In the manufacturing industry, the casting metal process is among those processes which have an extensive history. Humankind is using this process since ancient times, and it makes them equipped with some of the essential things. Gradually it became an integral part of metalworking. Nowadays, people are using it for making all sorts of apparatus and different components. Let’s learn the basics of the casting process with its benefits, limitations, types, and some of the fundamental defects.
Casting Metal
Let’s try to understand casting metal basics. It is simply the process in which the setting of molten metallic material takes place in a pre-designed mould.
- The end shape is attained after the molten metal cools.
- It gets the desired shape and becomes a solid metal object.
Casting is the process that can be achieved with numerous metals and different materials that are used for constructing the moulds as well as different equipment.

The following precautionary measures shall be taken care of, as follows:
- The casting process should be carried with the utmost care and safety precautions as it engages variable materials and techniques such as mould size and molten metals.
- This should be carried out under the supervision of trained specialists and also by acquiring all the safety precautions.
Basics of Casting Metal
Basic terminologies or gradual steps in the casting process helps to understand the core of the process. This is important to get a comprehensive and holistic view of the casting process.
Pattern development for Casting Metal
This is the foremost step that is a crucial one in the whole casting process. Pattern development or pattern making is the process of constructing the pattern as per the needs.
- This is one of the significant skilled practices that can only be attained through extensive learning.
- It is related to the mould making and tool and die-making.
- Mainly this process incorporated par quality woodworking.
Mould preparation
Mould preparation or mould making is an essential process in which a specific material is used for preparing the mould of the original model.
- Numerous materials can be used for mould preparation as per the preference and needs.
- One of the commonly used materials that are widely used in mould preparation is rubber.
You can explore, What is Saw?
Metal melting
This process holds the primary material and the whole melting process of the metal. It is one the foremost step without which the casting cannot be attained.
- Metal melting needs fundamental knowledge about the metals as well as their properties.
- This helps in getting the desired temperature at which the metal melts.
- It should be attained under expert supervision or with full safety as the contact to molten metal can be lethal.
Metal pouring for Casting Metal
Metal pouring is the technique through which molten metal is introduced into the moulds.
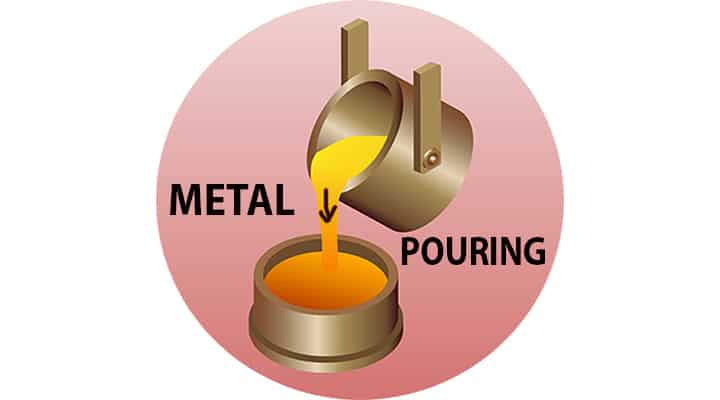
- It is one of the essential steps in the casting process as this is the process in which both crystallization happens.
- The metal acquires most of the physicomechanical attributes during this process.
Cooling period
After the metal pouring process, the molten metal keeps on for a cooling period.
- In casting the end-design cannot be attained before this process.
- Cooling helps in the crystallization of molten metal that attains different metal properties.
Part removal
After the cooling process in casting now, the next process is to part removal. Part removal is nothing but the process in which different parts of moulds are cleaned.
Specifically, this process involves some of the critical methods that help in part removal such as shakeout in which a vibrating device is used for shaking and casting out the flask from the mould.
Cleanup process
This is one of the simple processes that includes removing those materials which are in excess. These include risers, rough edges, impurities etc.
