What are spark plugs? A very common question in automobiles! In this article, we will learn all the basics of the spark plug, its definition, parts, construction, advantages, disadvantages, applications.
Let’s explore!
What are Spark Plugs? Definition & Meaning
Spark Plug Definition & Meaning
Automobile vehicles work on a wide variety of parts. One of the starting operations is initiated from the device known as the spark plug. It generates a spark to start the combustion of the charge inside the combustion chamber.
- It is used in spark-ignition engines though it is slowly replaced by fuel injection systems.
- But still, the spark plug remains an important part of automobile combustion systems.
- The spark plugs are mostly needed in the petrol engines because to ignite them at the right pressure to avoid knocking and detonation type abnormalities.

If you have a bike and repaired it someday, you may have seen the spark plug ones at least. If the vehicle is not starting or having late starting problems, usually the spark plug problems are there.
We will take a little deep dive into spark plugs. Interested in learning more about spark plugs?
Let’s tune in, starting from the history of spark plugs.
Spart Plug History
In 1860 Étienne Lenoir developed the first combustion engine and used the electric spark plug. Though Edmond Berger also received some credits regarding the invention of the spark plugs.
- Later the patents by Nikola Tesla and Robert Bosch were available.
- The first commercially available high-voltage spark plug changed and accelerated its integration and use in automobiles.
- It was a magneto-based ignition system developed by Robert Bosch engineer Gottlob Holland in 1902.
- That’s how the Spark ignition engines started to roll in the automobile sectors from then till now.
The Construction of Spark Plugs
The Spark plugs looks small but there is more running inside of it. It is basically composed of the shell, insulator, and the central conductor.
The spark plus also kind of seals off the combustion chamber against high pressure and temperatures if the vehicle is used for extensive times.
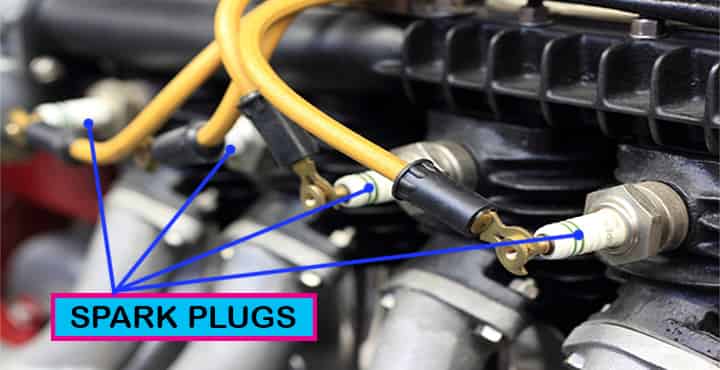
- The spark plugs come in different sizes, they are basically classified on the basis of size, thread or nut, sealing type, spark gap.
- The values of varies according to the regions, like in Europe 10 mm (16 mm), 14 mm (21 mm; sometimes, 16 mm), and 18 mm (24 mm, sometimes, 21 mm).
- In the United States, common thread (nut) sizes are 10mm (16mm), 12mm (14mm, 16mm or 17.5mm), 14mm (16mm, 20.63mm) and 18mm (20.63mm).
XPH is your home for BMW, Audi, Ford Mustang, VW, Porsche and Nissan GTR aftermarket parts.
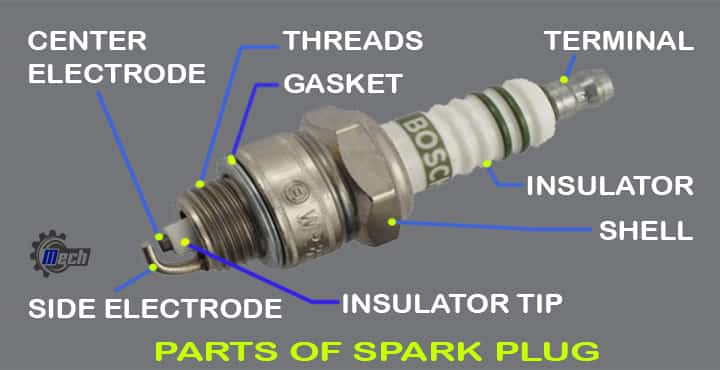
Parts of Spark Plugs
There are a few parts of a spark plug, are as follows,
- Terminal
- Insulator
- Insulator tip
- Seals
- Shell
- Center electrode, etc.
