Two (2) stroke engines are described along with all basic details, how does two-stroke engine works, along with many diagrams.
Let’s begin with two (2) stroke engines!
What are two (2) Stroke Engines?
Two (2) Stroke Engines Basics
The two-stroke engine is part of an internal combustion engine with only two strokes for its working.
It differs from the four-stroke engine based on stroke completed in two revolutions, whereas, in the four-stroke, the operation is completed in four 180 degrees rotations.
The name itself comes from its operation completing process in two revolutions. A stroke means the piston travels along with the cylinder.

- In the two-stroke engines, the two strokes get activated at the same time.
- Just like the end of combustion and the compression stroke happen simultaneously, and exhaust entry happens simultaneously.
- Two-stroke engines have a great weight to power ratio compared to four-stroke engines.
- The two-stroke engines are commonly seen in dirt bikes, mopeds, small motors, jet skies, etc.
- They are having limited use now due to their disadvantages in the commercial automobile vehicle sector.
Two (2) Stroke Engines Importance
There are some advantages of the two-stroke engines. We will discuss them later in this post.
- But the applications for which the two-stroke engines are used is due to they are light in weight due to less moving parts.
- The main difference between two-stroke and four-stroke is the required crack rotation for the operation.
- The crankshaft needs to complete about two rotations to complete operation in the four-stroke engine, whereas the two-stroke needs only one crank rotation to complete the operation.
- But you will not see the two-stroke engines in the car as much as four-stroke engines.
So, let’s know more details about the two-stroke engine parts and their work. These parts are the same as for any engine with slight changes.
Components of Two (2) Stroke Engines
The two-stroke engines have almost the same parts as the four-stroke engines, like,
- Fuel injectors
- Spark plug
- Inlet and outlet ports
- Piston
- Connecting rod
- Crankshaft
- Crank & crankcase
- Flywheel
- Counterweight etc.
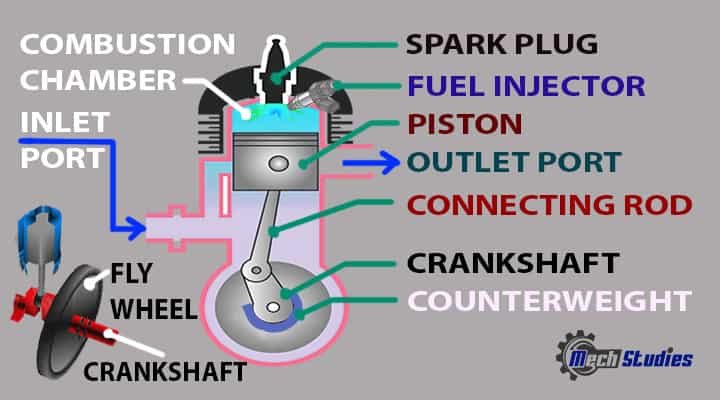
Let’s know the parts of the two-stroke engine in little detail.
Fuel injectors
The two-stroke engines get an advantage from the fuel injection systems rather than carburetors. However, carburetors are not used to that extent right now. Fuel injectors are used in diesel engines or C.I engines.
- In the case of two-stroke engines, the carburetor causes the problems of air-fuel mixtures directly going out.
- The direct fuel injection solves this problem.
- These injectors spray the fuel directly into the cylinder with the amount to the air required to get the correct amount of mixture of air and fuel.
- The fuel doesn’t pass through the case, so there is a need for lubrication.
No products found.
Spark Plug
The spark plug as the name suggests it ignites the fuel. It is connected to the battery; the current is received by the spark plug from the battery via a button start or using a kick. Spart plugs are used in a petrol engine or S.I engines.
- The fuel gets ignited due to the spark plug and the vehicle starts.
- If sometimes the vehicle is having problems to start, mostly there’s a spark plug problem, or sometimes when the vehicle just starts and stops suddenly.
- The spark plug has continuous work in case of two-stroke engines.
XPH is your home for BMW, Audi, Ford Mustang, VW, Porsche and Nissan GTR aftermarket parts.