Heat treatment
Heat treatment is a vivid process, but when it comes to casting, then this process is used for controlled cooling and heating that helps in attaining different properties of metals after crystallization.
- The properties that cast metal acquires are strength, hardness, toughness, elasticity, and ductility.
- This process can be achieved as per the need.
Optional upgrade treatment
There is a different consideration that comes when we design the material. In casting this method is an alternative step that may or may not is used. If there is something specific we need, then this upgrade treatment is used.
Miscellaneous finalization processes
Sometimes casting provides those end products that are equipped with rough edges or abnormal risers. To repair those one uses different finalization processes in which one of the best ones is machining.
Brief Working of the Casting Metal Process
The working of the casting metal process can be expressed, as follows:
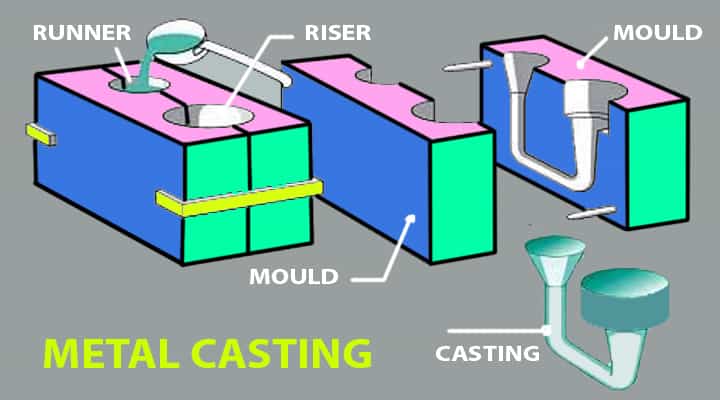
- The casting process uses a mould that is explicitly used for defining the shape of the final product.
- The mould is among the essential parts of the whole; casting process.
- It is two different pieces that form the entire pattern when connected.
- The mould acquires a closed look in which is tightly sealed except an opening that is known as a riser which is used explicitly for pouring molten materials in the mould.
- When the molten metal is poured into this, it is kept aside for drying, and when it gets cooled, it acquires a solid-state.
- Mould is an essential part of the casting, but several other procedures can be used in the whole casting process.
Benefits of Casting metal Process
Casting metal is a process that holds massive importance against different shaping processes such as,
The primary advantages that provide an upper hand to casting over other methods are as follows:
- Casting provides help in shaping some of the designs as there are numerous metals available that can only be attained with the help of casting. It is because there are different materials that have different physical properties and are complex to be remodeled into plates, bars, rods, or other shapes.
- When it comes to mass production, then this process is highly suitable. We can produce a large number of casting in a short period. One of the sectors that uses casting techniques abundantly is the automotive industry where there is bulk production of transmission cases, engine blocks, and other parts.
- There are specific light metal alloys that can only be produced with the help of casting due to their strength and weaknesses.
- The end product obtained by the casting technique shows the top of the grade bearing qualities. Apart from that, it also has design flexibility which can easily help in manufacturing complex and large parts.
Limitations of Casting Metal
Apart from the compelling advantages, there are some of the disadvantages of this process, but these are way minimal in comparison to the benefits. Some of them are as follows:
- Casting process requires effective process monitoring and control as there are specific steps which are quite delicate.
- In this process, the possibility of shrinkage porosity is maximum.
- Metallic projections are the core disadvantage that causes massive problems.
- The problems such as hot tearing, cold shuts, cracks make it quite tricky.
- Apart from all those problems, there are some other ones also present, such as misruns, insufficient volume etc., which are the limitations of this process.
- There are certain casting processes such as labour-intensive sand casting. Apart from that the possibility to cater the defects gets minimized as in this process moisture is also present in the sand.
Types of Metal Casting
Numerous types of casting can be categorized based on essential parts in which one of the prominent ones is moulds. The different kinds of casting can be further elaborated based on moulds permanence attribute. The two types of casting techniques based on moulds are as follows:
- Expendable casting
- Non-expendable casting
Expendable casting is the kind of casting technique that mainly uses clay, plastic, metal moulds and sand for the casting process. These moulds are only for one-time use and discarded after use.
