 1. | Turbochargers consists of compressor as well as turbine. | Superchargers are only compressors. |
| 2. | Turbochargers take power from the exhaust gases to rotate the turbine. | Superchargers takes power from the engine itself. |
| 3. | They are connected to intake through exhaust pipe, turbine, compressor to inlet manifold. | They are connected to intake manifold through compressor. |
| 4. | Mostly suitable for higher displacement engines. | Mostly suitable for smaller displacement engines. |
| 5. | Turbochargers are costly. | Superchargers costs less comparatively. |
| 6. | Takes time to give useful boost causing turbo lag. | Power delivery is immediate. |
| 7. | More efficient in fuel and overall engine efficiency because it draws the power from the exhaust. | Less efficient, because it takes the power from engine itself. |
These are the differences between turbochargers and superchargers.
Conclusion
If you want to prefer one, the turbocharger is a good deal. Turbochargers can help in overall efficiency in multiple ways. But there are engines available that use superchargers as well as turbochargers known as twin-charged engines. Any comments, please write to us!