Inlet, Outlet & Transfer Ports
Just like in the four-stroke engines, there are inlet, exhaust, and transfer ports in the two-stroke engine.
- The inlet port is located below height compared to the exhaust or outlet port.
- Transfer port is placed between inlet ports and outlet ports and it helps to transfer the air-fuel mixture from crankcase to cylinder.
- As the two-stroke are completed simultaneously the intake and exhaust ports are always at work.
- In the cross-flow arrangements, inlet and exhaust ports are located opposite to each other side.
Piston
The piston is one of the important aspects of every engine arrangement. In the two-stroke engine to complete the operation, pistons need to reciprocate which in turn causes the crack to rotate to get the power.

- The air-fuel mixture gets expanded in the cylinder and the piston moves downward causing the piston to reciprocate hence generating the motion to crack shaft through connecting rod.
- Piston has the oil rings to stop leakage of oil.
- The detailed working of the piston we will know in detail in working section.
Connecting rod
The connecting rod is connected to the piston as well as the crack shaft. It’s a long rod in which both the ends are connected to the piston and the crankshaft with the help of pins.
- The connecting rod accommodates the reciprocating motion of piston transfer to the rotational motion of the crank.
- Generally, it is made up of the I-beam section.
Spring is here! Save big on our best-selling WAGNER TUNING BMW F CHASSIS N55 CATTED DOWNPIPE
Crankshaft
The crankshaft is responsible for generating power. The motion received from the piston is the reciprocating movement crank converts it into rotational motion.
- This power is given to the flywheel and to the wheels.
- The wheels get powered and thus the vehicle propels.
- Crankshafts need to complete one revolution in the two-stroke engines, to complete the process compared to two revolutions in four-stroke engines.
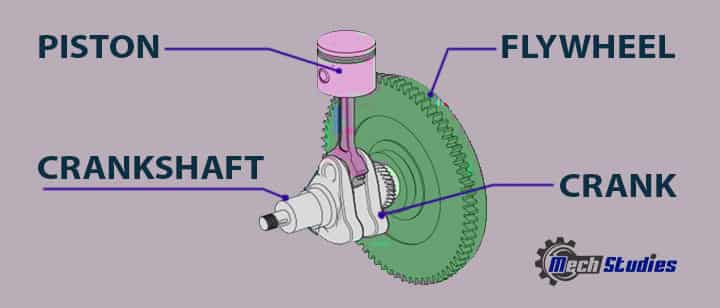
Crank & Crankcase
A crank is a piece of metal that is placed between the piston and crankshaft.
- It is basically a small arm attached to the rotating shaft at the right angle.
- It helps to change the circular motion into a reciprocating motion.
Flywheel
It’s the device that stores the generated power. The crankshaft has a connection to the flywheel using bearings and journals.
The flywheel is one that transfers the engine power to the wheels through a transmission.
Counterweight
In the two-stroke engines to avoid imbalance created by the rotating assembly, the crankshaft counterweights are used.
- It helps to achieve some higher RPM speed and the engine runs smoothly.
- The weight of the piston and connecting rod combination affects the size and placement of the counterweight.
- If this is not done, the engine will experience vibrations that will eventually tear up the main bearings and cause damage.
Now let’s know the detailed working of the two-stroke engines.
Working of the Two (2) Stroke Engine
Though the two-stroke engines do all the four operations like,
- Intake,
- Compression,
- Power and
- Exhaust
Intake —-> Compression —> Power —> Exhaust
Check a nice VIDEO from Physics and Animation!
These all steps are completed in just two-strokes. You can classify the two-stroke engine operation in two strokes,
- Compression stroke: It consists of intake & compression
- Power stroke: It consists of power & exhaust
Compression Stroke
So, the working starts when you start the engine and the spark plug ignites the fuel.
- The piston moves from the top dead centre (TDC) to bottom dead centre (BDC) causing the admission of the fuel and air mixture.
- When the piston is moving downward TDC to BDC a vacuum is created which causes the entry of the air-fuel mixture from the inlet port.