Non-expendable casting is the type of casting in which the moulds can be used for long runs. In a way, these moulds are for permanent usage. Mostly these moulds are made up of metal through the whole process of performing the casting is different from the expendable methods. These two casting types are the core types of methods. There are further subdivisions in each one of them which are categorized based on the use of material to construct the moulds.
Expendable Mould Casting Types
Expendable mould casting is further subdivided into three categories of casting processes. The following are the further elaboration of the same:
Sand Casting
Sand casting is a process in which the moulds are manufactured with chemicals and polymers. These moulds are of par level durability and can be used for other expendable casting methods. It can be used for long runs.
This process mainly depends upon silica-based materials such as naturally bonded or synthetic sand. The casting sand has some of the properties that make it quite apt for this process, such as spherical grains, finely ground. It helps in attaining a tight packing-which is capable of providing a smooth moulding surface.
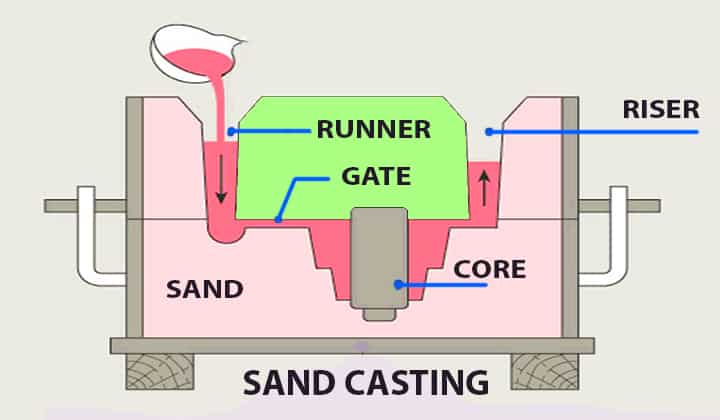
Reasons for using this method
This casting technique helps explicitly in reducing the probability of cracking, tearing and other defects by providing a moderate level of shrinkage and flexibility in the cooling phase of the whole process. The addition of clay helps the particles to be bonded effectively. One of the popular uses of this technique is in casting automotive products such as engine blocks.
Steps involved in sand casting
There are several steps involved in sand casting. The following are some of them:
- Patternmaking
- Moulding
- Melting
- Pouring
- Cleaning
Advantages of sand casting
- When there is low volume needs the inexpensive production costs to help in the best possible ways. This is the reason it is among the most widely accepted methods for casting.
- With this casting process, one can quickly fabricate massive and large components.
- This method can be used for casting both ferrous and non-ferrous materials.
- When it comes to post casting tooling, it engages low cost, which is a massive benefit.
Disadvantages of sand casting
- A lower degree of accuracy
- Difficult to cast those components which are pre-specified weight and size
- The yield products are equipped with the comparatively rough and improper surface finish.
Plaster Mould Castings
Plaster mould casting is the method of casting that is comparatively less durable than sand moulding. This consists explicitly of gypsum plaster. In this process, the time required to manufacture the mould is minimal.
Reason for using this method
Where there is a need for an optimal surface finish of the yielding material, this method is used. Steps involved in plaster mould casting: The essential steps in plaster mould casting are somehow similar to sand casting. However, in place of sand, it uses a mixture of gypsum, strengthening compound and water.
Advantages of plaster mould casting
- This process of casting provides a very smooth surface finish of the yield.
- With this, one can easily cast complicated shapes that are equipped with thin walls design.
- It has a comparatively low cost involved than other processes of casting in large parts.
- It has a higher degree of accuracy in comparison to sand casting.
Disadvantages of plaster mould casting
- It is more expensive than sand casting as it requires continuous replacements of the moulding material.