Terminal
The tope part of the spark plug is the terminal. The terminal is connected to the ignition system. Though the exact configuration of the terminal varies according to the manufacturers.
- The configuration varies according to the use of the spark plug.
- The terminal is connected to the high-tension cord from which the high voltage current flows.
- Also, the terminal nut is provided for support.
Also, some of the terminals are provided with the threads that is common for motorcycles.
Recently, the cup-styled terminal is introduced they allow the insulator made of ceramic to stay in the confined space.
Insulator
As the name suggests it is provided for the electric insulations. The main part of the insulator is made of sintered alumina (Al2O3) composition. It is a very hard ceramic material with high di-electric strength.
(Al2O3) composition. It is a very hard ceramic material with high di-electric strength.
- The major functions of this insulator include providing electrical insulation for the central electrode and providing mechanical support.
- The Sintered Alumina (Al2O3) also helped to reduce the tendency of the insulator to glow with heat and so light the mixture prematurely.
Tip of Insulator
The old spark plugs were using the mica stacked layers as the insulator tips generally in aircrafts. Later the lead deposits became problem for the mica layers use. Now the spark plugs after the 1930s are using the same sintered alumina as the tip of the insulators. It was made by Siemens in Germany.
- The sintered alumina is a good thermal conductor of ceramic, good mechanical strength, and has the ability to run at hot temperatures so it allows for self-cleaning temperatures without rapid degradation.
- The insulator dimensions and metal conductor dimensions decide the heat range of the plug.
- Short insulators are generally the cooler plugs whereas the lengthened path plugs are the hotter plugs.
Spring is here! Save big on our best-selling WAGNER TUNING BMW F CHASSIS N55 CATTED DOWNPIPE
Seals
As we have already seen the spark plugs also needs to seals off the chamber of engine once its installed. So, the seal is obviously necessary to ensure no leakage because leakage of the fuel mixture can have severe damages.
- The internal seals of the spark plugs are made of using compressed glass or metal powder.
- Talking about the external seals, it is made of a crush washer.
- There is also a cost-cutting method in which some manufacturers use a tapered interface and simple compression for sealing.
Just a little bit more about glass seal method. It uses the special mixture of glass powder and copper powder. The mixture is charged into the installation section of the insulator and center shaft and center electrode.
So even in some harsh conditions, the gaps will not occur and good airtightness is achieved.
Metal case or Shell
The metal case or shell sometimes even called as jacket of the spark plug. It has the work of withstanding the torque of the tightening the plug and serves to remove the heat from insulator and it passes on to the cylinder head.
It is housing forming an outer shell it surrounds the insulator and supports the insulator.
Center Electrode
The central electrode connected to the terminal through internal wire and a ceramic series resistance it results in reducing emissions of RF noise due to sparking.
- The tip of the center electrode is made using a combination of copper, nickel-ion, chromium, or noble metals.
- Talking a little bit about the technicalities, the hottest part of the spark plug is the one that ejects the electrons from cathode negative charges.
- Because basically, it’s easy to emit electrons from a hotter surface.
Side electrode
It is also known as the ground strap and made from high nickel steel and it welded to the side of the metal shell.
- The side electrodes run hot on the projected nose plugs.
- Due to this, copper was introduced to improve the heat conduction also, multiple side electrodes can be used.
- Adding platinum or iridium can increase the service life of these electrodes.
So, these are the parts of the spark plugs. The spark plus combining all the above parts is used in the automobile vehicles. The working is simple and easily understandable.
Now without going into much of a technical detail let’s understand how spark plugs work.
How Does Spark Plug Work?
The working principle of spark plugs are captured, as below
- You may have known about the ignition systems like battery ignition, magneto ignitions systems.
- So, the spark plug is connected to the high voltage ignition coil with the help of distributors available in the ignition systems.
- When the electricity flows from the coil the voltage difference will be created between the center electrode and ground/side electrode on the spark plug.
- There is some gap in the spark plug and the fuel so fuel doesn’t automatically light up immediately.
- As the voltage rises up approximately 20000 volts the gap can be breached and the spark is generated. Thus, the fuel will be fired.
- The heat generated by the spark plug ignition is immense and shapes like a fireball and moves through the cylinder (theory).
- The process will be repeated again at the starting of the vehicle.
Check a very nice ANIMATED VIDEO from saVRee,
Now we have seen the working of the spark plus, there is one important point mention in the spark plug working can you guess? It’s the spark gap. Let’s know more about it.