- The inlet gets uncovered and the fuel is entered. Now the main things start, when the piston reaches from the bottom dead centre (BDC) to top dead centre (TDC) the fuel gets compressed.
- Now again the spark plug fires up and ignites the fuel and the charge gets expanded.
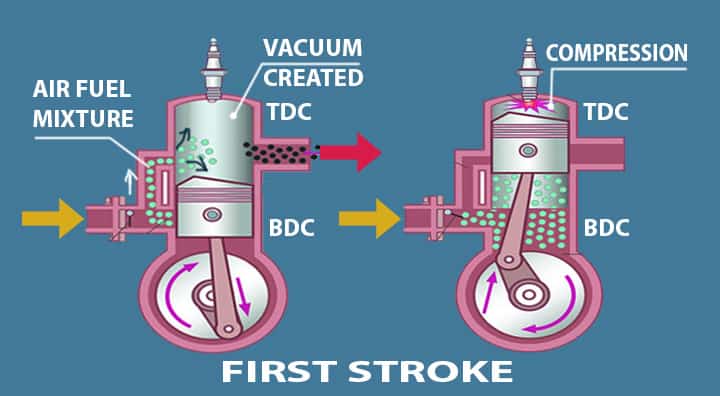
Piston ———————TDC—-> BDC : Vacuum Created ——> Fuel admission
Power Stroke
As we have seen in the previous upstroke the inlet port was open it allows the fuel to enter, due to which partial vacuum is created and there’s no fuel left behind.
- When the piston is reached at TDC the charge gets ignited by the spark plug and immediately the combustion process starts.
- Hence the compression, as well as the combustion process, start simultaneously. That’s the reason it’s called the two-stroke engine.
- The piston is doing a lot of work here continuously.
- In the power stroke, the piston goes downward as well as uncovering the exhaust port the exhaust gases are expelled out of the exhaust port.
- The exhaust gases get expelled on one side as well as the fuel comes from the inlet port again.
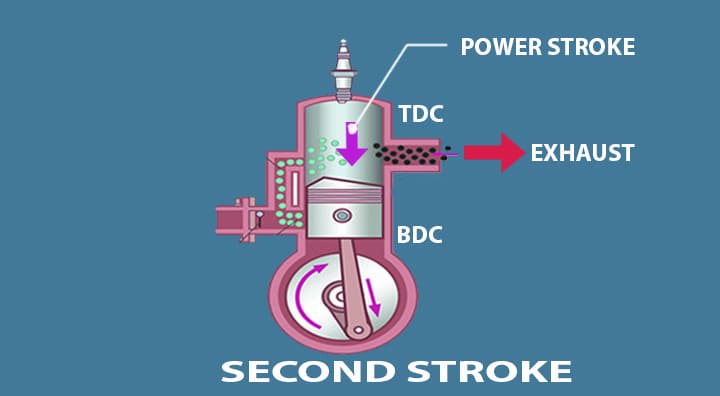
Piston ———————after compression—–> Power generated—->BDC—-> TDC —-> Power stroke —–> Exhaust
That’s the amazing thing about the two-stroke engines the two things happen at the same time. Because the two operations happen at the same time it doesn’t need so many moving parts as compared to the four-stroke engines.
Lubrication for Two (2) Stroke Engines
If you ever drive the two-stroke vehicle, you may be noticed that you need to mix up some oil alongside the fuel mixture. When you fill the fuel at any station you had to mix up some oil to run the vehicle, why is that?
So here is the answer, the two-stroke engine needs lubrication oil.
- In the case of the four-stroke engine, the lubrication system can be made separate without any issue.
- But in a two-stroke engine, the oil should be mixed with the fuel.
- In a four-engine the crank case is a whole different part but in two-stroke engine the crank case acts as pressurization chamber and it can’t hold any oil.
So, if you mix up the oil with the fuel it will get entered into the crankcase and the operation will be smoother. If you forget to add up the oil, the engine isn’t going to last long for sure.
The ratio of gas to oil is set by the engine manufacturer but ranges from 30:1 to 50:1 per volume unit.