- The application of this casting process is limited to casting copper and aluminium-based alloys.
Investment casting (or lost-wax casting)
Investment or lost wax casting is a process that is a technologically advanced method of casting that is suitable for getting durable and stable shapes. It is used for casting different shapes from massive to tiny pieces. It is the casting type that is suitable for complex geometries and alloys.
Reasons for using this method
This method is used where there is a need for casting complicated geometrical shapes. Mostly this method is used for the aerospace, power generation and automotive industries where there is a critical need for parts with complex shapes such as,
- turbine blade
 ,
, - engine blocks,
- propulsion blades etc.
Steps involved in investment casting
- Making of disposable wax pattern for each cast part
- Injection of wax into a mould
- Removal and coating with refractory material with a binding agent to form a thick shell.
- Assembling onto common sprues
- After hardening the inverted patterns are heated to remove the wax.
- Pouring of molten metal and kept for hardening
- Breaking of refractory shell
Advantages of investment casting
- It is capable of providing precise specifications of the yield and also a high degree of accuracy.
- Where there is a need for casting intricate geometrical design with thin-walled parts, this method of casting comes into play.
- This process has the capability of casting ferrous and ferrous materials with ease.
- This process can provide a comparatively par level of detailing and optimal quality surface finish in the final components.
Disadvantages of investment casting
- More expensive than other methods of casting
Non-expendable Mould Casting Types
Below mentioned are some of the subdivisions of non-expendable mould casting:
Die-casting
It is a casting method in which a die is formed that provides a horizontal pattern. This is the method that helps in moulding materials with the help of high pressure.
It is useful for non-ferrous metals and alloys such as copper, aluminium, zinc and tin.
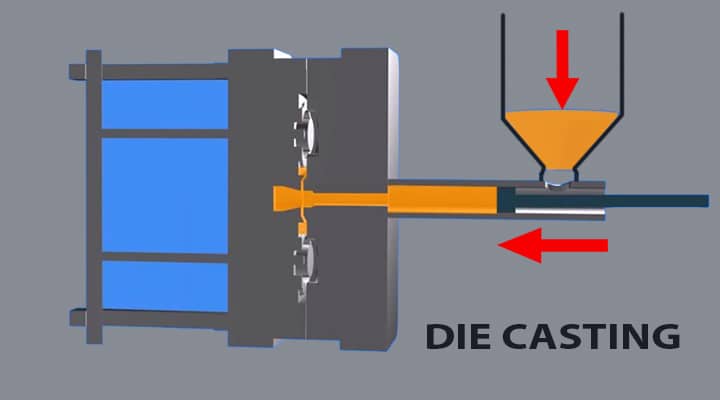
The process of casting involves pattern preparation, injection of molten metal into the die with high pressure. The high pressure continues until the yield gets solidified. The pressurized insertion helps in preventing the sections of material from getting hardened before being cast. Once the process gets completed, the yield is removed, and all the scrap material is removed.
Advantages of Die-Casting
- With die-casting method, it is relatively easy to attain compact shape and size tolerances.
- This type of casting enables us to get high dimensional consistency of the component and also helps in acquiring uniformity in design.
- The need for post-casting machining is reduced substantially.
- Effective for high-volume runs
- Mould can be used for producing different functions also as these don’t require destroying of mould after the usage.
Disadvantages of Die-Casting
- Comparatively high tool costs
- The different parts of the die-cast component do not get operational as structural parts.
Permanent Mould Casting
This is a non-expendable casting process in which metal moulds are used. These metal moulds can be used for long runs. However, the nature of mould is semi-permanent. This process shares a similarity between centrifugal and die-casting. The moulds in this method can be made up of graphite, steel etc. this casting method is used to cast materials such as magnesium alloys, lead, aluminium, zinc, cast iron, and certain bronze.
Advantages of Permanent Mould Casting
- This casting technique provides a smooth filling of moulds that reduces the risks of defects caused by turbulence and inclusions.