What is Spark Plug Gap?
The spark plug is not directly in contact with the fuel it has some gap known as the spark gap. It can be adjusted by the technician. Different engines may specify some different spark gaps. But generally, the automobiles have spark gap of 0.6 to 1.8 mm.
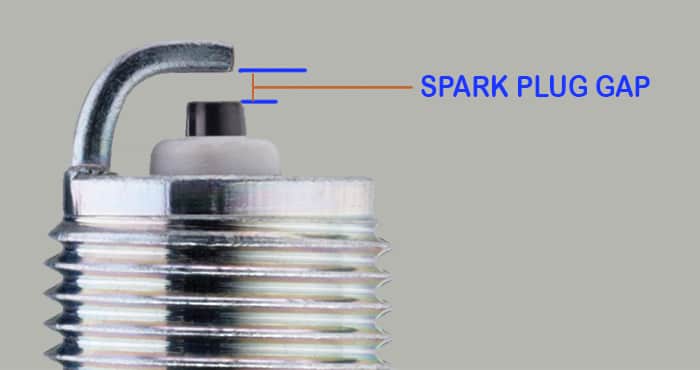
- The gap adjustment is very much important.
- Because the lower values or higher values can cause some inefficient working of the engine and affect the overall engine performance on large scale.
- For example, if the gap is narrow the spark the spark production will be narrow and the spark may ignite at every time continuously.
On the other hand, if the gap is wider it can prevent the fuel even from firing. Also, it may misfire in some cases. So, basically, the spark gap should be kept at the optimum levels so that the engine may achieve its highest possible efficiency and fuel efficiency.
- The spark plug tip as we have seen earlier is made of iridium and platinum.
- Iridium ones are the most effective ones now.
- Though copper electrodes are used widely their life span is short.
Let’s check out their advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages Iridium Spark plugs
Iridium spark plugs improve fuel economy
The iridium spark plugs will be beneficial for the fuel economy of the vehicle. It has the improved ignition profile which burns the fuel more efficiently.
Less voltage requirements
The electrical currents surges from the spark plugs. But the Iridium spark plugs doesn’t need that much of voltage to produce the power. Because it has small electrode energy saving during start-up phase ensures the driving experience.
More durability with Iridium spark plugs
The iridium has high strength and hence it has more durability compared to other copper and platinum alternatives. For example, if you get copper or platinum instead of iridium you may be getting just 50% of the lifespan of Iridium.
More corrosion resistance
The Iridium metal is the corrosion resistance one. It performs well in the engine compartments because of the corrosion resistance properties.
Stability
Stable spark generations even at harsh operating conditions.
Disadvantages Iridium Spark Plugs
- The cost is the primary disadvantage
- The cost of the Iridium spark plugs is the main disadvantage. It can be like 15$ for each piece. For example, for a V8 engine, you will need 15 X 8.
- Cars with smaller engines may not experience an increase in performance.
- Properly, pure Iridium components are needed for best results if some cheaper ones are used you may not receive good results.
- The coatings used on the Iridium may be brittle.
Applications of Spark Plugs
You may have already known the application of the spark plugs. The spark plugs are used in all of the petrol vehicles. Like, scooters, motorcycles, cars etc. The fuel is burnt with the help of spark plugs.
As we have seen earlier there are some types of spark plugs according to the material used.
- So, the applications of the same vary according to the requirements.
- Like, the copper spark plugs are the cheapest ones with low life-span, platinum ones stand in the middle, whereas the Iridium spark plugs are costly and have a better life-span compared to the others.
- The applications can be decided considering various parameters and requirements.
High Rated Automotive Engineering Course
Automotive 101: A Beginners Guide To Automotive Repair
Automotive Engineering: Automobile Fundamentals and Advanced
Automotive Engineering; Hybrid Electric Vehicles
Do it Yourself – Automotive Electrical Diagnosis – Beginner
Do it Yourself-Automotive Electrical Diagnosis-Intermediate
Automotive Engineering; Common Rail Direct Injection(CRDI)
Fundamentals of Internal Combustion Engines – IC Engines
Hybrid and Electric Vehicle for Beginners FULL Course 2021
Automobile Safety: Understanding Car Crashes for beginners
Hybrid Vehicles The Fundamentals & Operating Principles
Conclusion
Hence, we have learned the basics of spark plugs along with the definition, working, applications. If you have a question, please let us know.
Further Study
Refer out a few interesting articles for further study,