This is another disadvantage of the two-stroke engines, the oil gets burned along with the fuel. Two-stroke engines suffer oil starvation if rotated at speed with the throttle closed
There are some advantages and disadvantages of two-stroke engines. There are a lot of disadvantages that are the reason it’s not used by modern cars nowadays and its use is limited, one reason is above stated related to lubrication.
Let’s know more advantages and disadvantages of the two-stroke engines.
Advantages of Two-Stroke Engines
The two stroke-engines do not have any valves so it simplifies their construction compared to the four-stroke engine’s construction.
- It doesn’t have lots of moving parts and that contributes to its simplicity.
- It gives one power stroke per revolution of the crankshaft.
- High power to weight ratio and significant power boost.
- The two-stroke engines get a power boost because two-stroke engines fire once every revolution. Power is produced once during 2 strokes of the piston.
- Two-stroke engines are lighter comparatively.
- It has a high weight to power ratio.
- It is almost 30% lighter in weight compared to a four-stroke engine.
- The produced torque is uniform in the case of two-stroke engines because the power is produced during every alternate stroke of the piston.
- Due to a smaller number of parts, these are compact in nature. This is the reason these are suitable for small machinery like grass cutters.
Disadvantages of Two (2) Stroke Engines
- The life of the two-engines is not longer as compared to the four-stroke engines.
- Parts of the two-stroke engines are associated to wear a lot faster.
- As we have discussed before we have to use oil with the air-fuel mixture. If the two-stroke engine was used in a car you could burn a gallon of oil for 1000 miles of travel. Hence, they are more expensive to use.
- They are less efficient, produces lots of carbon deposits due to incomplete combustion, oil-burning along with the air-fuel mixture.
- The pollution is a lot and maybe these engines may disappear soon. The oil burned along with the air-fuel mixture then produces a lot of smoke.
- We have seen the working of the two-stroke engines when the intake valve is opened the fuel enters and sometimes some part of the fuel directly goes to the exhaust port. Because of this, you will get less fuel economy and fuel will be wasted.
- Since the power stroke is produced after every stroke, the engine will heat very quickly. So again, well lubrication and oiling are very necessary to keep the engine running in good condition.
- High vibration and noisy operation.
So, where these two-stroke engines are used? Let’s know them, as they have limited use now.
Applications of Two (2) Stroke Engines
- These engines are selected when there is a need for an excellent weight to power ratio.
- The handheld power tools are one of the good applications of these engines. By employing the oil use they can be handled with any orientation.
- Commonly used in outdoor power tools, like lawnmowers, chainsaws, and weed whackers.
- Two-stroke engines are used in motorcycles, etc.

In the past, the two (20 stroke engines were used in lots of main-stream vehicles. Like Swedish Saab, Japanese Suzuki, Subaru. In major bike racing events, the two-stroke powered bikes were so much popular in 1970s days. As compared to four-stroke engine these were emitting lots of pollution which caused their discontinuation from the automobile market.
These were used till the 1990s maximum in mopeds and dirt bikes. But due to the strict pollution guidelines and the disadvantages as stated above the use was slowly reduced and they are gone now from the vehicle market and are limited to small applications
High Rated Automotive Engineering Course
Automotive 101: A Beginners Guide To Automotive Repair
Automotive Engineering: Automobile Fundamentals and Advanced
Automotive Engineering; Hybrid Electric Vehicles
Do it Yourself – Automotive Electrical Diagnosis – Beginner
Do it Yourself-Automotive Electrical Diagnosis-Intermediate
Automotive Engineering; Common Rail Direct Injection(CRDI)
Fundamentals of Internal Combustion Engines – IC Engines
Hybrid and Electric Vehicle for Beginners FULL Course 2021
Automobile Safety: Understanding Car Crashes for beginners
Hybrid Vehicles The Fundamentals & Operating Principles
Conclusion
So, finally, we have got the basic idea of two (2) stroke engines along with the working principle. Thanks for being with us.
Further Study
Read more articles,