- By opting this technique, we can get an exceptional and par grade of physical attributes.
- The cast products are equipped with par quality finish which in turn helps in polishing.
- The casting of intricate designs and shapes can be easily attained through this process of casting.
- The mould dies have accurate dimension control that helps in getting par grade quality of the yield.
Disadvantages of permanent mould casting
- This process has a high tooling cost.
- This casting method is only limited to low-melting-point metals.
- The moulds manufactured are of short mould life.
Centrifugal Casting
Centrifugal casting is a type of non-expendable casting method that includes a large drum creating a centrifugal force by turning. It helps in pushing a molten metal into a mould that precisely fills out as per the design.
This method of casting helps produce intricate shapes and smaller pieces. One of the best uses of this casting technique is in the jewellery industry.
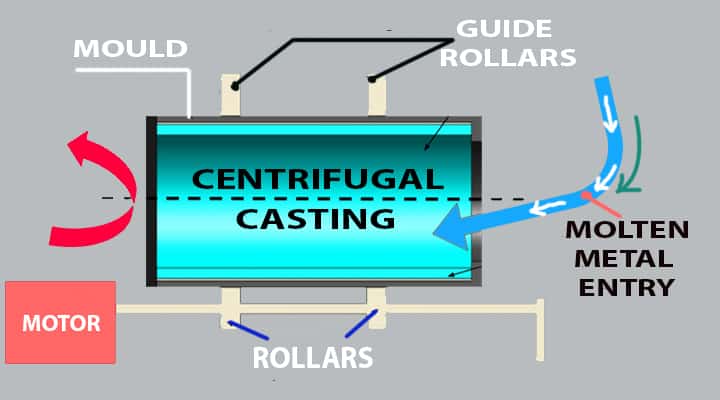
Advantages of centrifugal casting
- It helps to produce long parts which are in different shapes such as cylindrical ones.
- This method provides a casting yield that is free of voids and other defects.
- This method of casting has minimal requirements.
- With this, you can produce many pieces, and it can be used for a long time.
Disadvantages of centrifugal casting
- This process needs skilled laborers for the whole process.
- This casting process is only capable of producing some of the shapes.
- High investment is one of the core problems of this casting technique.
Metal Casting defects
The role of gas, mould, pouring of molten metal and metallurgical properties are foremost in this process. The significant defects that occur in the metal casting process come due to excess or shortage of the same.
Like welding defects, below mentioned are the common defects that affect the efficiency of this process,

Gas defects
Gas defects mainly include Blowholes and open blows, Air inclusions, Pinhole porosity, Shrinkage cavities.
Moulding material defects
Mould is among the foremost process that comes into play at every consecutive stage. Different kinds of defects persist due to the mould such as,
- Cuts and washes,
- Metal penetration,
- Fusion,
- Run out,
- Rat tails and buckles,
- Swell and Drop.
Metal defects while pouring
Pouring of molten metal can be a cumbersome process. This complexity results in different kinds of defects such as,
- Misruns,
- Cold shuts and
- Slag inclusions.
Metallurgical defects
Metals have different properties, and when the other thermodynamic processes are used, then it may cause metallurgical defects as well. Some of these defects are,
- Hot tears and
- Hot spots.
There are many other castings defects, incurred in various metals, as follows:
- Pinholes
- Open holes
- Blowholes
- Shrinkage defects
- Fusion
- Hot tears
- Short Pour etc.
Conclusion
In this excerpt, we have studied one of the oldest known manufacturing processes that have it’s own advanced and modern version. With the advancement in technology, we have utilized the same with this process also.
Apart from the core process here, we have emphasized different aspects of the casting techniques, it’s advantages and disadvantages with the possible known defects. However, there is a massive possibility to gain further insights into this process.
Our YouTube
Refer our YouTube Videos

Rattling clean web site, regards for this post.
I like what you guys are up too. Such intelligent work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my web site 🙂